Never Ever Say These 4 Things at a Funeral — No Matter the Situation
When it comes to funerals and expressions of sympathy, your words don’t need to be profound or poetic.

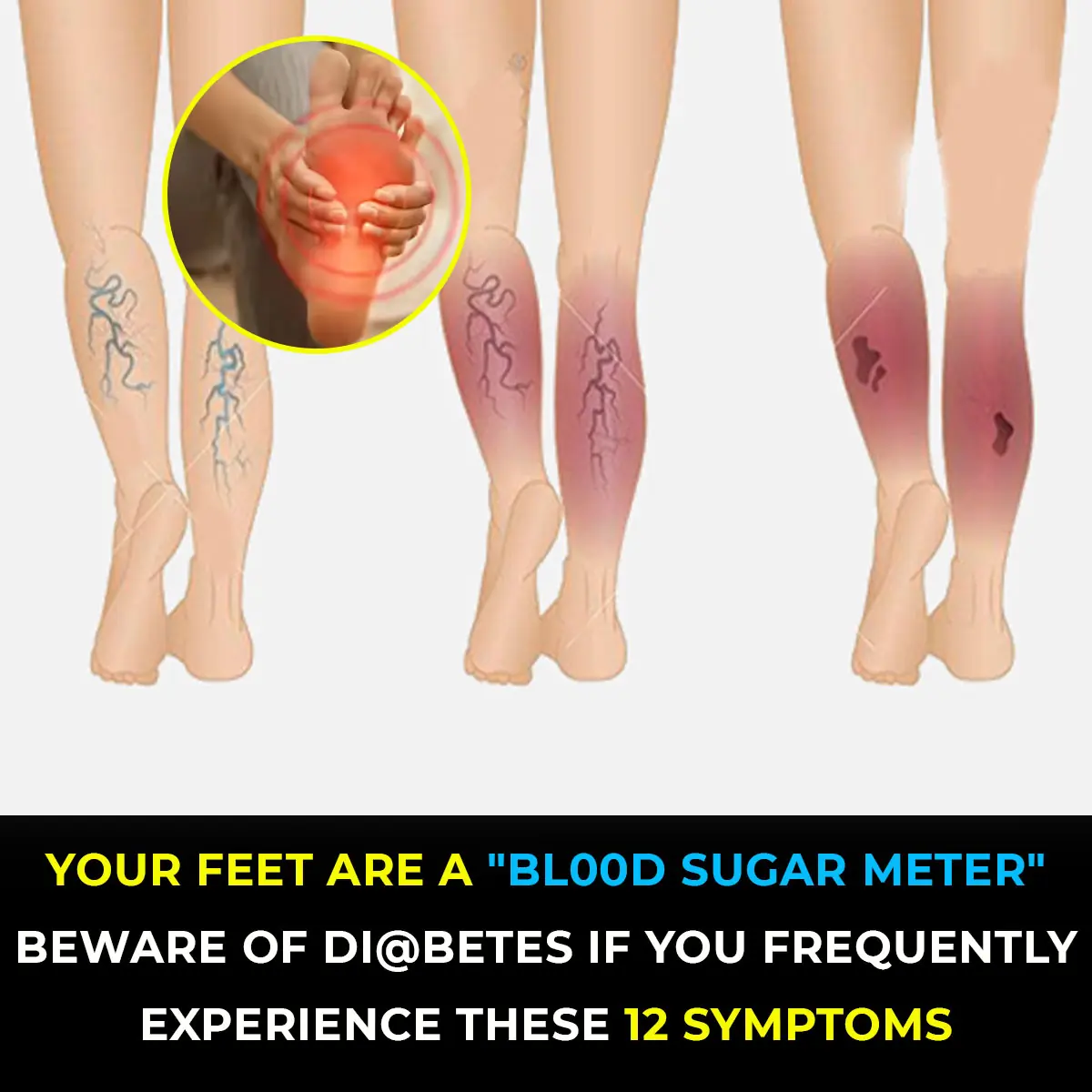
Ticks are small arachnids that survive by feeding on the blood of mammals, birds, and occasionally reptiles or amphibians. Though they may appear harmless, ticks can transmit serious illnesses to humans through their bites. Learning how to properly remove and dispose of ticks is an important step in reducing the risk of contracting tick-borne diseases.
Ticks are well-known carriers of dangerous infections, including Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and babesiosis. If not diagnosed and treated in time, these conditions can cause long-term health complications. For that reason, taking the right precautions when dealing with ticks is vital.
If you discover a tick on your skin, remove it carefully and without delay. The safest method is to use fine-tipped tweezers or forceps:
Grip the tick as close to your skin’s surface as possible.
Pull upward slowly and steadily in one continuous motion.
Do not twist or crush the tick, as this may cause it to release harmful bacteria into the wound.
Certain home remedies should be avoided at all costs. Methods like using matches, petroleum jelly, nail polish, or attempting to burn the tick can actually irritate it and increase the chance of transmitting disease. Likewise, squeezing the tick with your fingers can force pathogens into your bloodstream.
After removal, it’s just as important to dispose of the tick safely. Options include:
Sealing it in a bag or container to prevent further contact.
Flushing it down the toilet.
Wrapping it securely in tape before throwing it away.
If possible, some healthcare providers recommend saving the tick in a container so it can be identified later by a professional, especially if you develop symptoms.
Ticks don’t just pose a risk to people—your pets can also be affected. Regular inspections are essential, especially during warmer months, though ticks can survive even in cold conditions.
When examining your pets:
Check areas like the ears, armpits, groin, toes, and skin folds.
Run your hands through their fur to feel for small, firm bumps.
Use a fine-toothed comb to part the hair and spot hidden ticks.
The more frequently you check, the easier it becomes to detect ticks early.
Never remove a tick from your pet using your bare hands. Instead, use tweezers to grip the tick close to the skin and pull upward with steady pressure. Once removed:
Do not crush the tick.
Place it in a sealed container for possible veterinary identification.
If that’s not possible, dispose of it by sealing in a bag or wrapping in tape.
Flushing is another option, but some vets prefer to examine the tick to determine potential disease risk.
One of the most recognized tick-borne illnesses is Lyme disease, caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. Early signs include fever, headache, fatigue, and a red, circular rash known as erythema migrans. If untreated, Lyme disease can lead to more serious issues involving the heart, joints, and nervous system.
If you’ve been bitten, watch for warning signs that may indicate infection:
Flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, joint pain, and muscle aches.
A bullseye-shaped rash at the bite site.
Unexplained fatigue or persistent headaches.
Other tick-borne illnesses may cause similar symptoms, making medical evaluation important.
If you develop any concerning symptoms following a tick bite, contact a healthcare provider promptly. Let them know about the bite and describe your symptoms. Early detection and treatment are key to preventing complications from tick-borne diseases.
Ticks may be small, but the health risks they carry are significant. By learning how to remove them correctly, avoid harmful removal methods, and dispose of them safely, you greatly reduce your risk of infection.
Stay alert when spending time outdoors, check yourself and your pets regularly, and seek medical advice if you suspect exposure to a tick-borne illness. Taking these steps will help protect your health and that of your loved ones.

When it comes to funerals and expressions of sympathy, your words don’t need to be profound or poetic.



Ticks may be small, but their impact on human and pet health can be enormous.

Although they may look frightening or pitiful, they remain a natural example of how viruses can drastically alter an animal’s appearance.

If you love solving puzzles and challenges, this viral hidden words image is just for you!

That tiny hole in a safety pin isn’t just decoration - it’s proof that even the simplest everyday tools can hide smart design secrets.








A 33-year-old woman from Colorado was clinically d:ead for eight minutes—yet she insists she never lost awareness and discovered that death is only an illusion. Her extraordinary account challenges science, spirituality, and everything we think we know


Black butterflies carry meanings that are as mysterious as they are beautiful.



When it comes to funerals and expressions of sympathy, your words don’t need to be profound or poetic.