Forget Plaque: Alzheimer’s May Be a Brain Energy Crisis
For decades, Alzheimer’s research has focused heavily on one central target: plaque buildup in the brain. Amyloid deposits were believed to be the primary driver of memory loss and cognitive decline, shaping treatment strategies for generations. But emerging research suggests that plaques may be only part of the story — and not necessarily the root cause. A growing body of evidence now points to a more fundamental issue: the brain’s energy supply.
A recent study has revealed that brains affected by Alzheimer’s disease appear to be operating in a state of severe energy deficiency. Neurons, which are among the most energy-demanding cells in the human body, rely heavily on efficient mitochondrial function to maintain memory, communication, and repair processes. In Alzheimer’s brains, researchers observed widespread metabolic failure, reduced glucose utilization, and impaired energy production — essentially a neurological “power outage.”
In experimental models, scientists tested what would happen if this energy crisis were addressed directly. When researchers restored cellular energy metabolism in mouse brains — by improving mitochondrial function and fuel availability — they observed a reversal of key Alzheimer’s-like damage. Synaptic connections improved, inflammation decreased, and cognitive performance recovered significantly. Remarkably, these improvements occurred even without directly targeting plaque accumulation, suggesting that restoring energy flow may allow the brain to repair itself.
This finding challenges the long-standing assumption that plaque buildup is the primary driver of disease progression. Instead, plaques may represent a downstream effect — a byproduct of neurons failing to meet their energy demands. When brain cells lack sufficient power, essential processes such as protein clearance, synaptic maintenance, and neuroplasticity break down, creating an environment where damage accumulates more rapidly.
Scientists increasingly describe Alzheimer’s as a metabolic disease of the brain rather than purely a protein-aggregation disorder. Brain imaging studies have consistently shown reduced glucose metabolism years before clinical symptoms appear, indicating that energy failure may be one of the earliest events in the disease process. This perspective helps explain why many plaque-targeting therapies have struggled to deliver meaningful cognitive benefits despite successfully reducing amyloid levels.
The implications of this shift are profound. Instead of focusing solely on removing what builds up, future treatments may aim to restore what is missing: energy. Therapies designed to support mitochondrial health, improve glucose and ketone utilization, reduce oxidative stress, and enhance cellular resilience could offer broader protection than plaque removal alone. This approach also aligns with lifestyle research showing that physical activity, metabolic health, sleep quality, and cardiovascular function strongly influence Alzheimer’s risk.
Leading research institutions and peer-reviewed journals have increasingly explored this energy-centered model of neurodegeneration. Findings from organizations such as the National Institutes of Health, Alzheimer’s Association, and publications including Nature Neuroscience, Cell Metabolism, The Lancet Neurology, and Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease support the idea that impaired brain energetics play a central role in disease progression.
This does not mean plaques are irrelevant — but it suggests they may be symptoms rather than the cause. Just as fixing a city’s electrical grid restores function faster than cleaning up debris, restoring energy to the brain may address the underlying failure that allows damage to accumulate in the first place.
Bottom line: Alzheimer’s disease may be driven less by toxic buildup and more by a loss of cellular power. Fixing the brain’s energy crisis could unlock new, more effective paths to prevention and treatment.
News in the same category

🌙 If You Notice These 3 Signs at Night, Your Kidneys Are Likely in Great Shape

3 Selfish Habits of Husbands That Increase Their Wives’ Risk of Cervical Cancer – Stop Them Now Before They Harm the Whole Family

Restoring Brain Energy Reverses Advanced Alzheimer’s Pathology in Preclinical Models

Remission Is a Reminder of the Power of Belief
A Scientist Injected Herself With Viruses to Treat Cancer — and It Worked

HMGB1 Identified as a Key Regulator of Aging and Tissue Regeneration
Regenerative Ear Drop Therapy Restores Natural Hearing in Early Trials

ADHD Treatment in Childhood Linked to Higher Adult BMI and Slight Height Reduction

What It Really Means When Your Partner Starts Kissing You With Their Tongue More Often
Why Neck Skin Sags as We Age

Doctors Reveal: Eating Cabbage Can Trigger Hidden Health Problems If You’re Not Careful

The Winged Bean Secret: A Simple Vegetable With Big Benefits for Eyes, Immunity, and Heart Health
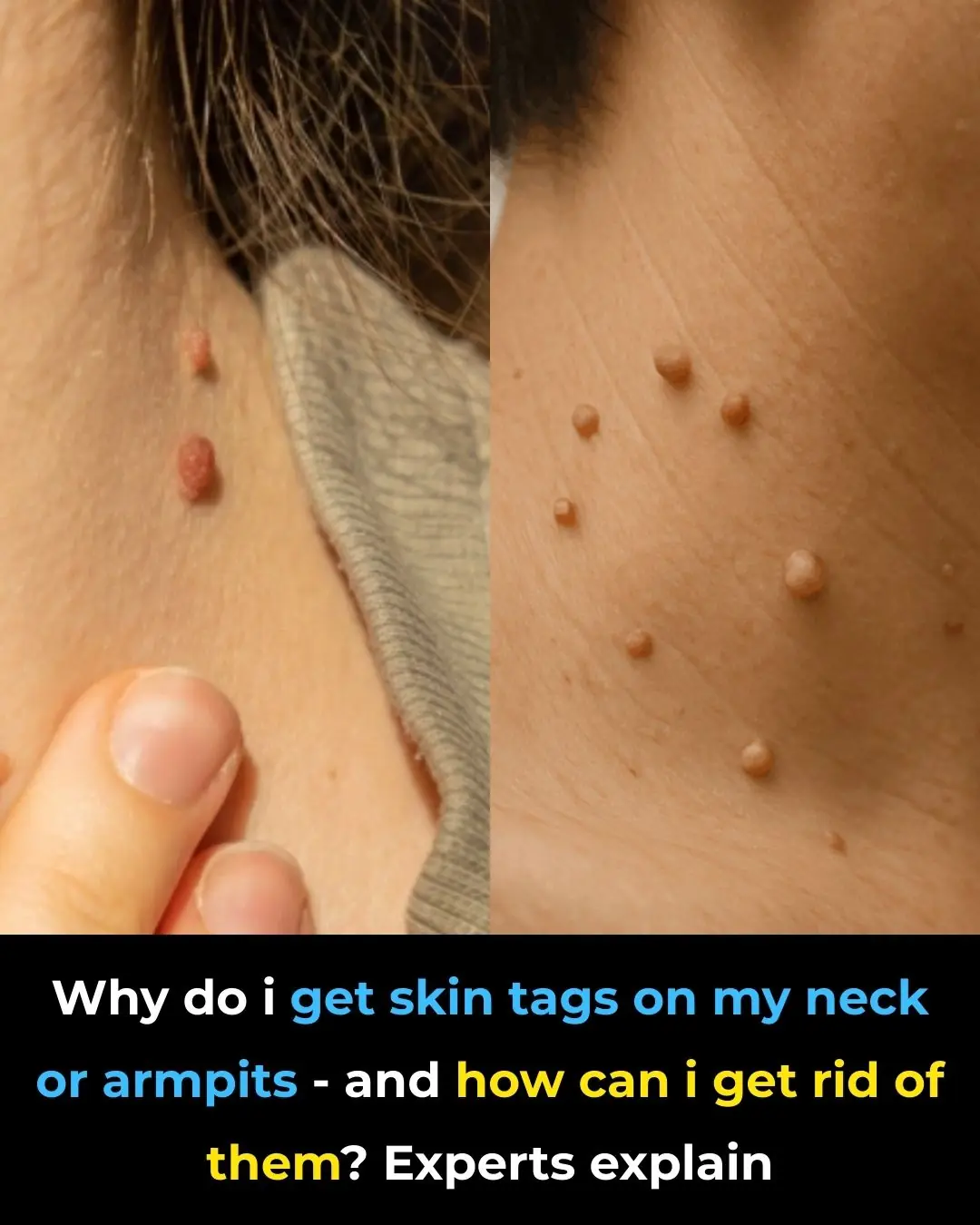
Why Do I Get Skin Tags on My Neck or Armpits—and How Can I Get Rid of Them? Experts Explain

Doctors Reveal What Eating Broccoli Really Causes in the Body

What Weak or Brittle Nails May Be Telling You About Your Health
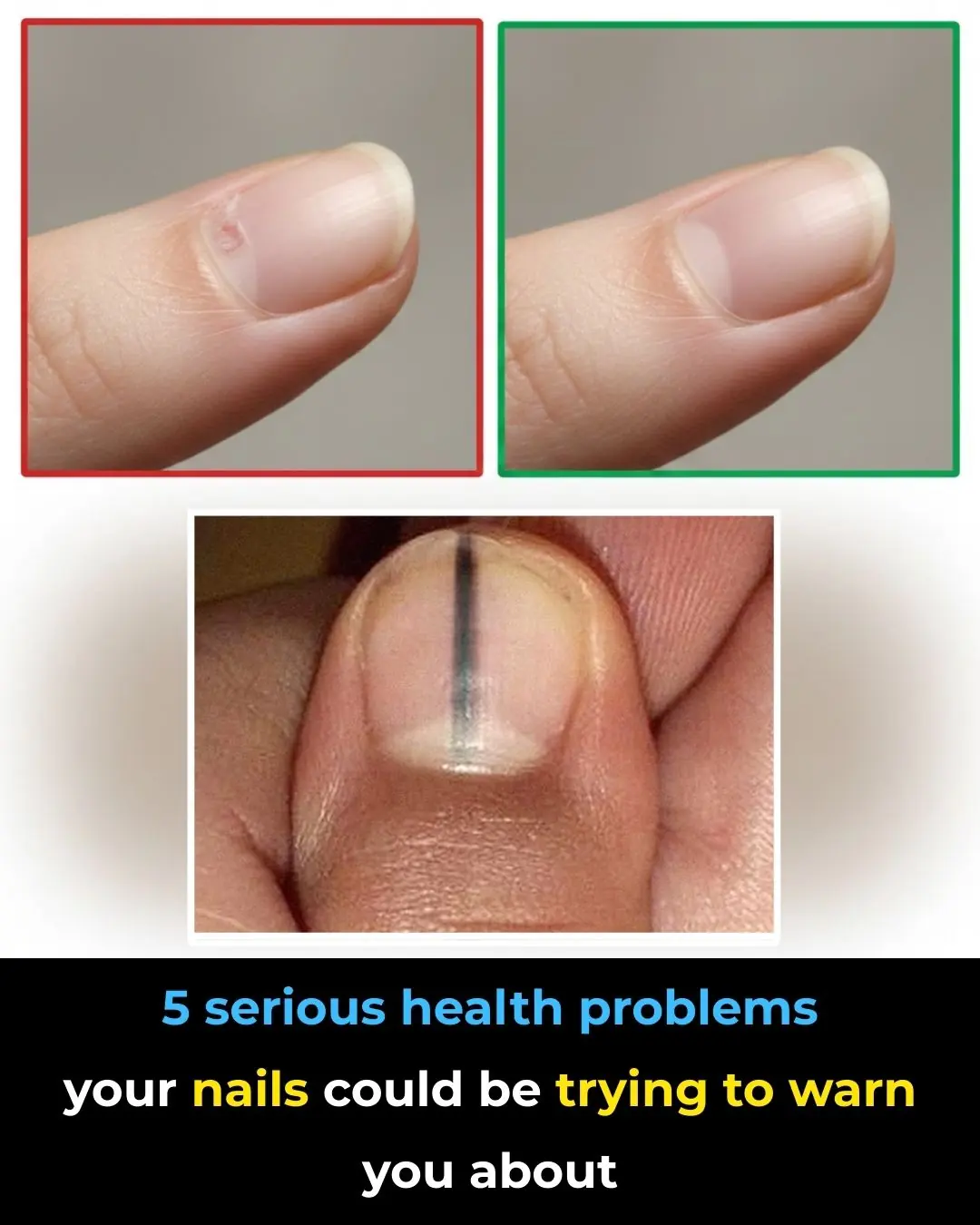
Nail Clues: 5 Health Problems You Shouldn’t Ignore
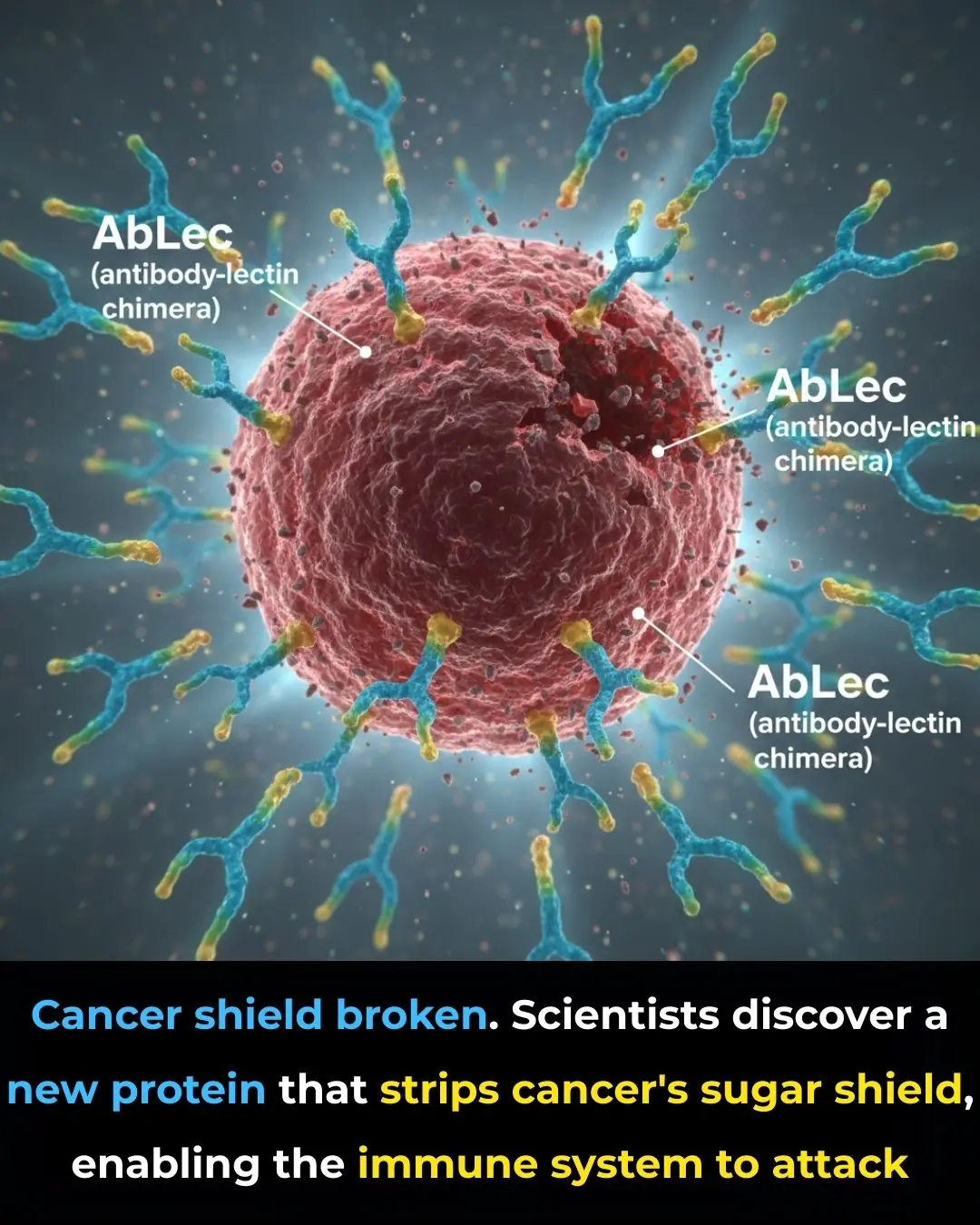
New Protein Breakthrough Unmasks Cancer Cells, Boosting the Power of Immunotherapy

Sugary Soft Drinks, Gut Bacteria, and Depression: How What You Drink May Shape Mental Health
News Post

Never Broken a Bone

🌙 If You Notice These 3 Signs at Night, Your Kidneys Are Likely in Great Shape

3 Selfish Habits of Husbands That Increase Their Wives’ Risk of Cervical Cancer – Stop Them Now Before They Harm the Whole Family

Washing blood stains from bed sheets with hot water or detergent is completely wrong; this method will remove them completely, leaving no trace.

Don't put tomatoes in the refrigerator: Here's how to keep them fresh for a whole week without them spoiling.

Bihar Jewellery Shops Restrict Face‑Covered Customers: Security vs. Freedom ⚖️✨
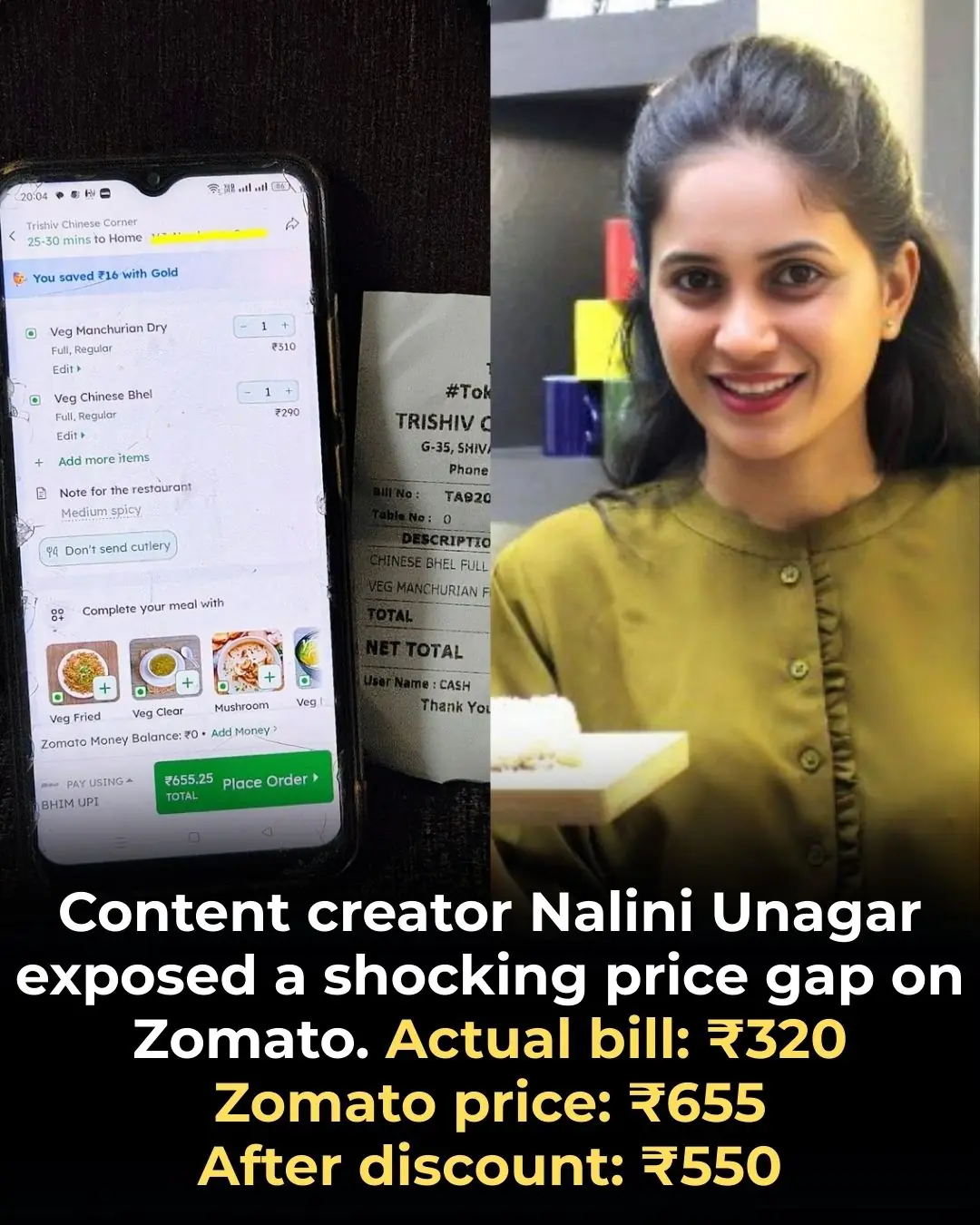
Nalini Unagar’s Viral Post Sparks Debate on Food Delivery Transparency 🍲📱

Tips for boiling okra to keep it vibrant green, not slimy, and retain all its nutrients.

Hrithik Roshan’s Birthday: A Celebration of Grace, Growth, and Mutual Respect 🎂✨❤️

Raghav Chadha Steps Into the Gig Economy: A Call for Labor Rights 🚴♂️📦

Thomas Fuller: The “Virginia Calculator” Who Defied Oppression 🧮✨

A Birthday Surprise That Touched Millions 🎂❤️

When frying pork fat, some people add salt, others add water, but chefs use pure white fat that lasts a long time without spoiling.

Restoring Brain Energy Reverses Advanced Alzheimer’s Pathology in Preclinical Models

Remission Is a Reminder of the Power of Belief

A Scientist Injected Herself With Viruses to Treat Cancer — and It Worked

HMGB1 Identified as a Key Regulator of Aging and Tissue Regeneration

Regenerative Ear Drop Therapy Restores Natural Hearing in Early Trials
