
He Drank Sugary Beverages Instead of Water — Doctors Removed Nearly 300 Kidney Stones
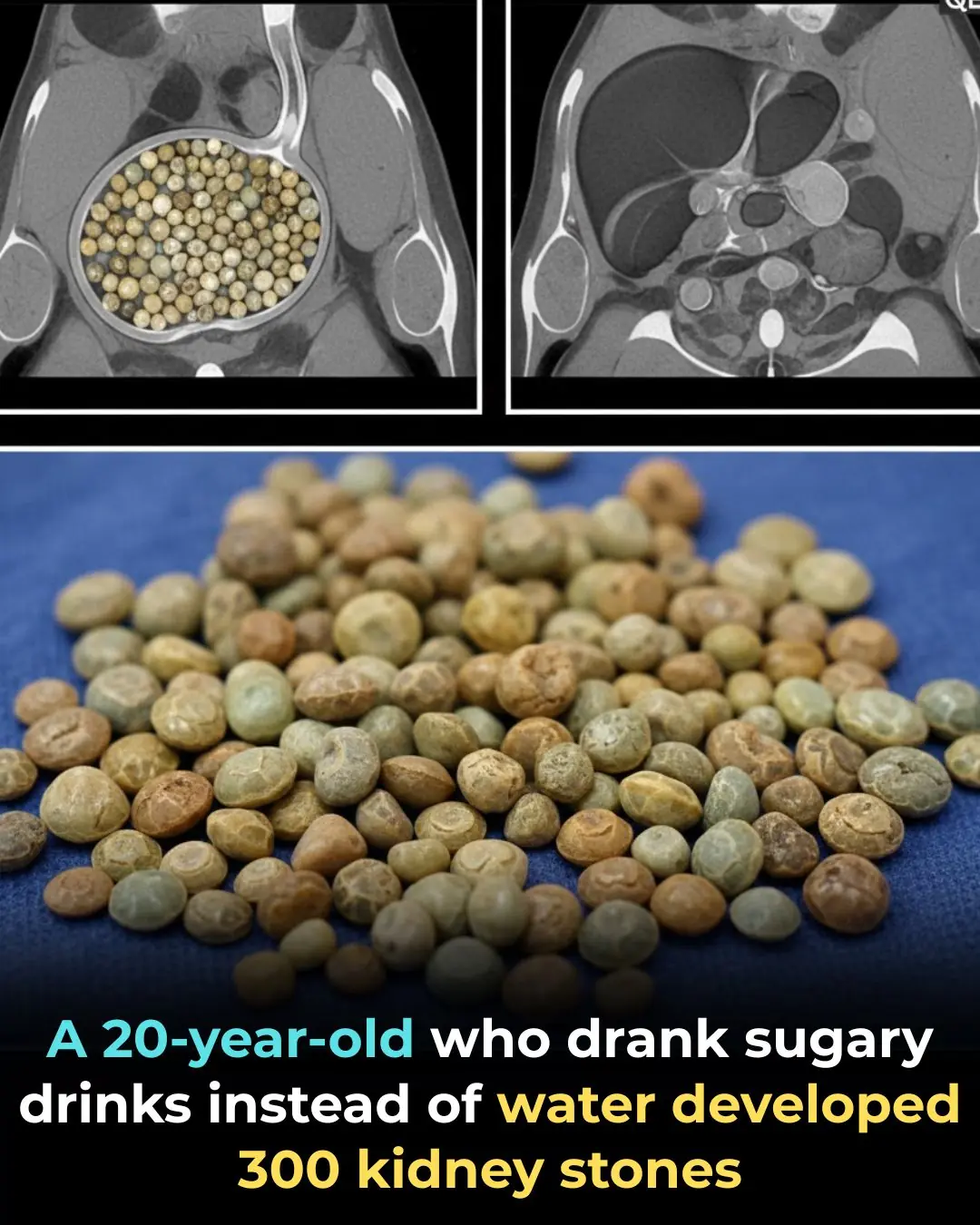
A shocking medical case from Taiwan has recently gone viral and has become a powerful reminder of the dangers of replacing water with sugary drinks. A 20-year-old man, who for years avoided plain water and relied almost entirely on bubble tea, sweetened juices, energy drinks, and alcohol, was rushed to the hospital after developing severe lower-back pain, fever, and persistent discomfort. What seemed like a simple infection soon revealed something far more alarming.
Diagnostic imaging left doctors speechless: nearly 300 kidney stones were jammed inside a single kidney. Some stones were as tiny as grains of sand, while others had grown into marble-sized clusters. Because of the sheer volume and size of the stones, surgeons had to carefully remove them one by one. This extraordinary case quickly spread across social media, raising concern among millions who regularly choose sugary beverages over water.
Doctors explained that the patient’s habits created the perfect conditions for stones to develop. Sugary drinks do not hydrate the body effectively; in fact, many may worsen dehydration due to their high sugar and caffeine content. Without enough water, urine becomes highly concentrated, allowing minerals such as calcium, oxalate, and phosphate to crystallize more quickly. High sugar intake also contributes to inflammation, metabolic strain, and increased kidney stone risk, as supported by numerous medical studies. In addition, bubble tea ingredients — especially tapioca pearls and certain flavor powders — often contain oxalates, which are known to accelerate stone formation when consumed in excess. Over time, the patient’s near-absence of water intake allowed these crystals to accumulate into hundreds of stones.
Although this case is extreme, experts emphasize that the underlying risk is widespread. Research consistently shows that people who consume large amounts of sugary beverages face a significantly higher likelihood of developing kidney stones. Studies from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health indicate that individuals who primarily drink soda or sugary juice have up to a 23% higher risk of stone formation. Findings published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) report that people who obtain more than 25% of their daily calories from added sugars also face a sharply increased risk of kidney stones and other metabolic disorders. Additionally, the National Kidney Foundation highlights chronic dehydration as one of the most powerful — and preventable — triggers for kidney stones. Even mild, long-term dehydration can silently cause mineral buildup that becomes painful only when stones are already well-formed.
To protect kidney health, specialists recommend following a simple hydration guideline. Water should always be the main beverage consumed daily. Sugary drinks should be treated as occasional indulgences rather than hydration sources. Most adults benefit from drinking 2–3 liters of water per day, with higher amounts recommended for those living in hot climates or engaging in heavy physical activity. Adequate water intake helps keep urine diluted, reduces mineral concentration, and dramatically lowers the risk of stone formation.
These recommendations are strongly supported by leading medical organizations, including the National Kidney Foundation, Mayo Clinic, Cleveland Clinic, and research institutions such as Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. Their findings consistently point to the same conclusion: proper hydration is essential for preventing kidney stones and maintaining long-term kidney function.
News in the same category


14 Warning Signs of Low Magnesium Levels and What to Do About It (Science Based)
Top 10 Foods to Heal Knee Pain and Boost Cartilage Naturally

Blood Type O Diet: What to Eat and What to Avoid
7 nutrients that actually repair nerves

This one vitamin could help stop you from waking up to pee every night

The Cold Room Sleep Trick That Can Transform Your Health

Why You Keep Waking Up at Night

Research reveals the #1 vitamin for eye protection
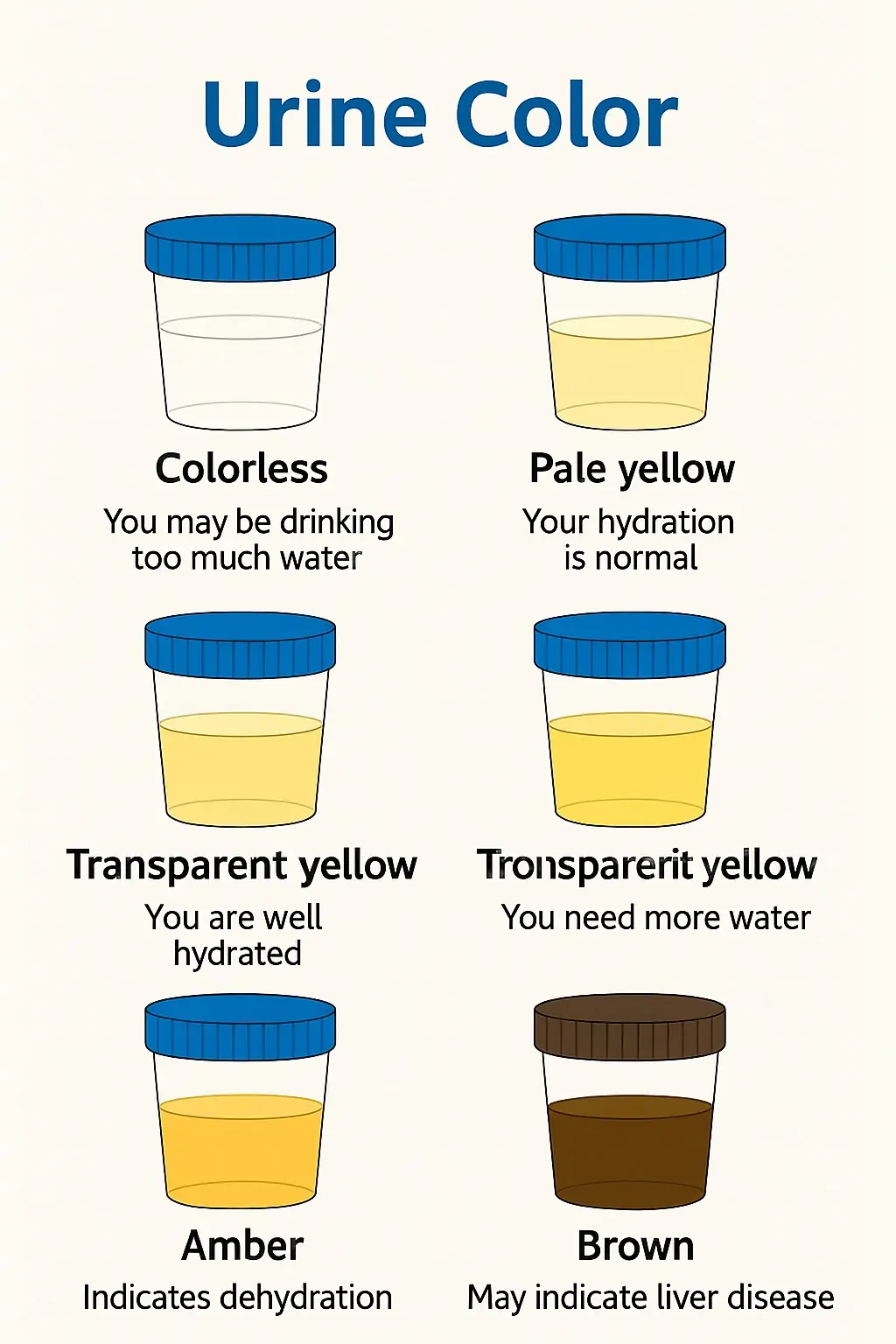
What Your Urine Color May Be Telling You (Gently & Naturally)

Soothe Leg Pain Naturally: Garlic & Clove Remedy for Joints, Circulation, and Comfort
Eat Garlic — But Avoid This Common Mistake! | 95% of People Don’t Know This Simple Trick
Home Remedies For Kidney Stones – 21 Remedies For Effective Pain Relief
Eat One Clove of Garlic Every Morning on an Empty Stomach – and Watch These 12 Health Benefits Unfold!

Never do this when flying; many people have ruined their lives because they didn’t know better

Public Health Experts Stress Vaccination as Key to Preventing Severe and Long COVID
People who are about to be affected by cancer often show three unusual signs in the neck; even having just one of them can be a warning for your health
4 vitamins to reverse neuropathy and damaged nerves – relieve foot & hand pain fast!

8 Amazing Foods To Clean Out Your Toxic Liver
News Post

Jamie Laing admits ‘I’m really scared’ as he shares baby update

Jane Seymour declares ‘70 is the new 50’ after finding love again following four marriages

Tom Cruise, 63, seen laughing with Sydney Sweeney, 28, at Governors Awards after split from Ana de Armas

Cruz Beckham, 20, banned from driving after getting 2 speeding tickets

Ex-Disney star ripped for ‘demonic’ app that lets users talk to AI versions of dead relatives: ‘Literally a ‘Black Mirror’ episode’

Cardi B feels ‘threatened’ after Offset’s paternity comment on singer’s baby with Stefon Diggs: ‘My life is in danger

Denise Richards speaks out after being granted permanent restraining order against ex Aaron Phypers

China’s New Hongqi Bridge Collapses Just Months After Opening

Fire Beneath the Ice: Antarctica’s Hidden Volcanoes

Rebecca Gayheart reveals living situation as ex Eric Dane battles ALS: ‘Super complicated’

10 Benefits of Vaseline For Skin, Lips & Hair

Denise Richards speaks out after being granted permanent restraining order against ex Aaron Phypers

Reason Sara Davies is ‘gutted’ Strictly Come Dancing star Vicky Pattison was voted out of the competition

Emmerdale star Bradley Riches shares lengthy social media message as he celebrates soap achievement

Prince William and Kate Middleton ‘to make Royal Variety performance return’ after two year hiatus

Jamie Laing admits ‘I’m really scared’ as he shares baby update

‘It Was Neglect’: Birmingham Police Haven’t Made an Arrest After Social Worker Left 3-Year-Old Boy In Hot Car to Die Following Shopping Trip; Outraged Family Demands Justice

ITV Emmerdale fans 'work out' villain will violently take down Celia in unexpected twist
