Did you know that if you get spots on your hands it means you have
What It Means When You Get Brown Spots on Your Hands
If you notice brown or dark spots appearing on your hands — especially as you age — they are most likely
age spots, also called liver spots or solar lentigines. Despite their name, they have nothing to do with your liver’s health.Instead, they are caused by years of exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays
, which trigger your skin cells to produce extra melanin, the pigment that gives your skin its color.Over time, this pigment gathers in certain areas, creating flat, brownish patches
that vary in size and shape.
🌞 Why It Happens
-
Sun exposure (main cause):
Every time your hands are exposed to sunlight — even for short periods — UV rays penetrate the skin and speed up melanin production. After years of accumulated exposure, this pigment forms visible spots. -
Aging:
As we age, our skin’s ability to regenerate decreases. The natural renewal of skin cells slows down, which means damaged and pigmented cells stay longer on the surface. -
Hormonal changes:
Hormones, especially estrogen, can influence melanin activity. This is why women often notice pigmentation changes during menopause. -
Genetics:
Some people are genetically more likely to develop these spots, even if they don’t spend much time in the sun. -
Smoking and environmental damage:
Smoking and pollution accelerate oxidative stress, leading to premature aging and pigmentation.
Health Implications
In most cases, these spots are harmless and are only a sign of
sun damage and skin aging, not a symptom of disease.However, they do serve as a warning sign — your skin has been overexposed to UV rays for years, which also increases your risk of skin cancer.
That’s why dermatologists recommend:
-
Keeping an eye on the size, color, and shape of these spots.
-
If a spot becomes irregular, grows quickly, changes color, or bleeds
, you must get it checked immediately.
How to Treat and Fade Them
1. Topical Creams and Serums
-
Retinol or Retinoids: Boost cell turnover, helping fade pigmentation over time.
-
Vitamin C serum:
Brightens the skin and prevents new dark spots. -
Hydroquinone (used under medical supervision): A bleaching agent that lightens dark spots.
-
Niacinamide: Reduces pigmentation and strengthens the skin barrier.
-
Glycolic acid or lactic acid creams:
Exfoliate the outer layer and promote new skin growth.
2. Professional Treatments
-
Laser therapy: Targets and breaks up melanin clusters, lightening dark spots.
-
Cryotherapy: Freezes and removes the pigmented cells.
-
Chemical peels: Remove the top layer of skin, allowing fresh, even-toned skin to appear.
-
Microdermabrasion: Gently sands away the damaged surface layer.
3. Natural Home Remedies (gentle but slower results)
-
Lemon juice: Its citric acid helps lighten spots naturally (apply 10 min, rinse, and moisturize).
-
Apple cider vinegar: Contains acetic acid, which can help fade pigmentation.
-
Aloe vera: Contains aloin, a natural depigmenting compound that soothes and repairs skin.
-
Castor oil with vitamin E: Promotes new cell growth and restores elasticity.
🧤 Prevention: Protect Your Hands Daily
-
Use sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) every day, even indoors or while driving — the hands are constantly exposed to sunlight.
-
Wear gloves while driving or working outdoors.
-
Moisturize daily to keep the skin barrier strong and prevent further damage.
-
Avoid tanning beds — they cause the same type of UV damage.
-
Eat antioxidant-rich foods like blueberries, oranges, spinach, and nuts to protect skin cells from oxidative stress.
🌟 The Good Side
Even though age spots can be frustrating, remember this:
They’re not a sign of illness — they’re your skin’s story, a reflection of all the days you lived under the sun.
Taking care of your skin now can slow further damage and even reverse some of the visible signs.
🩺 In Short:
-
Cause: Long-term sun exposure → excess melanin → dark spots.
-
Not dangerous, but they indicate past UV damage.
-
Treatment: Sun protection, brightening creams, or professional procedures.
-
Prevention: Daily sunscreen, gloves, and antioxidants.
News in the same category

🌙 If You Notice These 3 Signs at Night, Your Kidneys Are Likely in Great Shape
3 Selfish Habits of Husbands That Increase Their Wives’ Risk of Cervical Cancer – Stop Them Now Before They Harm the Whole Family
Why Neck Skin Sags as We Age
Proven Inflammatory Foods to Avoid According to Science
14 Signs Your Blood Sugar Is Way Too High (And 14 Ways to Reduce It)

Walking Barefoot at Home

Stronger Than Eggs? The Affordable Seeds That May Support Muscle After 75

How to Prepare Okra Water to Naturally Support 17 Aspects of Health
Papaya Seeds for Joint Relief: A Simple Home Habit to Explore for Knee, Back, and Spine Comfort
Be amazed by this vitamin that can improve leg circulation and help protect against clots!

Discover Simple Everyday Herbal Habits That Can Naturally Support Kidney Health
Woman reveals five colon cancer symptoms that should not be ignored

What Are Eye Floaters? Here What To Do If you Start Seeing Them, According to an Eye Doctor

5 warning signs of cancer developing in the body

5 Concerning Red Flags That May Signal Colon Cancer
Essential vitamins for strong and cramp-free legs

Master Tonic: A Powerful Natural Drink for Immune Strength and Vitality 🌿🍋

11 Little-Known Secrets About Eating Grilled Corn — Even If You Love It, Remember These

12 Powerful Reasons to Drink Milk with Garlic Every Day
News Post

Never Broken a Bone

🌙 If You Notice These 3 Signs at Night, Your Kidneys Are Likely in Great Shape

3 Selfish Habits of Husbands That Increase Their Wives’ Risk of Cervical Cancer – Stop Them Now Before They Harm the Whole Family

Why Neck Skin Sags as We Age
Senior Slaps Freshman Girl—Her Ex-Con Brother’s Response Shocks Everyone
One Powerful Leaf That Supports Blood Sugar, Blood Pressure, Pain Relief, Cholesterol, and Healthy Circulation
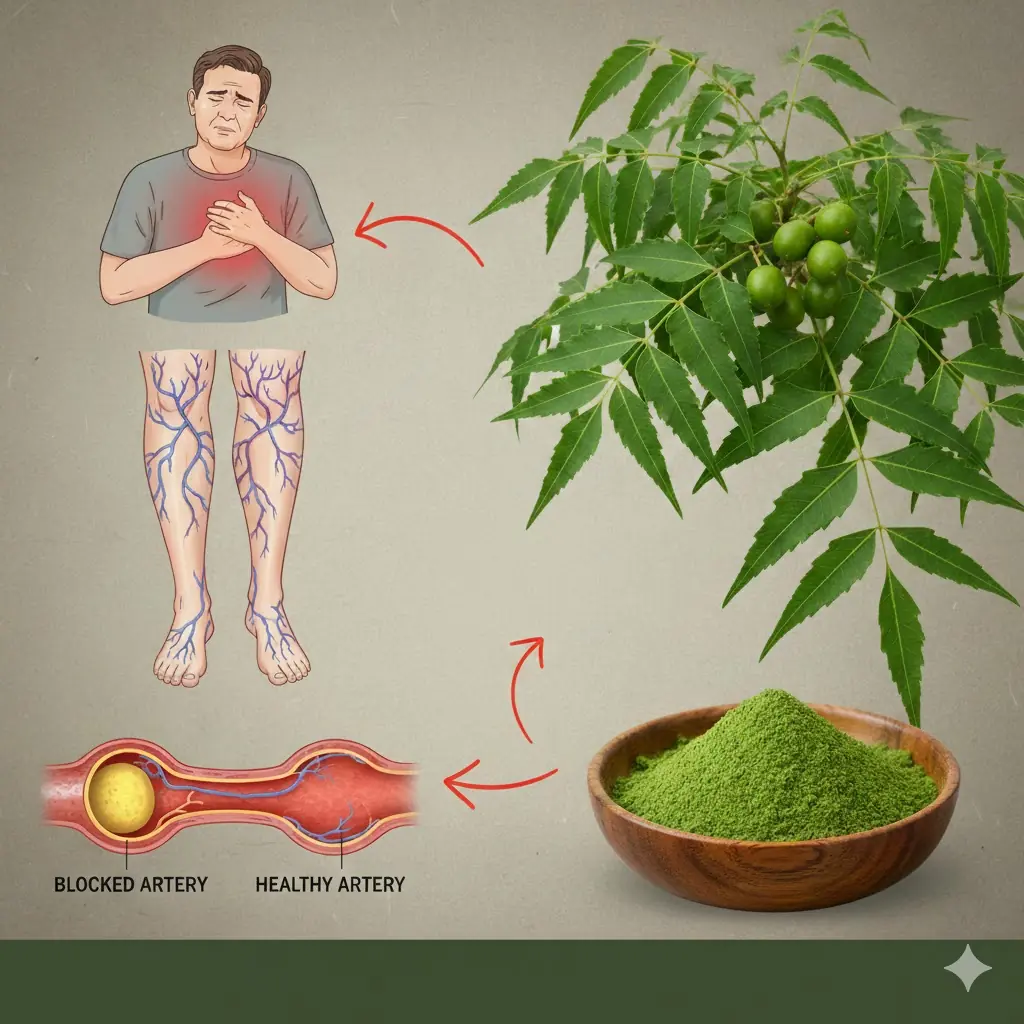
Discover the Power of a Single Leaf That Can Support Your Health Naturally 🌿💚
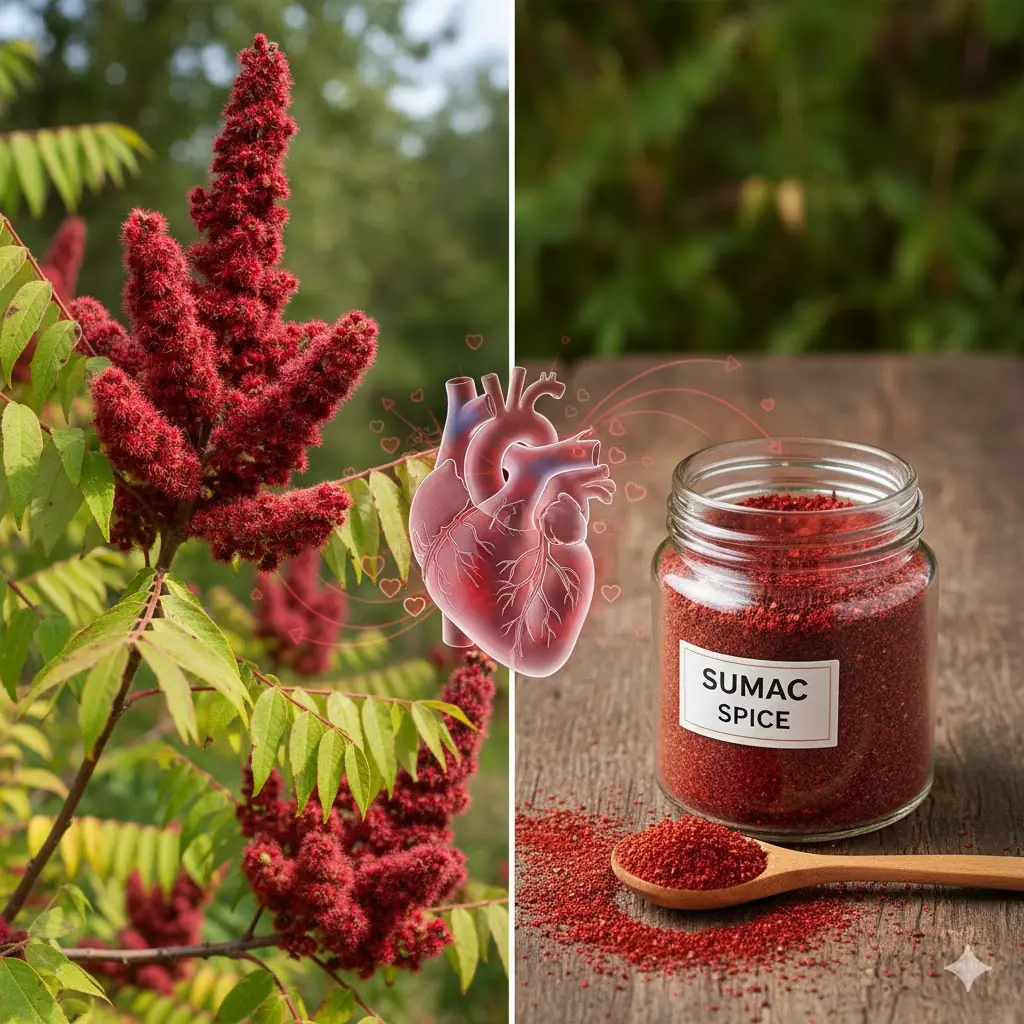

Sumac Tree Benefits – A Powerful Medicinal and Culinary Plant
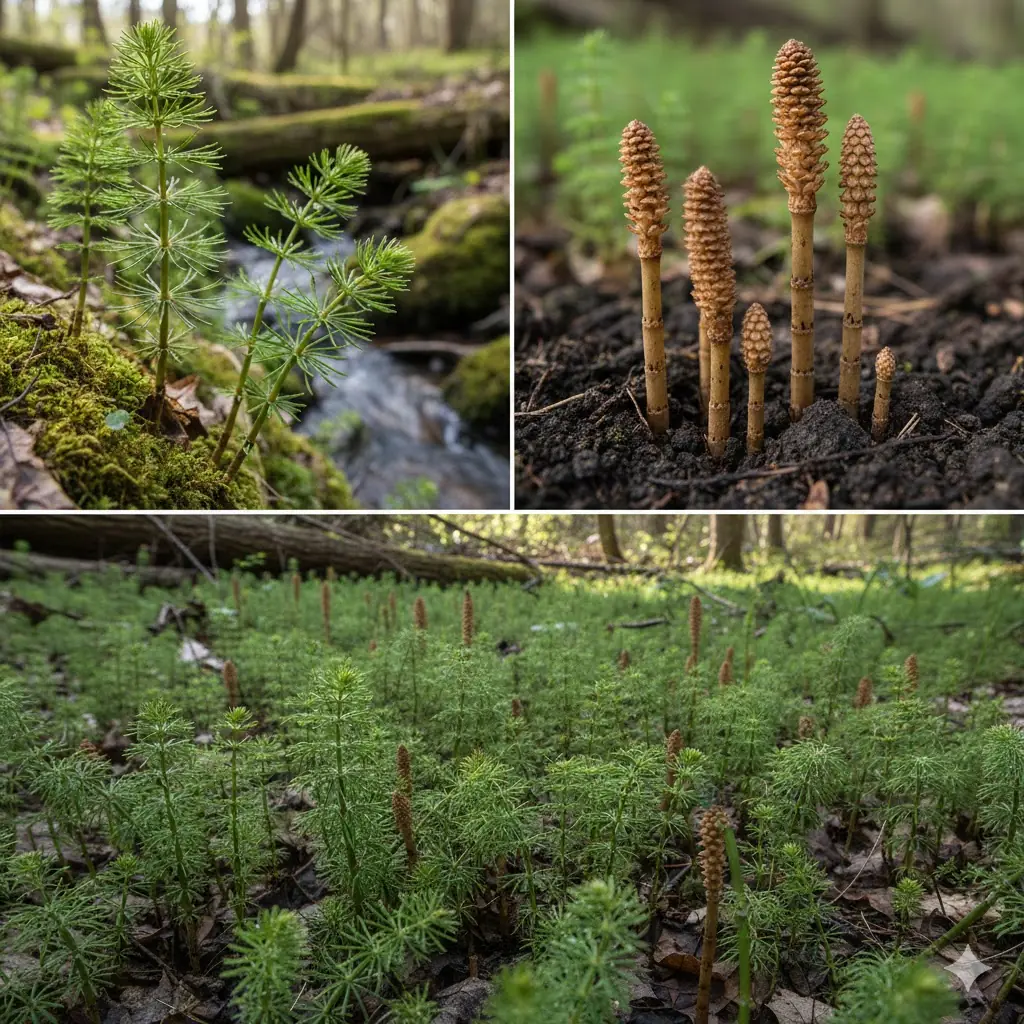

The Benefits of Horsetail: A Natural Remedy for Health and Wellness
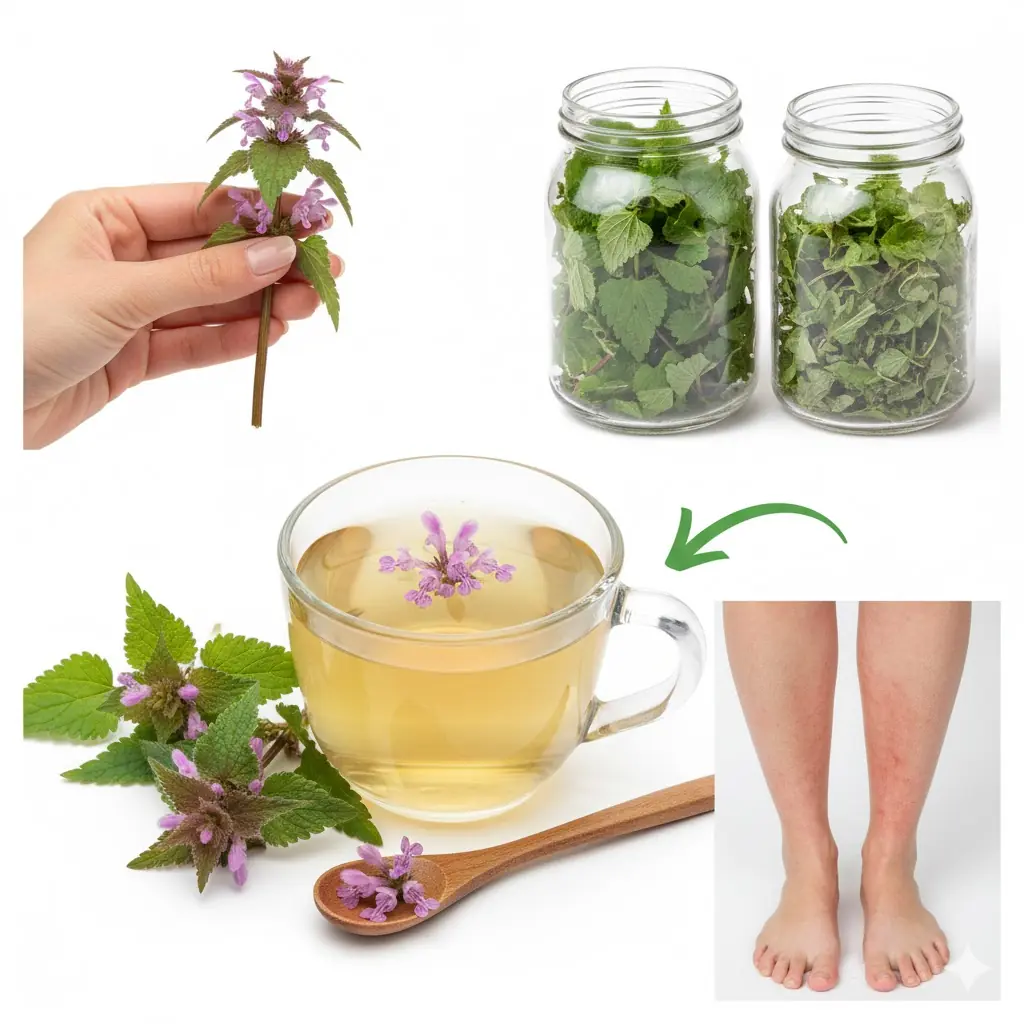

Purple Dead Nettle – Benefits and Uses of This Surprising Wild Herb

Alishan Thistle (Cirsium arisanense): Health Benefits, Traditional Uses, and Natural Healing Properties

Bully Beats Up “Weak” Kid 15 Times—Kid Was State Wrestling Champion

Star Wrestler Punched Girl Who Beat Him—Her Dad Was Olympic Coach

Karen Screams At Cashier For 20 Minutes… Then Learns Who He Really Is

Blogs This Voicemail Broke the Internet
What Is Stomach Cancer?
What Is the Adam’s Apple

Proven Inflammatory Foods to Avoid According to Science

14 Signs Your Blood Sugar Is Way Too High (And 14 Ways to Reduce It)
