Never Ever Say These 4 Things at a Funeral — No Matter the Situation
When it comes to funerals and expressions of sympathy, your words don’t need to be profound or poetic.
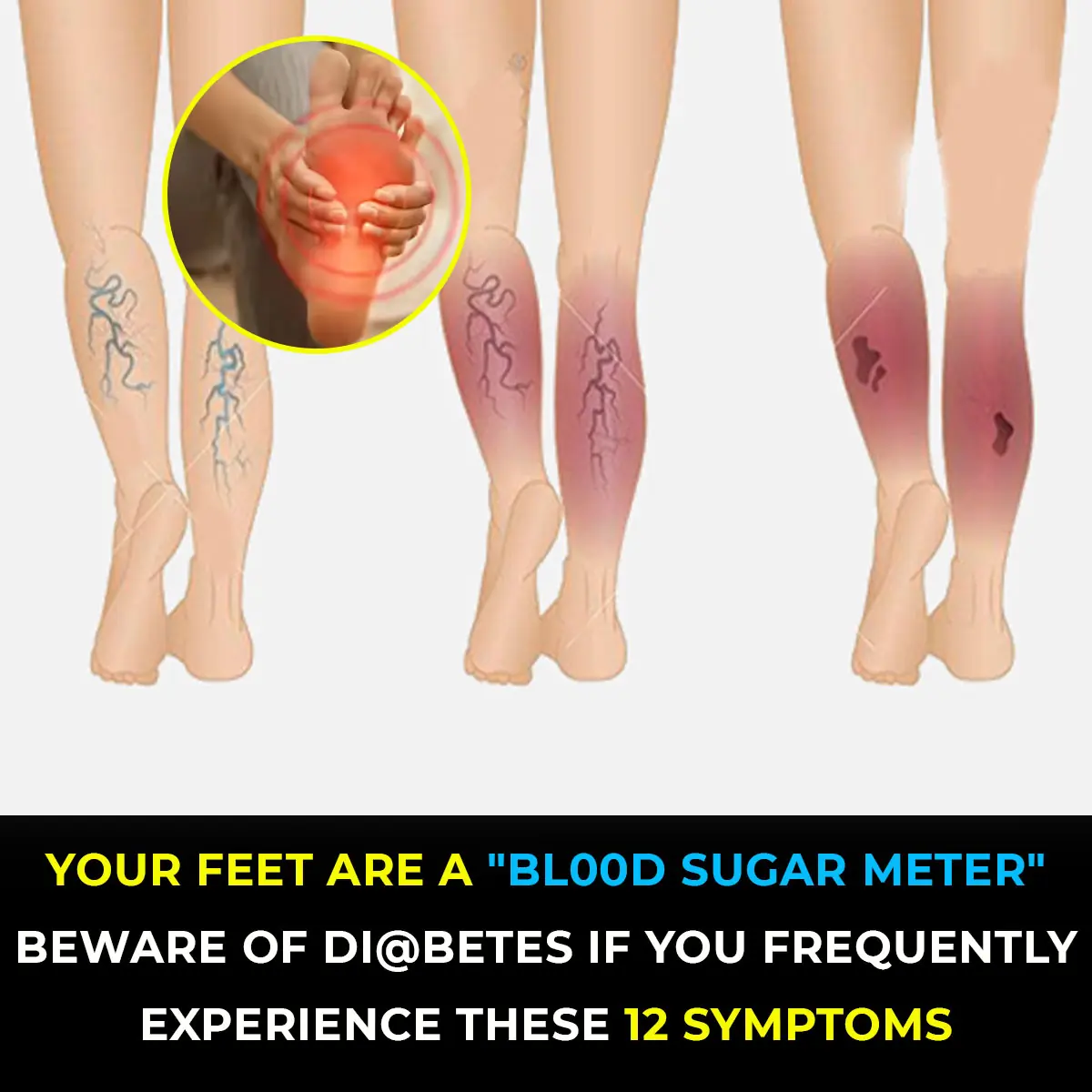
A bizarre virus is turning ordinary rabbits into grotesque creatures covered in horn-like growths and tentacle-shaped tumors. Wildlife officials are warning the public not to approach these so-called “Frankenstein rabbits,” which are spreading across parts of the United States.
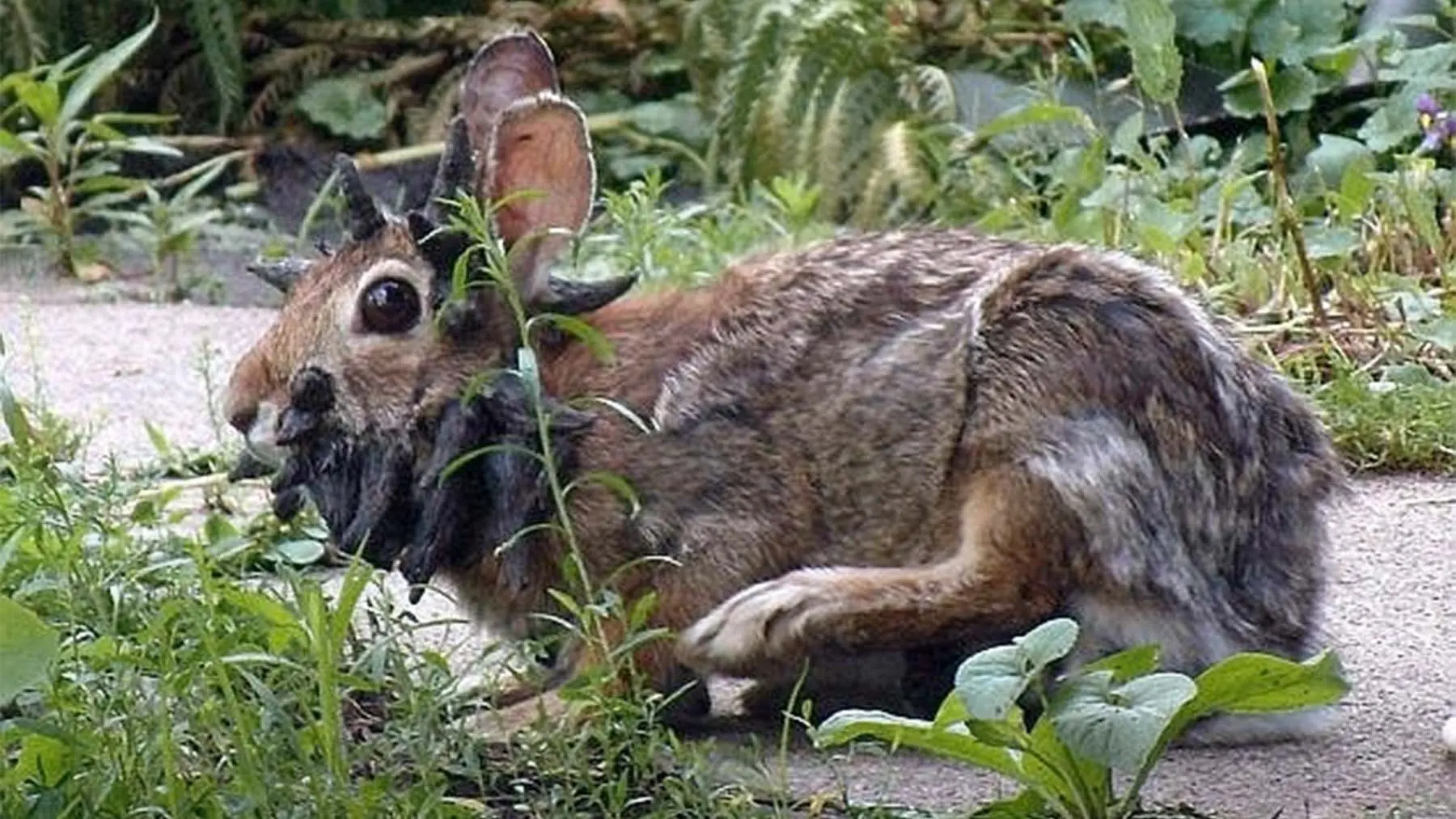

Strange Sightings of Mutant Rabbits
Reports of these disturbing-looking rabbits have been increasing, particularly in Fort Collins, Colorado, where locals have spotted animals with twisted, black growths covering their faces. The phenomenon first gained attention in 2024, when a resident uploaded a shocking photo showing a rabbit whose head was coated in black, spike-like projections.
Susan Mansfield, a local witness, described what she saw: “It looked like black quills or black toothpicks sticking out all around its mouth. I thought he’d die off during the winter, but he didn’t. He came back a second year—and it grew.”
The Virus Behind the Transformation
Scientists have identified the culprit as the cottontail papilloma virus (CRPV), also called the Shope papilloma virus. This DNA-altering virus causes tumors to form on or around a rabbit’s head. Initially appearing as small red patches, the growths develop into wart-like structures that eventually harden into horn-shaped keratinized papillomas. These growths can resemble horns, spikes, or even black tentacles, giving rise to the “Frankenstein rabbit” nickname.
According to Colorado Parks and Wildlife (CPW), the infection spreads primarily through bites from mosquitoes and ticks. Direct contact between rabbits is less common, and there are no documented cases of the virus being transmitted to humans or pets. Still, wildlife experts urge people to avoid touching infected animals under any circumstances.
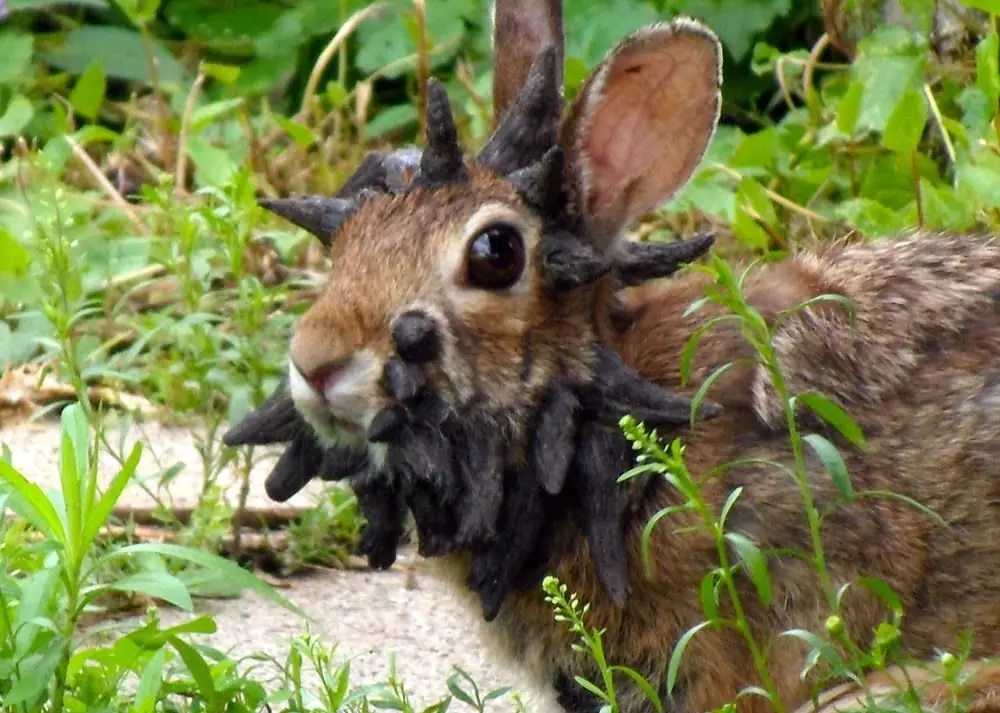

d:eadly Consequences for Rabbits
While some of these growths may shrink or heal on their own, many rabbits are not so fortunate. Over time, the tumors can grow excessively large, blocking the animal’s mouth and preventing it from eating, which often leads to starvation. Growths on the eyes or ears can impair vision and hearing, further reducing their chances of survival in the wild.
Veterinary experts warn that some papillomas can transform into squamous cell carcinoma, a form of skin cancer that is often fatal if left untreated. For pet owners, veterinarians recommend preventive measures such as keeping rabbits away from insects. Infected pets can sometimes undergo surgery to remove tumors before they become malignant.
A Viral Sensation — and a Dark Legend
As photos of the horned rabbits circulate online, social media users are debating whether it would be more humane to euthanize infected animals or simply let nature take its course. Despite the unsettling appearance of these creatures, experts emphasize that the virus poses no risk to human health and that intervention is unnecessary.
Interestingly, tales of horned rabbits are not new. Folklore surrounding the mythical “jackalope”—a rabbit with antelope-like horns—has often been linked to sightings of rabbits suffering from this very virus. Historical records show depictions of horned rabbits as far back as 1789, in works such as the Tableau Encyclopédique et Méthodique.
Final Warning from Experts
Wildlife officials stress that the safest action is simple: observe from a distance. If you encounter one of these horned or tentacle-faced rabbits, do not touch or attempt to help it. Although they may look frightening or pitiful, they remain a natural example of how viruses can drastically alter an animal’s appearance.
These “Frankenstein rabbits” may resemble creatures out of legend, but they are a real reminder of how powerful and unpredictable nature can be.

When it comes to funerals and expressions of sympathy, your words don’t need to be profound or poetic.




Ticks may be small, but their impact on human and pet health can be enormous.

If you love solving puzzles and challenges, this viral hidden words image is just for you!

That tiny hole in a safety pin isn’t just decoration - it’s proof that even the simplest everyday tools can hide smart design secrets.








A 33-year-old woman from Colorado was clinically d:ead for eight minutes—yet she insists she never lost awareness and discovered that death is only an illusion. Her extraordinary account challenges science, spirituality, and everything we think we know


Black butterflies carry meanings that are as mysterious as they are beautiful.



When it comes to funerals and expressions of sympathy, your words don’t need to be profound or poetic.