
All It Takes Is One Boiled Egg To Control Sugar Levels In The Blood

Every time you eat, your blood sugar levels go up. This is especially true for individuals who have type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance. Having to learn how to control your blood sugar levels within a healthy range is by no means an easy task.
It can take months for a newly diagnosed patient to learn what to eat and what to avoid. And during this period of time, someone with type 2 diabetes is likely to experience high blood sugar levels, which is detrimental to their overall health.
Too much sugar in the blood for long periods of time can increase your risk of heart disease and stroke, kidney disease, vision problems, and nerve problems. (1)
How To Control Blood Sugar Levels
For the majority of healthy individuals, normal blood sugar levels are as follows: Between 4.0 to 6.0 mmol/L (72 to 108 mg/dL) when fasting. Up to 7.8 mmol/L (140 mg/dL) 2 hours after eating. (2)
For people with insulin resistance, their blood sugar levels remain high long after having finished their meal.

Fortunately, there are many foods you can eat that can help you control blood sugar levels naturally. As you’ll learn eventually, relying on expensive diabetes drugs in the long-run can have negative side effects on your body.
Below is a powerful remedy that combines three simple ingredients to prevent your blood sugar levels from going rampant.
For this recipe all you will need is apple cider vinegar, water, and a boiled egg.
See also: Reversing diabetes Type-2
Instructions:

Boil an egg in the afternoon, and peel it. Pierce the egg 2-3 times using a toothpick. Put the egg in a mason jar and pour just enough vinegar over it so that it is completely covered. Close the jar and let it soak overnight in your refrigerator.
The next morning, drink a glass of warm water and eat your egg.
Repeat this every day, and you will soon notice an improvement in your blood sugar levels.
Why It Works
A few hard-boiled eggs can be a handy high-protein snack or breakfast if you have diabetes. The protein will help keep you full without affecting your blood sugar. Protein not only slows digestion, it also slows glucose absorption, which is very helpful to diabetics. (3)
Apple cider vinegar makes you more sensitive to insulin and reduces blood sugar spikes, particularly after eating starchy food. The findings of one study showed positive results for people with type 2 diabetes when taken before a glucose-heavy meal. (4)
Your health is in your own hands. A hard-boiled egg and apple cider vinegar are relatively cheap to purchase compared to common diabetes drugs. Plus, they’re much better for you in the long run.
News in the same category

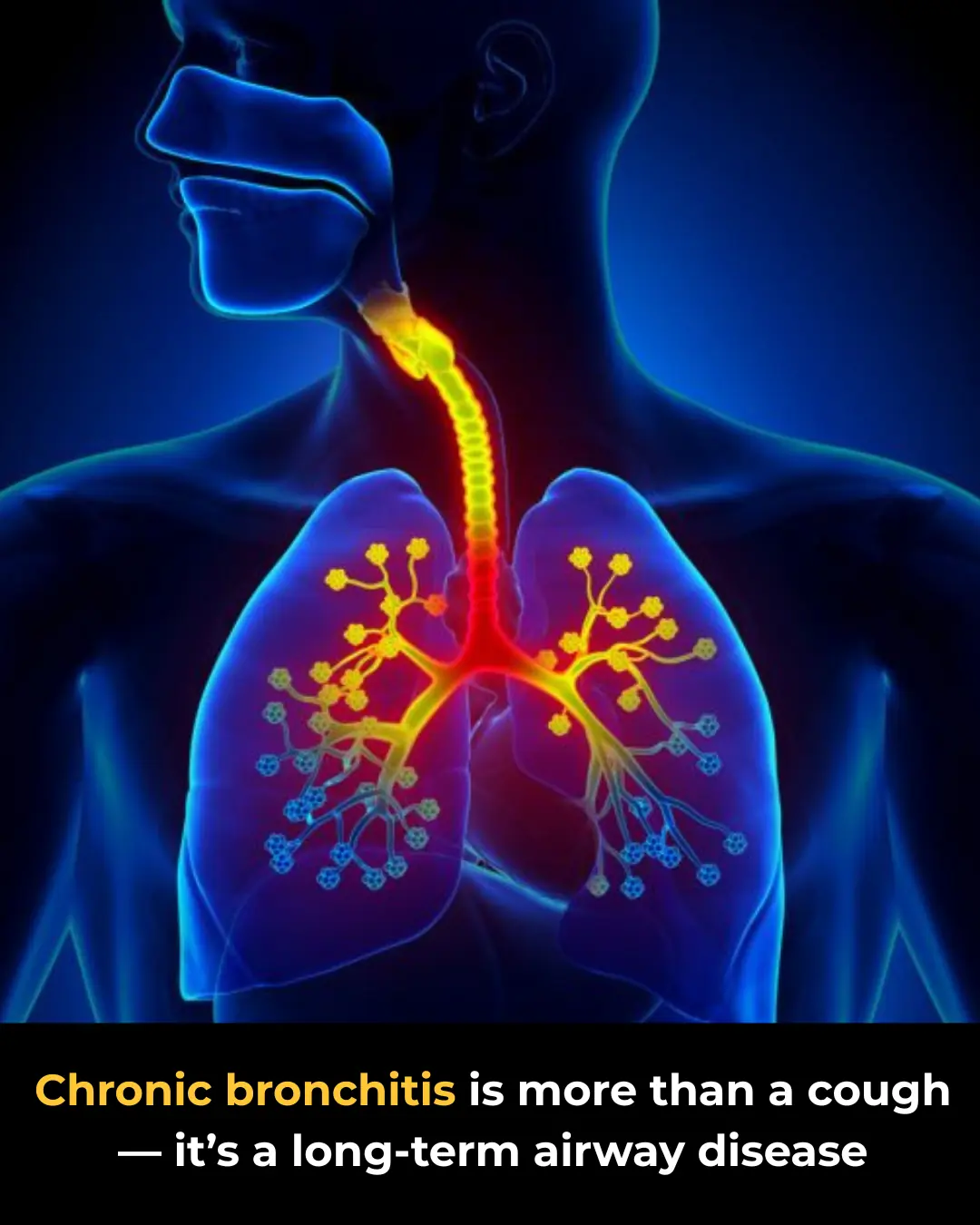
Chronic Bronchitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Home Care Tips
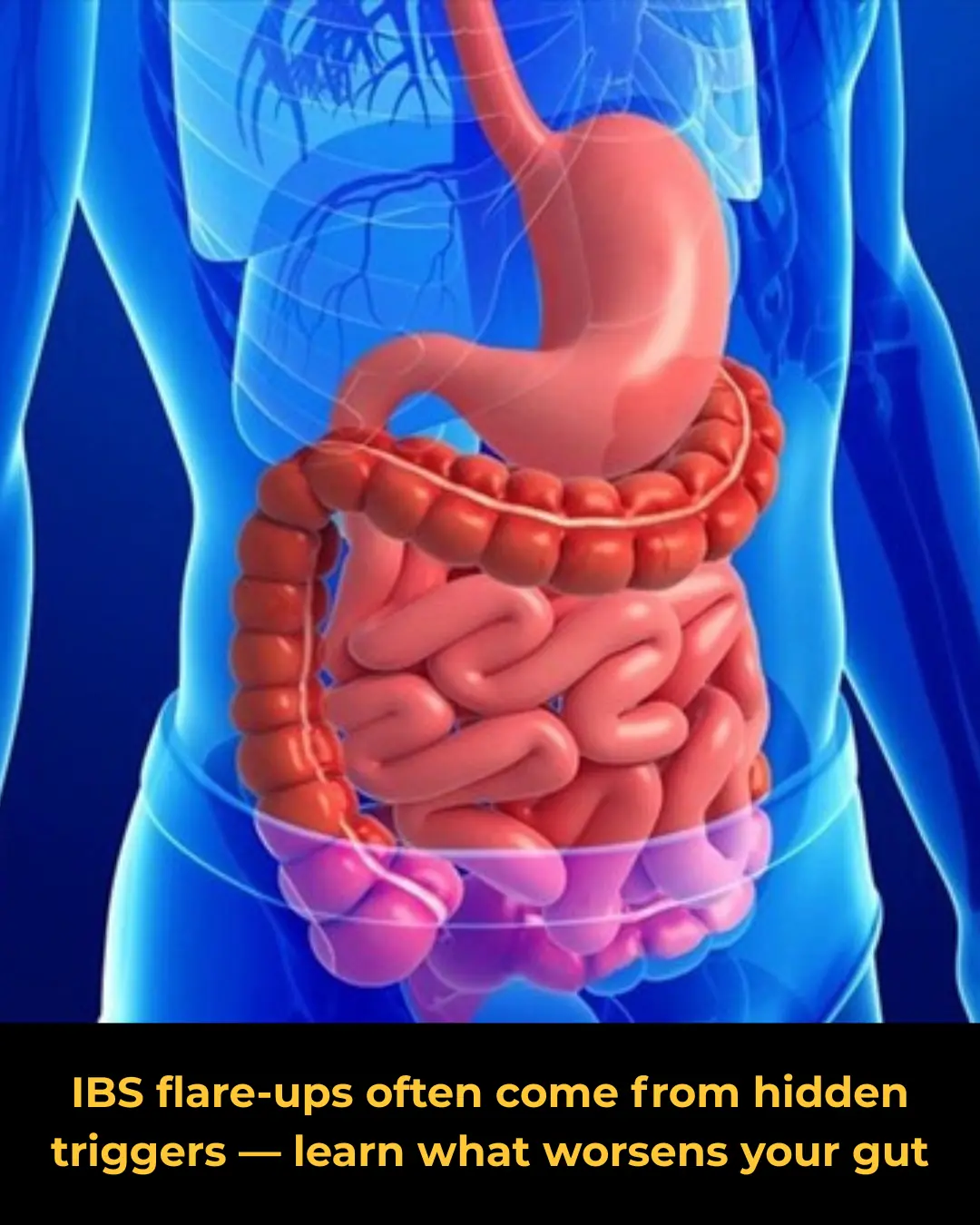
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): What Makes the Condition Worse?
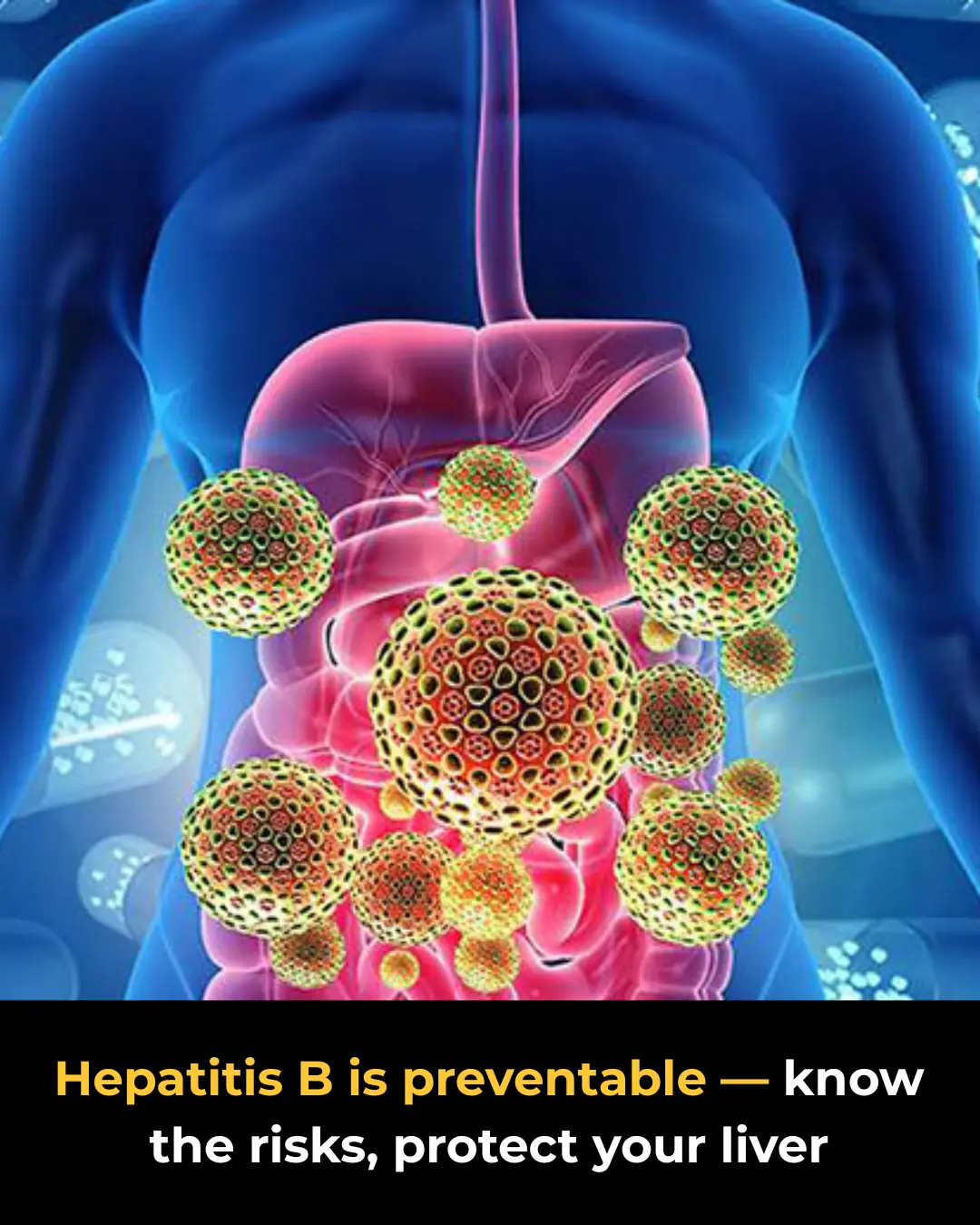
Hepatitis B: High-Risk Groups and Prevention Measures
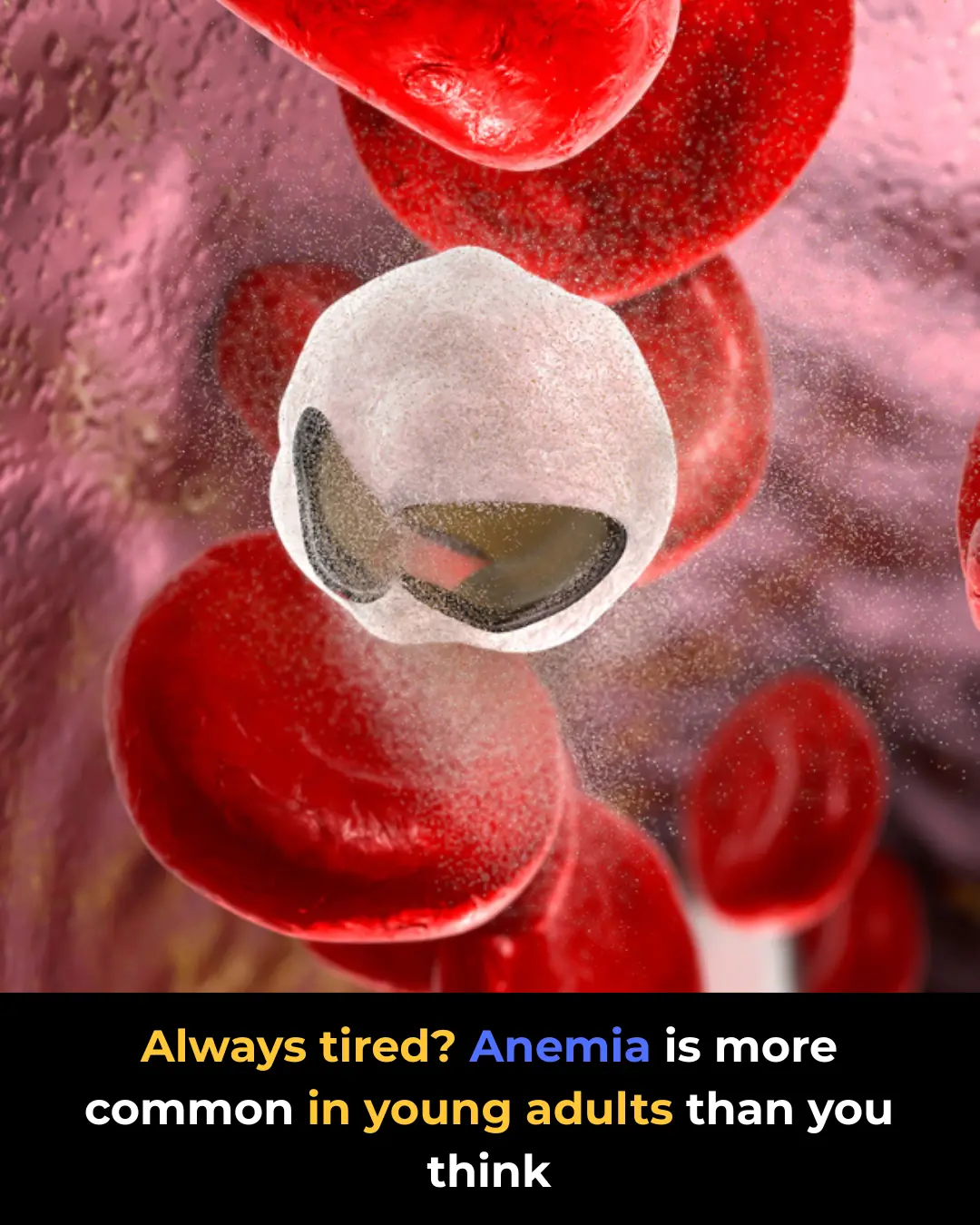
Anemia in Young Adults: Common Causes and How to Treat It

Anxiety Disorder: Psychological Signs People Often Misunderstand

Seven Days Without Sugar Changes Your Body in Ways You Never Expected

Cucumber water regenerates joints and nourishes your brain and 8 other benefits for your health

The Surprising Benefits of Foot Massages
Natural Home Remedies That Eliminate Muscle Pain Quickly

Nobody Told You This Vitamin Deficiency Might Be Behind Your Migraines

The Hidden Symptoms of Low Magnesium That Are Silently Draining Your Health

Lemon in Coffee? The Simple Morning Twist People Are Loving

What Happens When You Drink Baking Soda Water Before Bed? A Gentle 2-Week Wellness Practice

More Than Just Flavor: The Gentle Power of Onions for Wellness

Man has stroke after bathing right after meal: 3 mistakes you shouldn’t make
12 Weird Diabetes Skin Problems You Need To Know

Top 5 Drinks To Improve Vision Naturally

Exact Age You Should Cease Beer Consumption
News Post
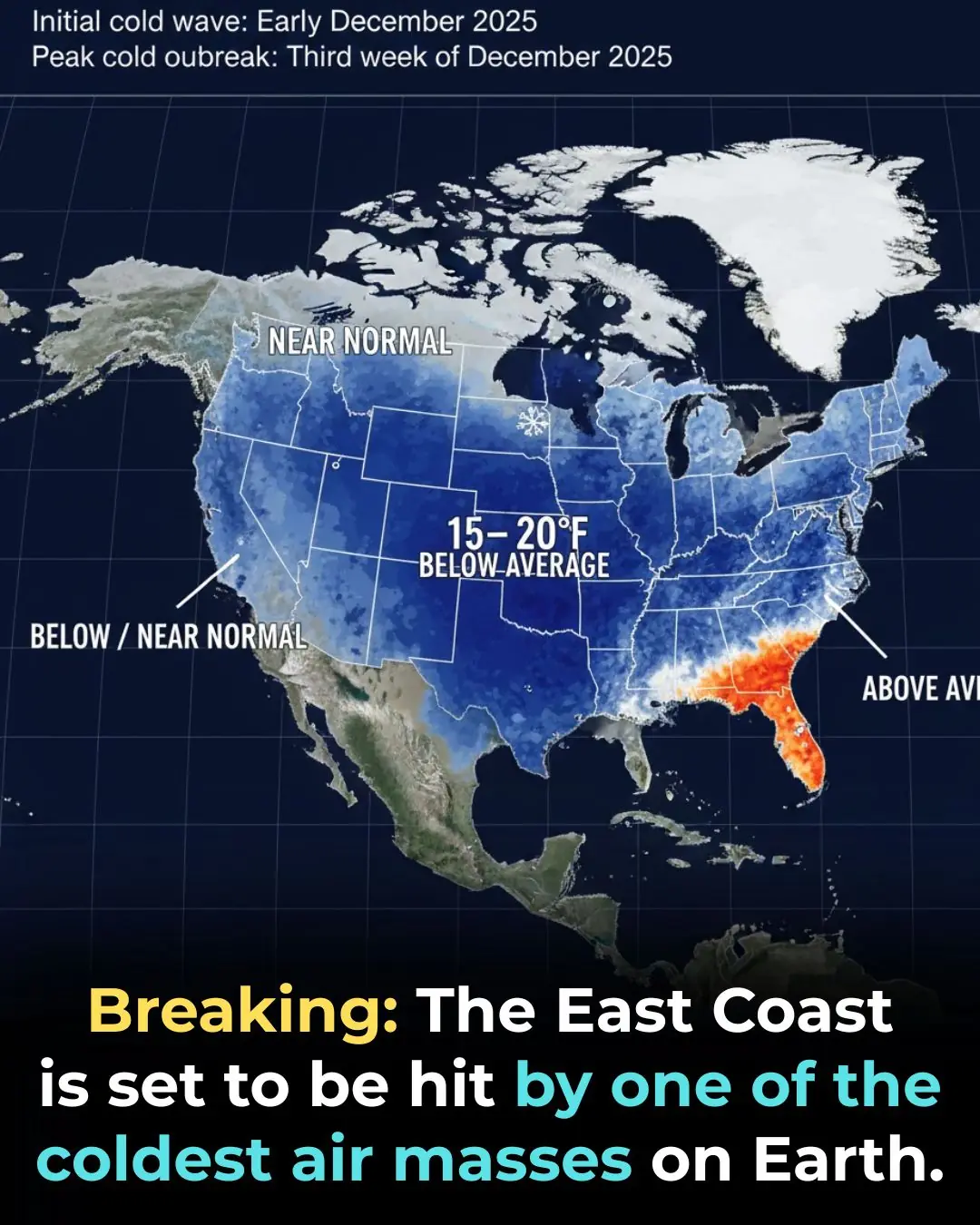
Deep Freeze Set to Slam the Eastern U.S. This December

Nike Co-Founder Phil Knight Makes Historic $2 Billion Donation to Cancer Research

Dutch Engineers Tackle the Pacific’s Plastic Crisis with 600-Meter Ocean Vacuum

Chronic Insomnia: When Sleeplessness Becomes a Serious Health Issue

Chronic Bronchitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Home Care Tips

Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): What Makes the Condition Worse?
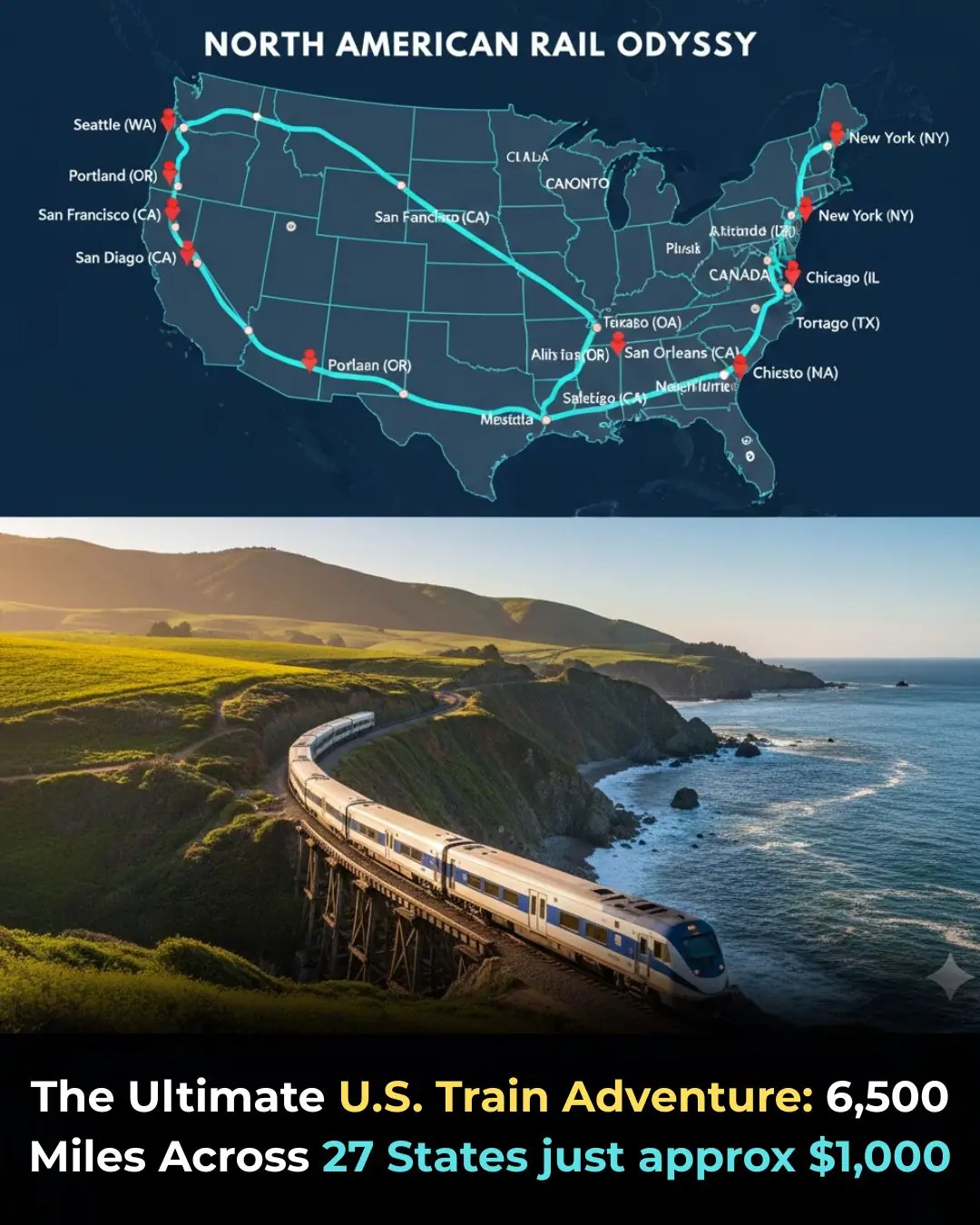
How to Take a Loop of the Entire U.S. by Train

The Quiet Rise of Everyday Health-Tracking Technology

Hepatitis B: High-Risk Groups and Prevention Measures

Anemia in Young Adults: Common Causes and How to Treat It
The Hidden Toll of People-Pleasing: How Emotional Suppression Can Trigger Autoimmune Disorders

The Pudu: The World’s Tiniest Deer and Its Role in South America's Forest Ecosystems

Deep Water Cycle: Scientists Discover Hidden Ocean Beneath Earth's Surface

Mexico City’s Sweeping Bullfighting Ban Marks Major Shift in Cultural and Animal-Welfare Policy

Anxiety Disorder: Psychological Signs People Often Misunderstand

Los Angeles County Erases $180 Million in Medical Debt for 39,000 Residents

The 2025 Atlantic Hurricane Season Intensifies: A Heightened Risk for Major Storms

Seven Days Without Sugar Changes Your Body in Ways You Never Expected

Europe Faces Unprecedented Heatwave: Rising Temperatures Strain People, Infrastructure, and Agriculture
