
Inflammation Is On Your Plate: 20 Foods That Harm Your Body And 20 That Heal

The foods we eat every day have a far greater impact on our health than many people realize. Behind a surprising number of chronic illnesses lies a quiet but powerful culprit: inflammation. While this natural bodily response is designed to defend against threats and repair damage, it can become harmful when it persists too long. This is exactly what happens when unhealthy foods are consumed regularly, creating a low-level, ongoing inflammation that can quietly undermine the body over time.
Understanding Chronic Inflammation
Inflammation is essentially the body’s built-in defense mechanism. When injury or infection occurs, specialized inflammatory cells rush to the affected area to combat threats and initiate healing. The result is often redness, swelling, warmth, or discomfort—clear signs that the body is repairing itself.
However, not all inflammation is beneficial. Chronic inflammation arises when the immune system is constantly activated due to poor diet, environmental toxins, stress, or other lifestyle factors. Unlike acute inflammation, which resolves after healing, chronic inflammation lingers quietly, gradually damaging tissues and organs over months or even years. Many people remain unaware of its presence until symptoms appear or a medical diagnosis reveals its effects.
Over time, chronic inflammation has been linked to a wide array of serious conditions, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, arthritis, and certain cancers. The good news is that this process is not entirely out of our control—diet plays a major role in either fueling or reducing inflammation.
20 Foods That May Promote Inflammation
Some foods are more likely to aggravate the body’s inflammatory response. Frequent consumption of these items can keep the immune system in a constant state of stress, leading to fatigue, tissue damage, and increased vulnerability to disease. Here are twenty common inflammation-promoting foods:
-
Refined Carbohydrates – White bread, pasta, and baked goods spike blood sugar and provide minimal fiber.
-
Fried Foods – French fries, fried chicken, and other deep-fried items contain unhealthy fats that can worsen inflammation.
-
Sugary Beverages – Sodas, sweetened teas, and energy drinks overload the body with sugar.
-
Processed Meats – Bacon, hot dogs, and deli slices often contain nitrates and preservatives linked to inflammation.
-
Excess Red Meat – Frequent beef and pork consumption is associated with higher inflammatory markers.
-
Artificial Trans Fats – Found in margarine and packaged snacks, these disrupt cellular function.
-
Certain Vegetable Oils – Corn, soybean, and sunflower oils, when consumed in excess, can upset the balance of omega fatty acids.
-
White Rice – Low in fiber, it can lead to rapid blood sugar spikes.
-
Pastries and Cakes – Combination of refined flour and sugar makes these particularly inflammatory.
-
Excess Alcohol – Chronic drinking stresses the liver and promotes inflammation.
-
Candy and Sweets – Sugar-heavy, nutrient-poor treats.
-
Pizza – Often contains processed meats, refined dough, and excess cheese.
-
Cheese (in large amounts) – High in saturated fat despite its calcium content.
-
Ice Cream – Sugar and dairy together can exacerbate inflammation.
-
Energy Drinks – Packed with caffeine, sugar, and additives.
-
Microwave Popcorn – Often contains unhealthy oils and additives.
-
Instant Noodles – Highly processed, loaded with sodium and preservatives.
-
Processed Granola Bars – Appear healthy but frequently contain sugars and unhealthy oils.
-
Crackers and Chips – High in refined grains, salt, and oils.
-
Fast Food Meals – Typically high in sodium, unhealthy fats, and artificial ingredients.
Regularly consuming these foods can leave the body inflamed, tired, and vulnerable to illness, creating a perfect environment for chronic disease to develop.
20 Anti-Inflammatory Foods That Support Healing
On the flip side, many natural, nutrient-dense foods have the power to reduce inflammation and enhance long-term health. Incorporating these items regularly can help the body repair itself and maintain balance:
-
Leafy Greens – Spinach, kale, and collard greens are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
-
Berries – Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are packed with anti-inflammatory compounds.
-
Fatty Fish – Salmon, sardines, and mackerel are high in omega-3 fatty acids that reduce inflammation.
-
Turmeric – Contains curcumin, a potent anti-inflammatory compound.
-
Ginger – Has long been used to soothe digestion and calm inflammation.
-
Olive Oil – Extra virgin olive oil offers healthy fats and protective antioxidants.
-
Tomatoes – Rich in lycopene, especially effective when cooked.
-
Nuts – Almonds and walnuts provide protein, fiber, and healthy fats.
-
Chia Seeds – Packed with omega-3s and fiber.
-
Flaxseeds – Anti-inflammatory fats and lignans support overall health.
-
Garlic – Contains sulfur compounds that modulate immune response.
-
Green Tea – Full of antioxidants that reduce inflammation markers.
-
Avocados – High in potassium, fiber, and heart-healthy fats.
-
Broccoli – Contains sulforaphane, which may lower inflammatory processes.
-
Sweet Potatoes – Rich in beta-carotene and fiber.
-
Mushrooms – Shiitake, maitake, and other varieties support immune health.
-
Beets – Betalains give them anti-inflammatory properties.
-
Citrus Fruits – Oranges, lemons, and limes are vitamin C powerhouses.
-
Whole Grains – Oats, brown rice, and quinoa help reduce C-reactive protein levels.
-
Dark Chocolate (in moderation) – Cocoa contains flavonoids with anti-inflammatory effects.
By prioritizing these foods in daily meals, the body is better nourished, protected, and equipped to repair itself naturally.
Creating a Balanced, Anti-Inflammatory Plate
Managing inflammation isn’t about eliminating everything you enjoy—it’s about making smarter choices. For example, swap white bread for whole-grain alternatives, replace sugary sodas with herbal teas or infused water, and balance meat-heavy meals with plant-based dishes throughout the week.
Small, sustainable changes often lead to the most significant long-term results. Cooking methods also matter: even the healthiest foods can lose their benefits if deep-fried or covered in heavy sauces. Steaming, grilling, roasting, or lightly sautéing ingredients preserves nutrients while reducing inflammation triggers.
Lifestyle Factors That Influence Inflammation
Diet is only one part of the puzzle. Sedentary behavior, poor sleep, chronic stress, and smoking all exacerbate inflammation. A truly anti-inflammatory lifestyle combines:
-
Regular physical activity
-
Quality sleep
-
Stress management techniques
-
Proper hydration
-
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol
Pairing healthy eating with these lifestyle habits strengthens the immune system, boosts energy, and enhances overall well-being.
The Bottom Line
While inflammation cannot always be completely avoided, it can certainly be managed. Every meal presents an opportunity to either feed inflammation or support healing. The journey to optimal health begins with mindful choices—small steps, or even single bites, that gradually tip the balance in favor of well-being. With the right nourishment, the human body has remarkable capacity to heal itself from the inside out.
News in the same category

Does This Drink Really Harm Your Bones? The Truth Behind Soda and Your Health

Oregano: The Small Plant with Big Health Benefits
Fatty liver disease: 6 symptoms you need to know
Liver Damage Linked to Supplement Use Is Surging, Sparking Scientific Alarm

No More Fillings? Scientists Successfully Grow Human Teeth in the Lab

Lab Study Shows Dandelion Root Kills Over 90% of Colon Cancer Cells In Just Two Days

7 Red Flag Phrases Narcissists Use to Exert Control During Arguments

If These 8 Activities Energize You Instead of Drain You, You’re Likely a Highly Intelligent Introvert
Inflammation Is On Your Plate: 20 Foods That Harm Your Body And 20 That Heal
The Hidden Power of Garlic: 7 Powerful Uses Beyond Cooking

Children Who Are Hugged Often Have Stronger Immune Systems, Studies Show

1 Cup to Cleanse Your Lungs of Phlegm and Toxins

Study Finds This Popular Sweetener Damages the Brain’s Protective Barrier

Highly Contagious Stomach Bug Doubles in Midwest Ahead of Holiday Season

Lactose Intolerance: Why It Develops Later in Life and How to Manage It
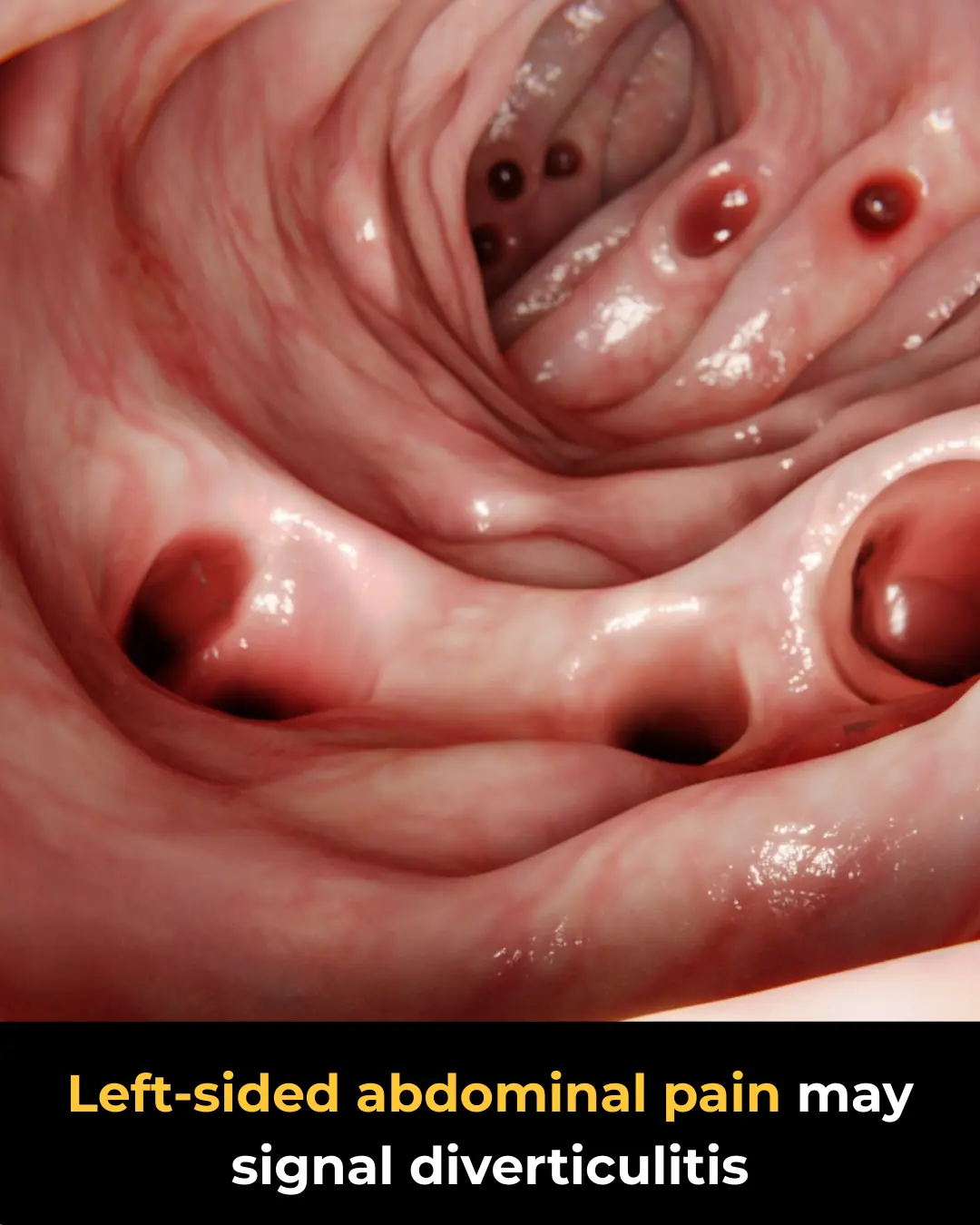
Diverticulitis: Pain Patterns and Treatment Guidelines
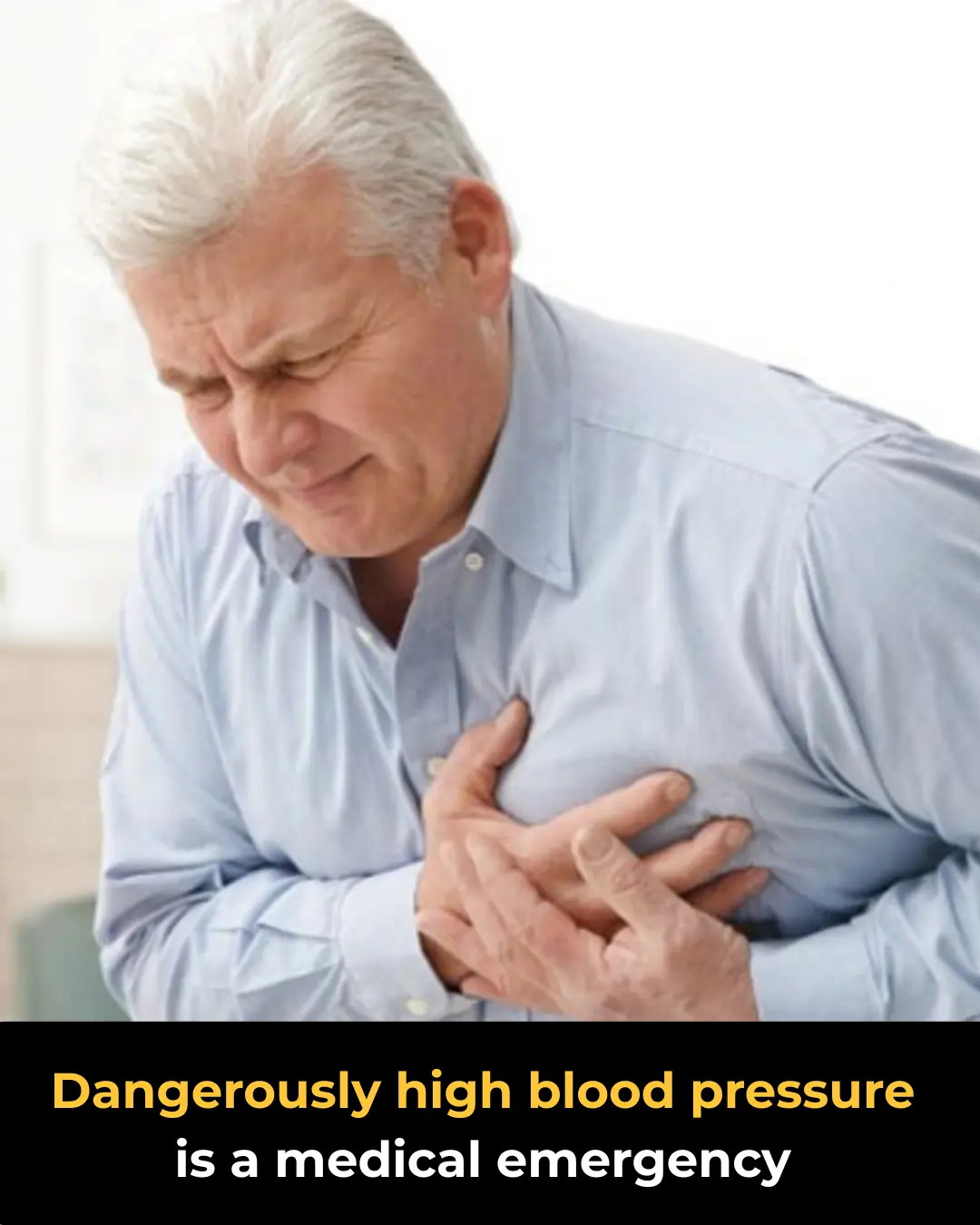
Hypertensive Crisis: Symptoms That Require Immediate Attention
High Triglycerides: Why They Matter More Than You Think
News Post

25 Remarkable Benefits of Guava Leaves and How to Use Them Safely

Study Finds This Popular Sweetener Damages the Brain’s Protective Barrier

Study Finds a Mother’s Early Bond With Her Baby Can Shape a Child’s Sleep for Years

Gramma the Tortoise: A Remarkable Life Spanning Three Centuries

California Surpasses Japan to Become the Fourth-Largest Economy in the World

Why Aging Skin Develops a Distinct Body Odor—and What Science Says Can Help

Photographer Captures Dream Shot of Full Moon Over Christ the Redeemer After Three Years of Effort

China Successfully Tests 3D-Printed Micro Turbojet Engine in Landmark Flight Achievement

Swiss Researchers Trial Blood Filtration Device for Alzheimer's Treatment

Bear Takes Over Truckee Diner in Hilarious Culinary Heist

Many people believe they need to walk ten thousand steps daily to stay healthy

The Quieting Skies: A Stark Decline in North America's Bird Population

Does This Drink Really Harm Your Bones? The Truth Behind Soda and Your Health

Oregano: The Small Plant with Big Health Benefits

Sea Otter Takes Over Santa Cruz Surf Scene: A Bold and Unpredictable Presence
Australia's Revolutionary Bionic Eye: A New Era in Restoring Vision

10 Best Collagen Gels For Wrinkle Free Glowing Skin

Why You Might Want to Stop Removing Tomato Suckers: What Gardeners Are Starting to Realize

Banana Blossom: Health Benefits, Recipes, and Traditional Uses
