
Inflammation Is On Your Plate: 20 Foods That Harm Your Body And 20 That Heal
The foods eaten each day influence the body far more profoundly than many people realize. Long before symptoms appear or diagnoses are made, diet quietly shapes internal processes that determine long-term health. One of the most significant of these processes is inflammation—a biological response that can either protect the body or slowly undermine it.
Inflammation itself is not the enemy. In fact, it is essential for healing. Problems arise when inflammation becomes chronic, smoldering beneath the surface for years due to repeated exposure to poor dietary choices, stress, and lifestyle habits. When that happens, the very mechanism designed to protect the body begins to damage it instead.
Over time, chronic inflammation has been linked to heart disease, type 2 diabetes, arthritis, autoimmune disorders, digestive issues, and even certain forms of cancer. The encouraging news is that inflammation is highly responsive to lifestyle changes—especially diet. What is placed on the plate each day can either intensify inflammation or help calm it.
Understanding which foods contribute to inflammation and which actively reduce it can be a powerful step toward better health.
Understanding Inflammation: Friend and Foe
Inflammation is the body’s built-in defense system. When injury, infection, or tissue damage occurs, immune cells rush to the affected area. Swelling, heat, redness, and pain are signs that the body is working to heal itself.
However, inflammation is meant to be temporary. When the immune system is constantly triggered—by processed foods, excess sugar, unhealthy fats, chronic stress, or environmental toxins—it never fully shuts down. This leads to chronic inflammation, a low-grade but persistent state of internal stress that gradually damages cells, blood vessels, and organs.
Because chronic inflammation often develops silently, many people are unaware it’s happening until fatigue, pain, or disease emerges. This makes prevention through daily habits especially important.
20 Foods That May Increase Inflammation
Certain foods are known to promote inflammatory responses when consumed regularly. While occasional indulgence is unlikely to cause harm, frequent consumption can keep the immune system in a constant state of overdrive.
Here are twenty common foods associated with increased inflammation:
-
Refined carbohydrates – White bread, pastries, and pasta lack fiber and rapidly raise blood sugar.
-
Fried foods – Deep-fried items contain oxidized oils that promote inflammation.
-
Sugary drinks – Sodas and sweetened teas flood the body with added sugars.
-
Processed meats – Bacon, sausages, and deli meats contain preservatives linked to inflammation.
-
Red meat (excessive intake) – Regular overconsumption is associated with higher inflammatory markers.
-
Artificial trans fats – Found in some margarines and packaged snacks.
-
Vegetable oils high in omega-6 – Corn, soybean, and sunflower oils can disrupt fatty acid balance.
-
White rice – Low in fiber and nutrients, leading to blood sugar spikes.
-
Cakes and pastries – Combine refined flour with added sugars.
-
Excess alcohol – Places stress on the liver and immune system.
-
Candy and sweets – High sugar with little nutritional value.
-
Pizza – Often made with refined flour, processed meats, and excess cheese.
-
Cheese (large amounts) – High in saturated fat.
-
Ice cream – Combines sugar and dairy, which may trigger inflammation.
-
Energy drinks – Packed with sugar, caffeine, and chemical additives.
-
Microwave popcorn – Often contains unhealthy oils and additives.
-
Instant noodles – Extremely processed and high in sodium.
-
Commercial granola bars – Frequently disguised as healthy but loaded with sugar.
-
Chips and crackers – Made with refined grains and inflammatory oils.
-
Fast food meals – High in salt, sugar, unhealthy fats, and additives.
When these foods dominate the diet, the body is left fatigued, inflamed, and more susceptible to chronic disease over time.
20 Anti-Inflammatory Foods That Support Healing
Fortunately, many whole foods actively work against inflammation. These foods are rich in antioxidants, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats that help regulate immune responses and repair cellular damage.
Here are twenty foods known for their anti-inflammatory benefits:
-
Leafy greens – Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are nutrient-dense and antioxidant-rich.
-
Berries – Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries combat oxidative stress.
-
Fatty fish – Salmon, sardines, and mackerel provide omega-3 fatty acids.
-
Turmeric – Contains curcumin, a powerful natural anti-inflammatory compound.
-
Ginger – Helps reduce inflammation and supports digestion.
-
Extra virgin olive oil – A cornerstone of anti-inflammatory diets.
-
Tomatoes – High in lycopene, especially when cooked.
-
Nuts – Almonds and walnuts supply healthy fats and fiber.
-
Chia seeds – Rich in omega-3s and plant-based protein.
-
Flaxseeds – Support hormone balance and inflammation control.
-
Garlic – Regulates immune responses.
-
Green tea – Packed with polyphenols that reduce inflammation.
-
Avocados – Provide potassium, fiber, and monounsaturated fats.
-
Broccoli – Contains sulforaphane, linked to lower inflammation.
-
Sweet potatoes – Rich in beta-carotene and complex carbohydrates.
-
Mushrooms – Especially shiitake and maitake, which support immunity.
-
Beets – Contain betalains that fight inflammatory damage.
-
Citrus fruits – High in vitamin C and protective antioxidants.
-
Whole grains – Oats, quinoa, and brown rice help regulate blood sugar.
-
Dark chocolate (moderation) – Cocoa flavonoids can reduce inflammation.
When these foods become dietary staples, the body is better equipped to heal, recover, and defend itself naturally.
Building an Anti-Inflammatory Plate
Reducing inflammation does not require perfection or extreme restriction. Instead, it involves thoughtful substitutions and balance. Whole grains can replace refined ones. Water, herbal teas, or sparkling water can take the place of sugary drinks. Meals centered on plants can gradually replace those dominated by processed meats.
Cooking methods also matter. Even healthy foods lose their benefits when deep-fried or heavily processed. Steaming, baking, grilling, and roasting preserve nutrients and reduce inflammatory compounds.
Lifestyle Habits That Influence Inflammation
Diet plays a central role, but it works best alongside healthy lifestyle choices. Chronic inflammation is also fueled by inactivity, poor sleep, unmanaged stress, smoking, and dehydration.
An anti-inflammatory lifestyle includes:
-
Regular physical activity
-
Consistent, quality sleep
-
Stress reduction practices such as meditation or deep breathing
-
Adequate hydration
-
Limiting alcohol and avoiding smoking
When nutrition and lifestyle work together, energy improves, immunity strengthens, and overall well-being increases.
Final Thoughts
Inflammation cannot be eliminated entirely—and it shouldn’t be. But it can be managed. Each meal presents a choice: to intensify inflammation or to calm it. Over time, these choices accumulate, shaping health outcomes in powerful ways.
With mindful eating and supportive habits, the body demonstrates an incredible ability to restore balance and heal itself. Often, the path to better health begins not with medication, but with what’s placed on the fork.
News in the same category

Does This Drink Really Harm Your Bones? The Truth Behind Soda and Your Health

Oregano: The Small Plant with Big Health Benefits
Fatty liver disease: 6 symptoms you need to know
Liver Damage Linked to Supplement Use Is Surging, Sparking Scientific Alarm

No More Fillings? Scientists Successfully Grow Human Teeth in the Lab

Lab Study Shows Dandelion Root Kills Over 90% of Colon Cancer Cells In Just Two Days

7 Red Flag Phrases Narcissists Use to Exert Control During Arguments

If These 8 Activities Energize You Instead of Drain You, You’re Likely a Highly Intelligent Introvert
The Hidden Power of Garlic: 7 Powerful Uses Beyond Cooking

Inflammation Is On Your Plate: 20 Foods That Harm Your Body And 20 That Heal

Children Who Are Hugged Often Have Stronger Immune Systems, Studies Show

1 Cup to Cleanse Your Lungs of Phlegm and Toxins

Study Finds This Popular Sweetener Damages the Brain’s Protective Barrier

Highly Contagious Stomach Bug Doubles in Midwest Ahead of Holiday Season

Lactose Intolerance: Why It Develops Later in Life and How to Manage It
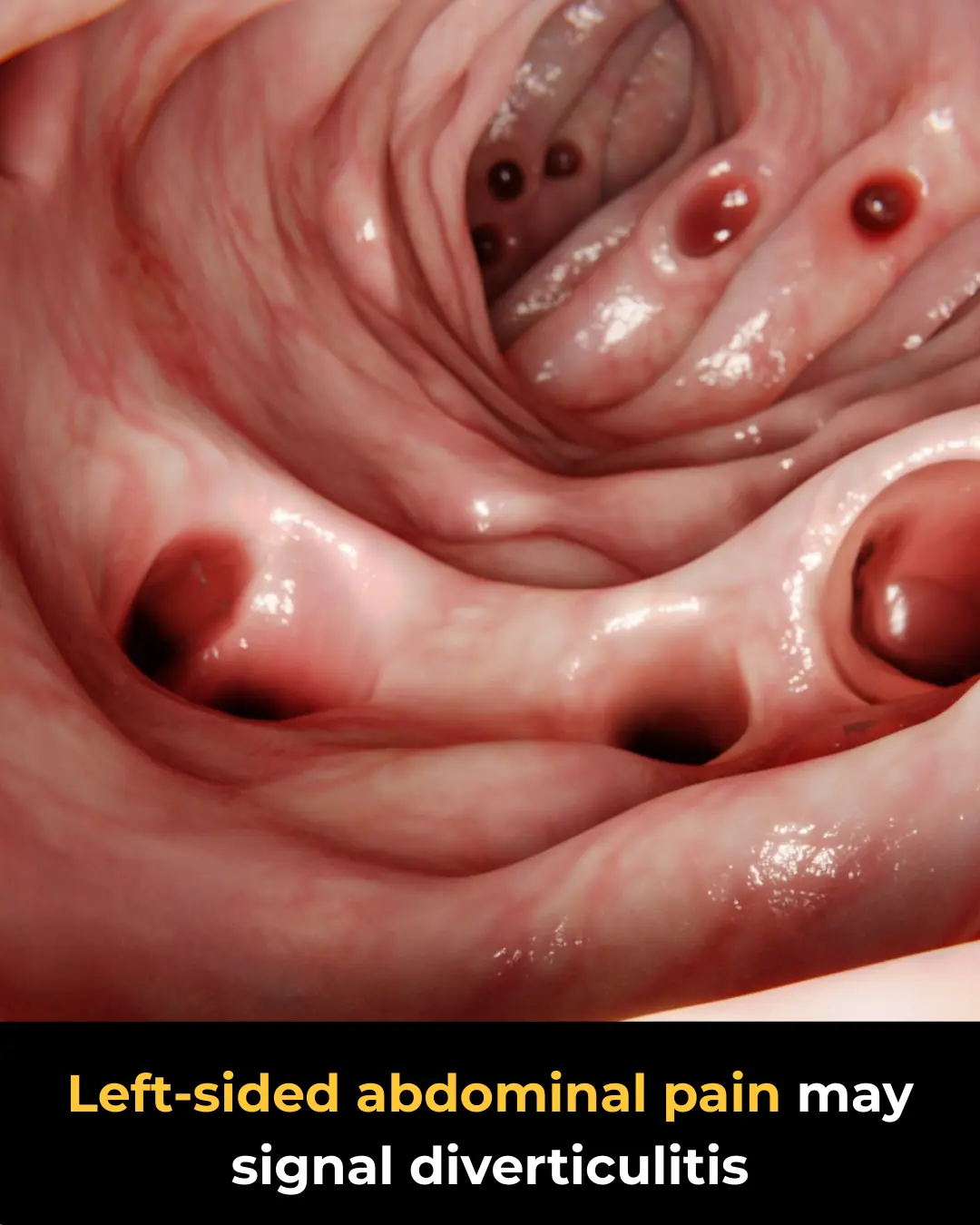
Diverticulitis: Pain Patterns and Treatment Guidelines
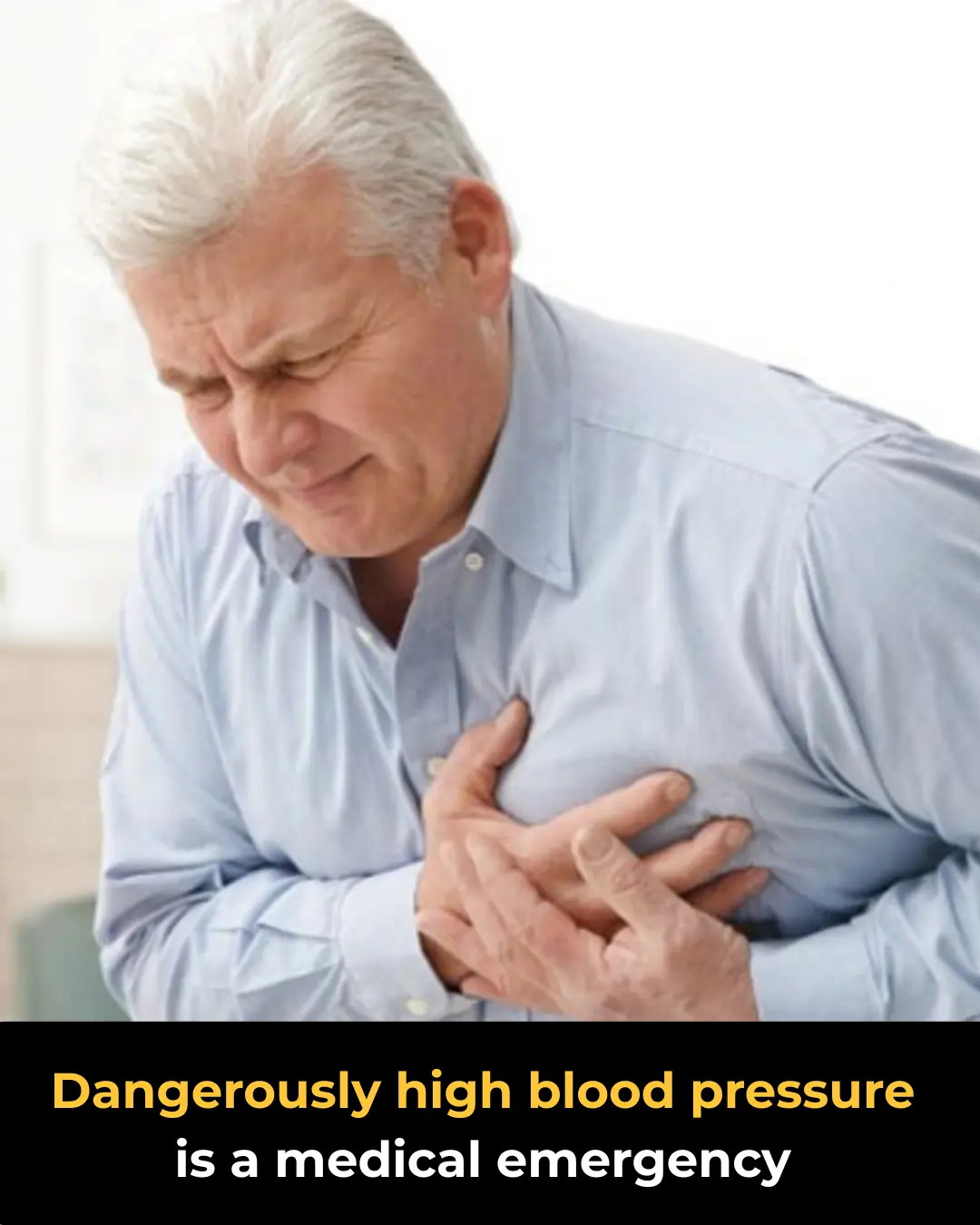
Hypertensive Crisis: Symptoms That Require Immediate Attention
High Triglycerides: Why They Matter More Than You Think
News Post

25 Remarkable Benefits of Guava Leaves and How to Use Them Safely

Study Finds This Popular Sweetener Damages the Brain’s Protective Barrier

Study Finds a Mother’s Early Bond With Her Baby Can Shape a Child’s Sleep for Years

Gramma the Tortoise: A Remarkable Life Spanning Three Centuries

California Surpasses Japan to Become the Fourth-Largest Economy in the World

Why Aging Skin Develops a Distinct Body Odor—and What Science Says Can Help

Photographer Captures Dream Shot of Full Moon Over Christ the Redeemer After Three Years of Effort

China Successfully Tests 3D-Printed Micro Turbojet Engine in Landmark Flight Achievement

Swiss Researchers Trial Blood Filtration Device for Alzheimer's Treatment

Bear Takes Over Truckee Diner in Hilarious Culinary Heist

Many people believe they need to walk ten thousand steps daily to stay healthy

The Quieting Skies: A Stark Decline in North America's Bird Population

Does This Drink Really Harm Your Bones? The Truth Behind Soda and Your Health

Oregano: The Small Plant with Big Health Benefits

Sea Otter Takes Over Santa Cruz Surf Scene: A Bold and Unpredictable Presence
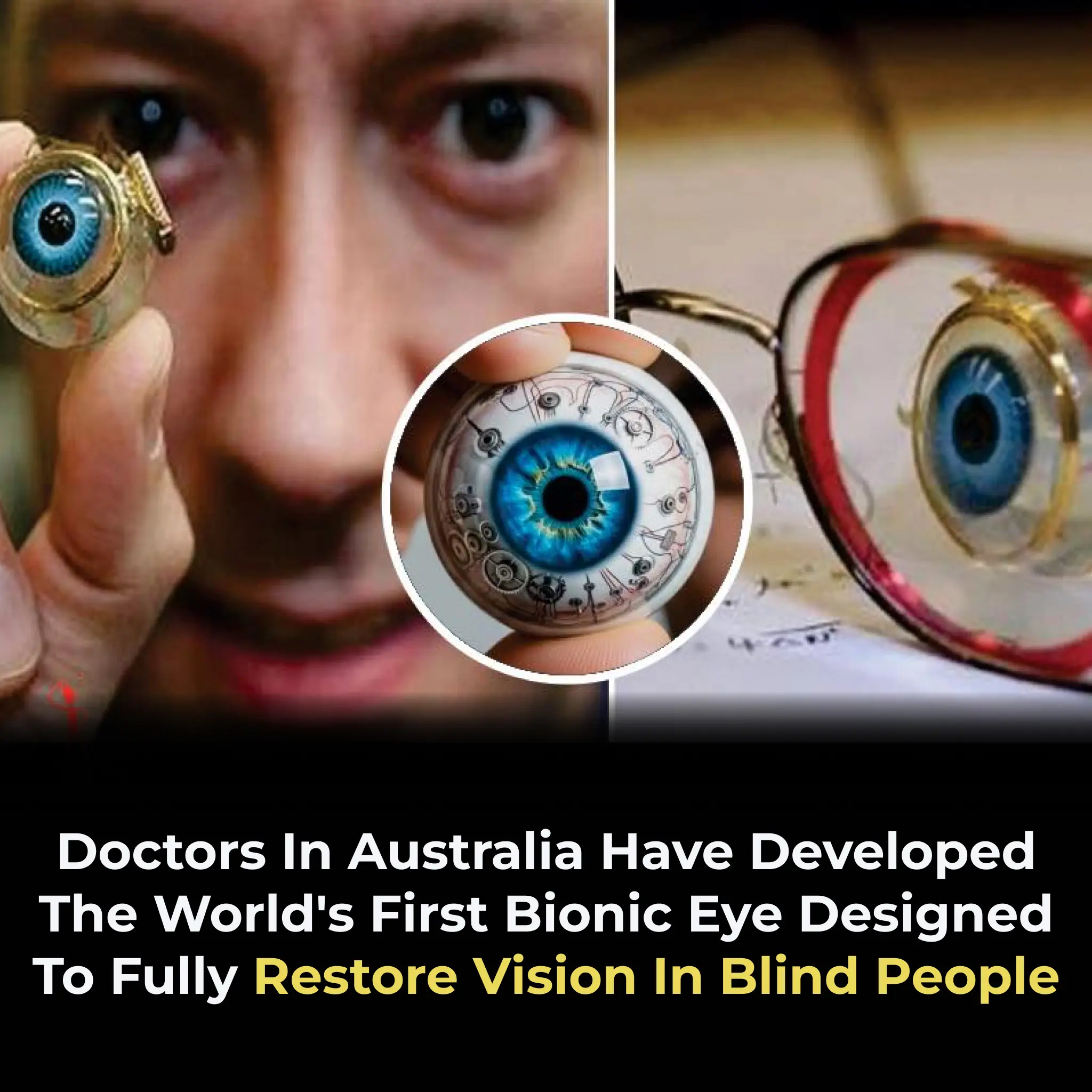
Australia's Revolutionary Bionic Eye: A New Era in Restoring Vision

10 Best Collagen Gels For Wrinkle Free Glowing Skin

Why You Might Want to Stop Removing Tomato Suckers: What Gardeners Are Starting to Realize

Banana Blossom: Health Benefits, Recipes, and Traditional Uses
