How to treat nerve pain in the foot, toes & legs

Peripheral neuropathy is a complex and often debilitating condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It commonly presents as nerve pain, burning sensations, tingling, numbness, or weakness in the feet, toes, and legs. For many people, these symptoms interfere with sleep, mobility, balance, and overall quality of life. Early recognition and proper management are essential to prevent progression and long-term complications.
In this article, we examine the underlying causes of peripheral neuropathy, the importance of accurate diagnosis, available treatment options, and practical strategies to manage symptoms effectively.
Key Takeaways
-
Peripheral neuropathy can result from metabolic disorders, toxic exposure, nutritional deficiencies, autoimmune conditions, or physical nerve injury.
-
Accurate diagnosis is critical to identify and address the underlying cause.
-
Treatment typically involves a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, and supportive therapies.
-
Simple home practices can significantly improve comfort and function.
What Is Peripheral Neuropathy?

Peripheral neuropathy refers to damage or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves—the network of nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. These nerves transmit sensory information (such as pain and temperature), motor signals (muscle movement), and autonomic functions (heart rate, digestion).
When peripheral nerves are damaged, communication between the brain and the rest of the body becomes disrupted. Symptoms often begin in the longest nerves of the body, which is why the feet and lower legs are frequently affected first.
Common symptoms include:
-
Burning or stabbing pain
-
Tingling or “pins and needles” sensations
-
Numbness or reduced sensation
-
Muscle weakness
-
Loss of balance or coordination
Common Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy
1. Diabetes
Diabetes is one of the leading causes of peripheral neuropathy. Chronically elevated blood glucose levels can damage small blood vessels that supply nerves, reducing oxygen and nutrient delivery. Over time, this leads to diabetic neuropathy, most commonly affecting the feet and legs.
Strict blood sugar management is essential to prevent progression.
2. Chronic Alcohol Use
Excessive alcohol consumption can cause direct nerve toxicity and contribute to vitamin deficiencies, particularly thiamine (B1). Alcoholic neuropathy may present with burning pain, numbness, and muscle weakness, particularly in the lower extremities.
3. Physical Injury or Nerve Compression
Trauma from accidents, repetitive strain, herniated discs, or spinal stenosis can compress or damage nerves. For example, sciatica occurs when the sciatic nerve is compressed, causing radiating pain down the leg.
4. Nutritional Deficiencies
B vitamins—especially B1, B6, B9 (folate), and B12—are vital for nerve function and myelin sheath integrity. Vitamin E deficiency may also impair nerve conduction. A deficiency in B12, in particular, can lead to demyelination, resulting in numbness and neurological impairment.
5. Other Medical Conditions
Peripheral neuropathy can also arise from:
-
Hypothyroidism
-
Autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis)
-
Guillain-Barré syndrome
-
Chronic kidney disease
-
Infections such as shingles, Lyme disease, or HIV
-
Exposure to certain chemotherapy drugs
Because neuropathy has many possible causes, identifying the underlying trigger is crucial for effective treatment.
The Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Many individuals mistakenly assume they have peripheral neuropathy when symptoms may stem from other conditions such as spinal nerve compression, vascular disease, or musculoskeletal disorders.
A proper medical evaluation may include:
-
Neurological examination to assess reflexes, sensation, and muscle strength
-
Nerve conduction studies (NCS) and electromyography (EMG) to evaluate nerve signaling
-
Blood tests to detect diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, thyroid dysfunction, or autoimmune markers
-
Imaging tests such as MRI to identify structural compression
-
Foot examination by a podiatrist to rule out localized conditions
An accurate diagnosis allows for targeted treatment rather than symptom-based management alone.
Treatment Options
Management of peripheral neuropathy typically involves addressing the underlying cause while controlling pain and improving nerve function.
Medications
Pain Relievers:
Mild pain may respond to over-the-counter medications. For moderate to severe neuropathic pain, prescription options may be considered.
Antidepressants:
Tricyclic antidepressants (such as amitriptyline) and SNRIs (such as duloxetine) can modify pain-processing pathways in the brain and reduce nerve pain.
Anti-Seizure Medications:
Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed to stabilize overactive nerve signals responsible for neuropathic discomfort.
Topical Treatments:
Capsaicin creams or lidocaine patches may help reduce localized pain by desensitizing nerve endings.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle plays a powerful role in nerve health.
Nutrition:
A diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, leafy greens, nuts, and antioxidant-rich fruits supports nerve repair and reduces oxidative stress. Diabetic patients must prioritize tight blood sugar control to prevent further nerve damage.
Exercise:
Regular low-impact exercise—such as walking, swimming, or yoga—improves circulation, reduces inflammation, enhances balance, and strengthens muscles.
Avoid Alcohol and Smoking:
Both substances impair blood flow and worsen nerve damage. Eliminating these risk factors may slow progression and improve symptoms.
Home-Based Supportive Measures
Proper Footwear:
Supportive, cushioned shoes with adequate toe space reduce pressure and friction. Custom orthotics may further alleviate discomfort.
Stretching and Massage:
Gentle stretching promotes flexibility and circulation. Massage can reduce muscle tension and enhance blood flow.
Warm Foot Soaks:
Warm (not hot) water may relax muscles and improve circulation. Individuals with reduced sensation must exercise caution to prevent burns.
Epsom Salt Baths:
Magnesium in Epsom salt may promote muscle relaxation and symptom relief for some individuals.
Alternative and Adjunct Therapies
Acupuncture:
Some patients report symptom improvement through acupuncture, which may stimulate natural pain-relieving mechanisms.
TENS Therapy:
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation uses low-voltage electrical currents to block pain signals and stimulate endorphin release.
Physical Therapy:
A structured rehabilitation plan can improve strength, coordination, and fall prevention.
Compression Therapy:
Compression stockings may enhance circulation and reduce swelling, particularly if vascular insufficiency contributes to symptoms.
When to Seek Advanced Care
If symptoms persist, worsen, or significantly impair daily function, further medical evaluation is warranted. In cases involving structural nerve compression, surgical decompression may provide relief. Advanced pain management options such as nerve blocks or spinal cord stimulation may be considered in severe, treatment-resistant cases.
Additionally, sudden onset of weakness, loss of bladder control, or rapid progression of symptoms requires immediate medical attention.
Conclusion
Peripheral neuropathy can significantly affect physical comfort and quality of life, but it is not without management options. A thorough diagnostic evaluation, combined with a comprehensive treatment plan—including medication, nutrition, exercise, and supportive therapies—can greatly reduce symptoms and slow progression.
By addressing underlying causes and adopting proactive lifestyle measures, individuals living with peripheral neuropathy can regain function, reduce discomfort, and improve overall well-being. Early intervention remains one of the most important factors in achieving favorable outcomes.
News in the same category

Why your legs cramp at night and how to stop it from happening
1 teaspoon a day melts away fatty liver naturally

What Causes Pain Under Your Left Rib Cage?

What Causes Your Toenail To Turn Black?

Doctor Warns Popular Medication May Lead to Organ Failure

The military sleep method that can help you fall asleep in just two minutes
5 warning signs of stroke in young adults

20 Early Signs Your Body is Fighting Cancer

9-year-old dies after dental procedure
The HEALTHIEST FRUIT on Earth: what happens to your body if you eat just 3 a day

Garlic & Cloves: The Timeless Duo for Stronger Veins and Better Circulation

Taro: The Tropical Treasure Your Kitchen — and Your Body — Will Love
Benefits and How to Use This Powerful Herb
The cause of Alzheimer’s may lie within your mouth

5 Most Common Deathbed Regrets, According to Palliative Care Nurse
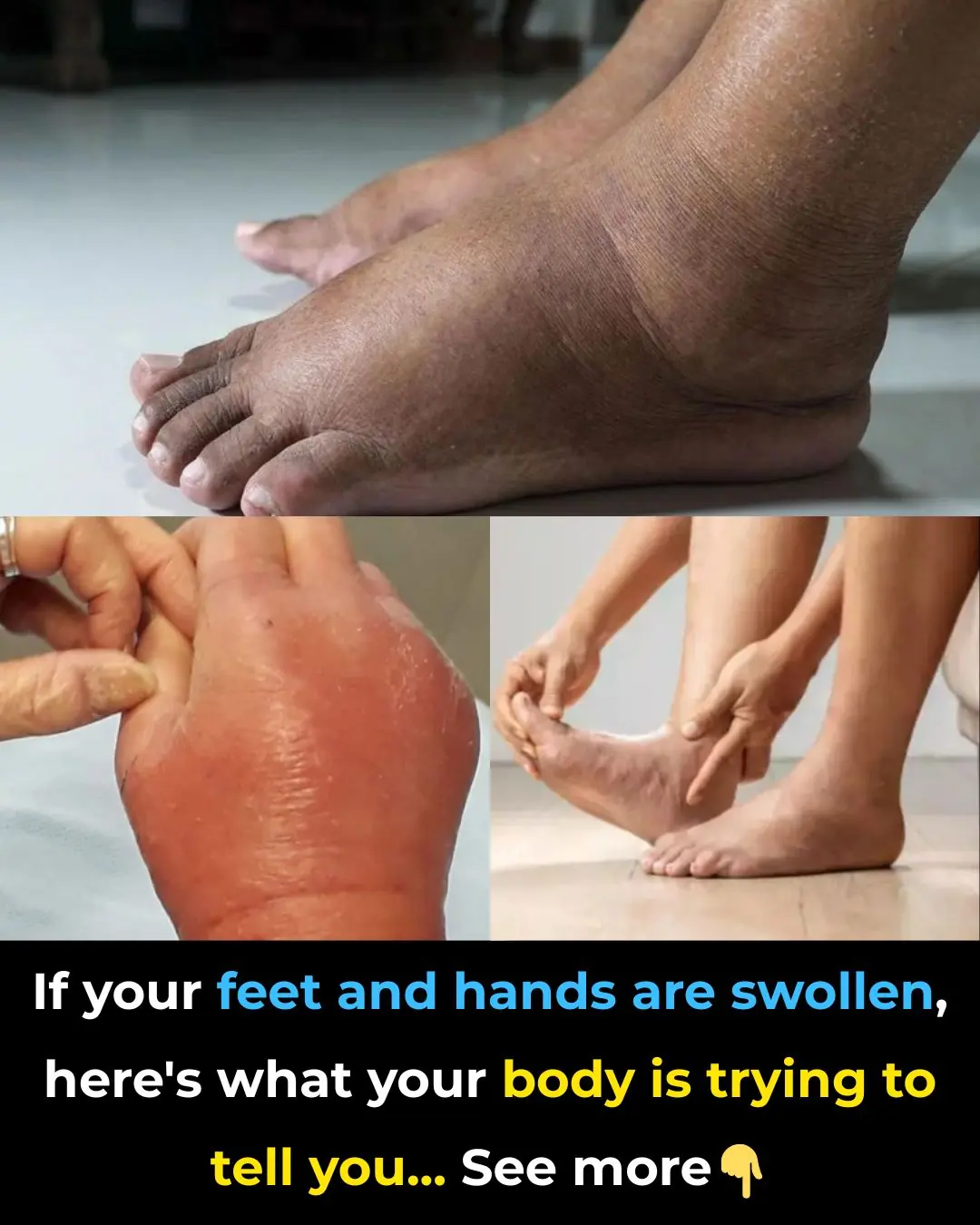
Foods that can ease swelling in hands and feet

Canadian researchers discover new evidence that vitamin D shuts down cancer cells

The Benefits of Holy Basil (Tulsi) for Better Oral Health
News Post
I spent a couple of nights at my friend’s previous apartment and saw these unusual bumps
Found this on my son’s scalp. Have no idea what it is and we can’t get a doc appt soon. Tips?

Top 10 signs of a gallbladder attack

Why your legs cramp at night and how to stop it from happening

1 teaspoon a day melts away fatty liver naturally

Are You the One?

The Secret She Was Never Meant to See
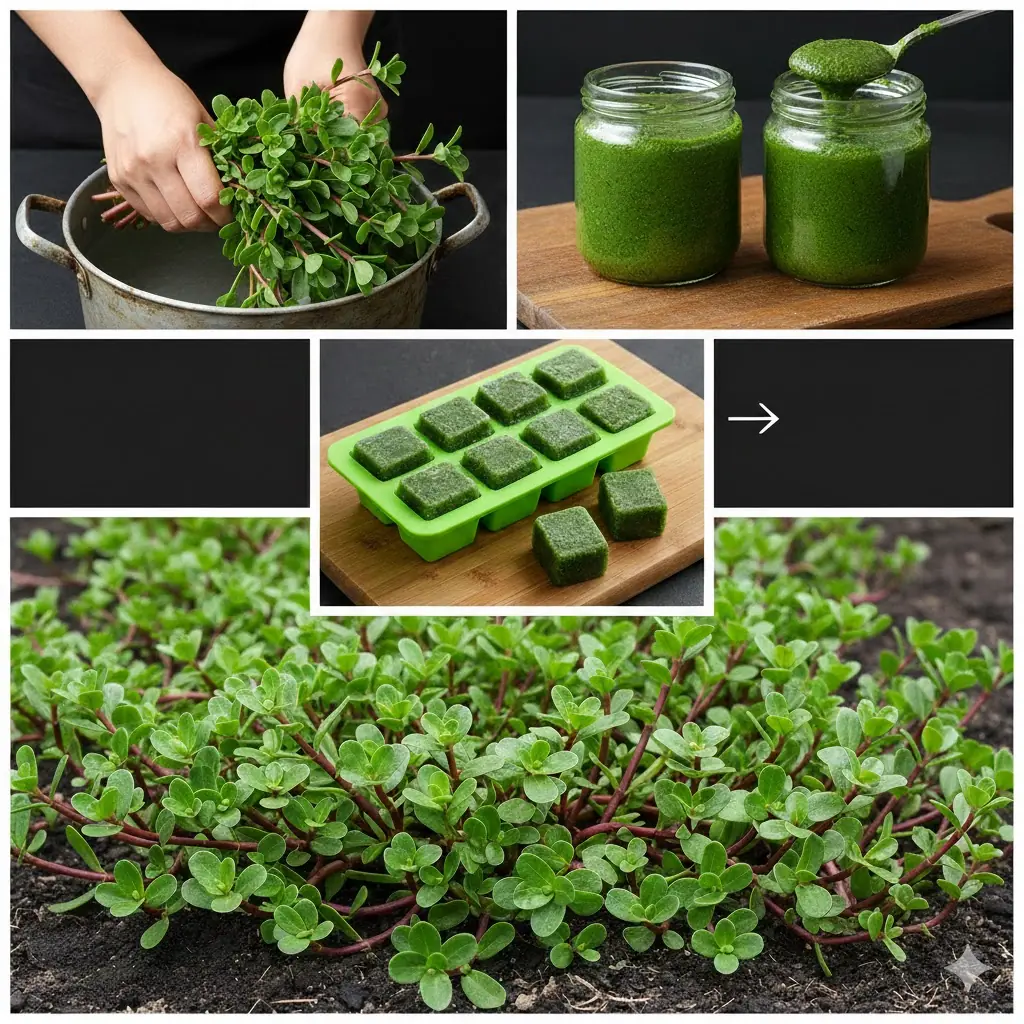

Purslane: The Superfood That Tastes Better Than Meat – 7 Reasons to Grow It in Your Garden
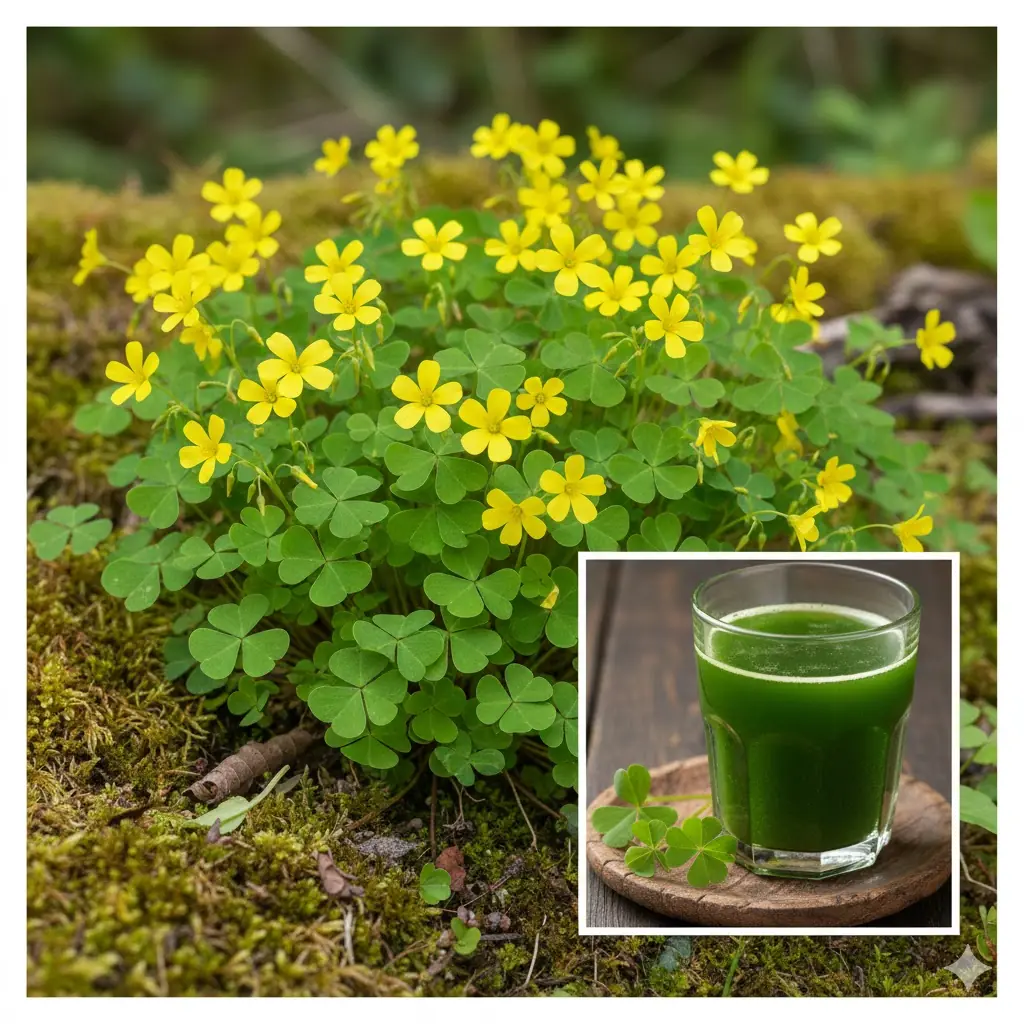

Wood Sorrel Benefits and Uses
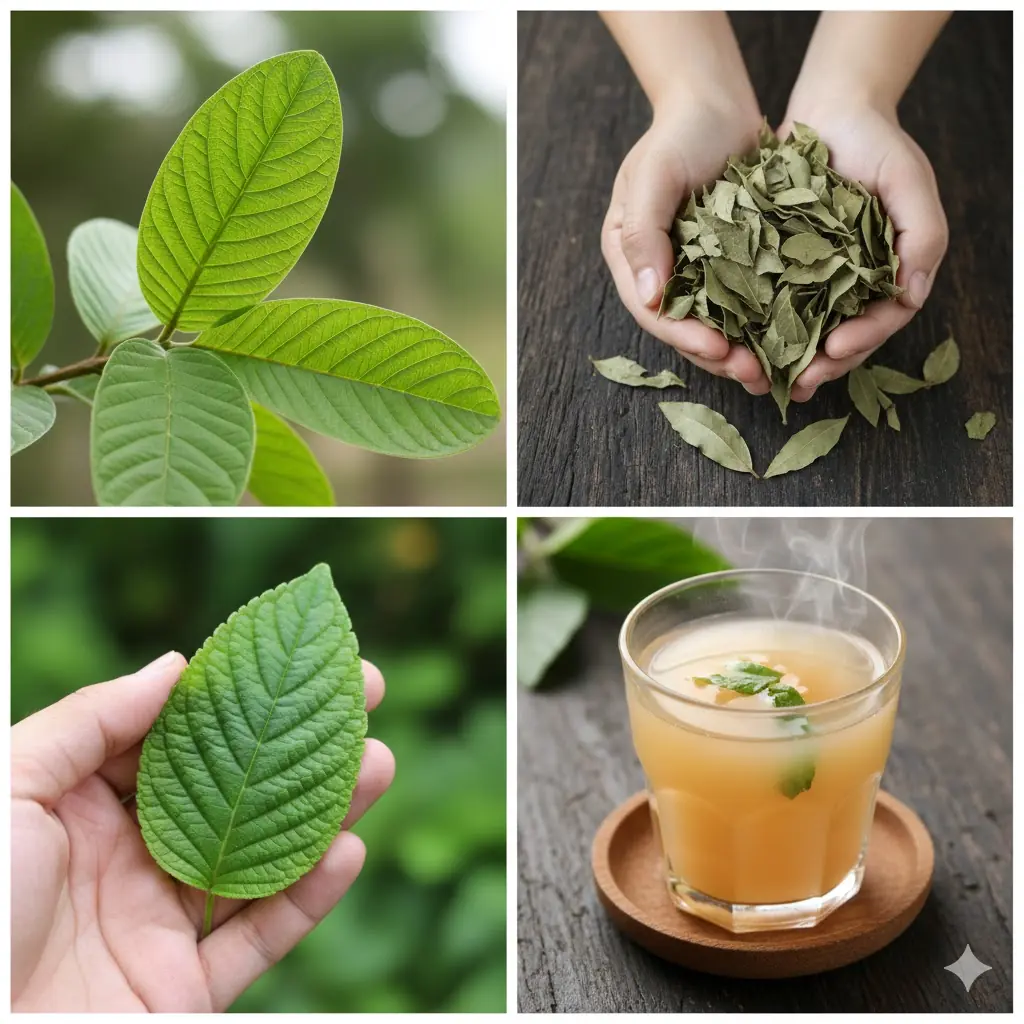

Guava, Oregano, and Bay Leaves: The Healing Leaves used in traditional medicine for centuries

🌿 Yarrow: A Timeless Herbal Ally with Amazing Health Benefits – Unlock Nature’s Ancient Healing Power!

✅ Thyme: The Tiny Herb with Big Healing Power in 2025 🌿✨
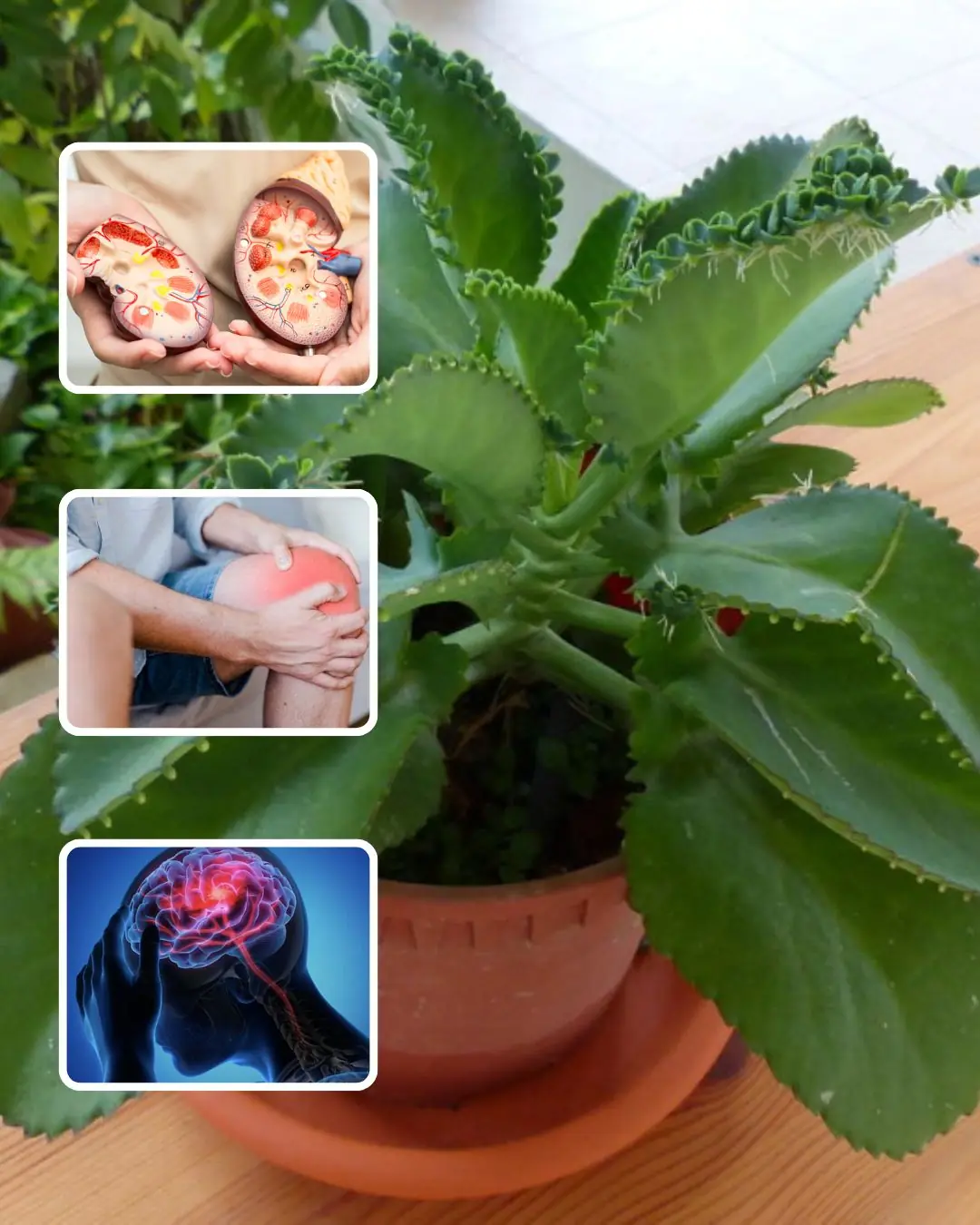

🌿 Bryophyllum Calycinum (Kalanchoe Pinnata): The "Miracle Leaf" with Powerful Healing Benefits

Love vs. Blood

What Causes Pain Under Your Left Rib Cage?

What Causes Your Toenail To Turn Black?

Doctor Warns Popular Medication May Lead to Organ Failure
Why Do You Get Thick Toenails?
