
Hepatitis B: High-Risk Groups and Prevention Measures
Hepatitis B is one of the most widespread and dangerous viral infections affecting the liver. Despite advancements in medicine, Hepatitis B remains a silent global threat—many infected people do not show symptoms for years, allowing liver inflammation to progress quietly into fibrosis, cirrhosis, or even liver cancer.
Understanding who is at highest risk and how to prevent the disease is essential. This article breaks down the key facts every individual, parent, and healthcare-conscious reader should know.
I. What Is Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a viral infection caused by the Hepatitis B virus (HBV). It targets the liver, causing acute or chronic inflammation.
There are two types:
-
Acute infection: Short-term, may resolve on its own.
-
Chronic infection: Long-term, lasting more than 6 months; can lead to liver scarring, liver failure, or cancer.
The virus spreads when infected blood or bodily fluids enter another person’s bloodstream.
II. High-Risk Groups
Although anyone can contract HBV, certain groups face significantly higher risk:
1. Infants Born to HBV-Positive Mothers
This group has the highest likelihood of developing chronic infection because their immune systems cannot fight the virus effectively.
2. Healthcare Workers
Doctors, nurses, lab technicians, and emergency responders face constant exposure to blood and sharps injuries.
3. People Living With an Infected Family Member
Sharing razors, toothbrushes, or even surfaces contaminated with blood increases risk.
4. Individuals With Multiple Sexual Partners
HBV can be transmitted through sexual activity, especially when protection is not used.
5. People Who Inject Drugs
Shared needles or syringes are one of the fastest transmission routes.
6. Patients Undergoing Dialysis
Frequent exposure to medical equipment raises the risk of transmission.
7. Travelers to High-Prevalence Regions
Areas such as parts of Asia, Africa, and the Pacific Islands have high rates of chronic HBV.
III. Signs & Symptoms
Many people never show signs. When symptoms appear, they may include:
-
Fatigue
-
Jaundice
-
Loss of appetite
-
Dark urine
-
Persistent nausea
-
Right upper abdominal pain
Chronic Hepatitis B often remains silent for decades.
IV. Prevention Measures
Hepatitis B is almost entirely preventable. The following strategies are globally recommended:
1. Vaccination (Most Important)
The HBV vaccine is 95% effective.
Schedule:
✔ Birth dose
✔ Followed by 2–3 additional doses
Adults can vaccinate anytime.
2. Practice Safe Sex
Use condoms and avoid risky sexual behaviors.
3. Avoid Sharing Personal Items
Razors, clippers, toothbrushes, and needles should never be shared.
4. Safe Piercing & Tattooing
Ensure equipment is sterilized and licensed.
5. Screen Pregnant Women
Early detection prevents mother-to-child transmission.
6. Regular Testing for High-Risk Groups
Blood tests include HBsAg, anti-HBs, and anti-HBc.
V. When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if you:
-
Have been exposed to infected blood
-
Show signs of liver issues
-
Are pregnant (HBV screening is mandatory)
-
Have a family history of liver disease
News in the same category


Common pain meds trick doctors into heart failure misdiagnosis

Top 6 Nutrients To Reduce Knee Osteoarthritis Pain

Could your toes be warning you about your lifespan? Foot expert explains

Could your morning orange juice be supporting your heart more than you think?

Top 10 Signs of Kidney Problems You ABSOLUTELY Must Be Aware Of…

Chronic Insomnia: When Sleeplessness Becomes a Serious Health Issue
Chronic Bronchitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Home Care Tips
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): What Makes the Condition Worse?
Anemia in Young Adults: Common Causes and How to Treat It

Anxiety Disorder: Psychological Signs People Often Misunderstand

Seven Days Without Sugar Changes Your Body in Ways You Never Expected

All It Takes Is One Boiled Egg To Control Sugar Levels In The Blood

Cucumber water regenerates joints and nourishes your brain and 8 other benefits for your health

The Surprising Benefits of Foot Massages
Natural Home Remedies That Eliminate Muscle Pain Quickly

Nobody Told You This Vitamin Deficiency Might Be Behind Your Migraines

The Hidden Symptoms of Low Magnesium That Are Silently Draining Your Health

Lemon in Coffee? The Simple Morning Twist People Are Loving
News Post

Unlock the Ancient Secret of Peach Tree Resin: 15 Life-Changing Benefits You’ll Wish You Knew Sooner

Aloe Vera & Cinnamon: The Traditional Duo That Naturally Supports Your Health, Vitality, and Vision

Why Germany Makes New Dog Owners Take a Test

The Gut-Heart Connection: How Your Gut Microbiome Affects Your Heart Health

One Glass to Flush Your Colon Clean in Just 10 Minutes!

The 11 surprising baking soda uses that actually have science behind them

Common pain meds trick doctors into heart failure misdiagnosis

12 Health Hacks Doctors Rarely Share: Secrets for Optimal Health and Well-being

Top 6 Nutrients To Reduce Knee Osteoarthritis Pain

Could your toes be warning you about your lifespan? Foot expert explains

Could your morning orange juice be supporting your heart more than you think?

Top 10 Signs of Kidney Problems You ABSOLUTELY Must Be Aware Of…

A Parade Moment That Became Global Joy

Nick Vujicic: Living Proof That the Human Spirit Knows No Limits

You’re Made of Stardust – Literally! 🌌🚀

Sea Levels Are Rising Faster Than At Any Time In 4,000 Years 🌍

Your Dog Might Actually Love You More Than Food
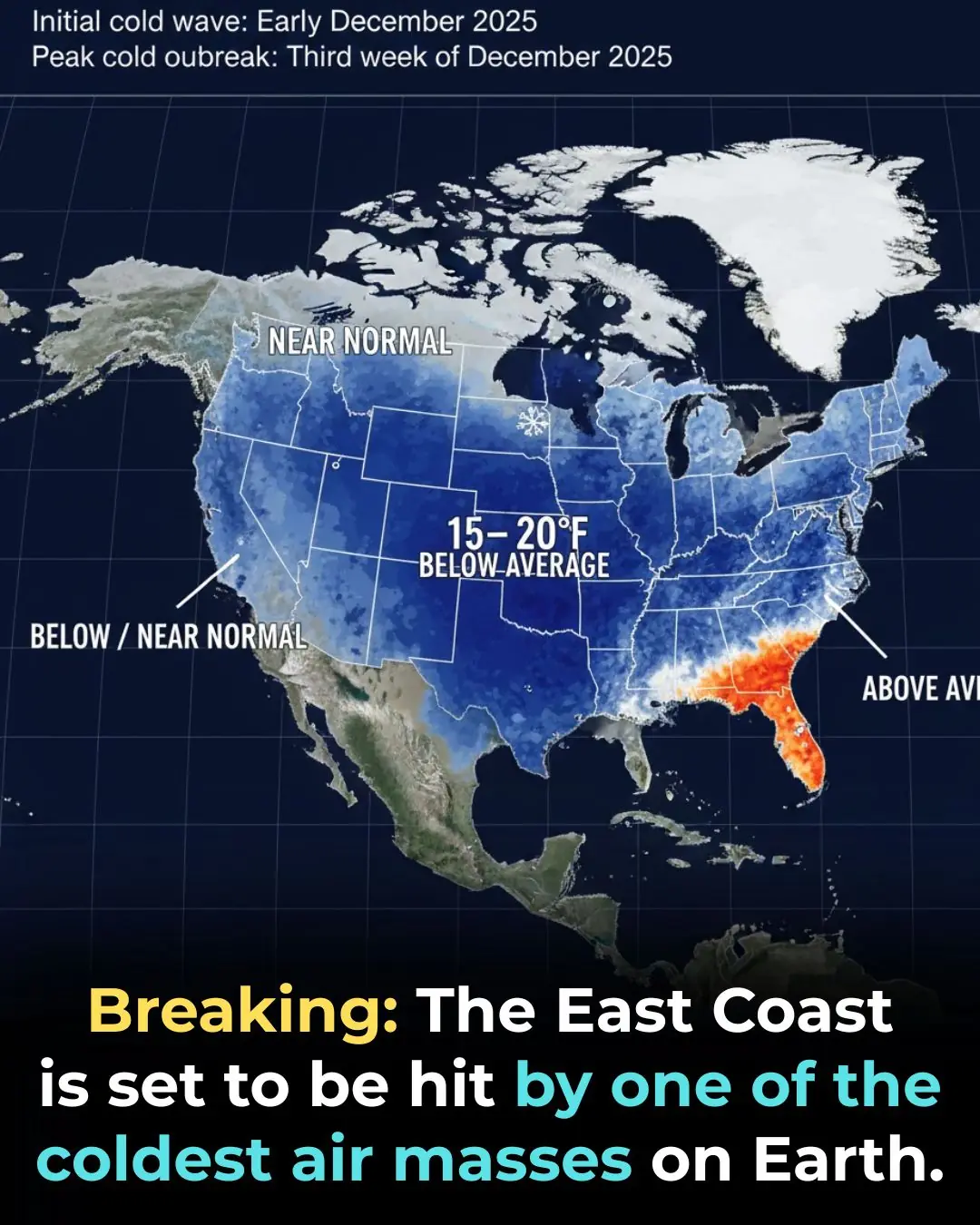
Deep Freeze Set to Slam the Eastern U.S. This December

Nike Co-Founder Phil Knight Makes Historic $2 Billion Donation to Cancer Research
