One powerful vitamin that could end your tinnitus for good!

Tinnitus—the persistent ringing, buzzing, hissing, or whooshing sound in the ears—is a surprisingly common issue that affects millions of people. Even though it feels like a condition on its own, tinnitus isn’t actually a disease. Instead, it’s a symptom that signals something else is going on in the body. For many, it can interfere with concentration, sleep, and overall quality of life.
This expanded guide explores what tinnitus is, why it happens, and how certain vitamins may play a supportive role in managing symptoms.
What Is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus occurs when you hear sound in one or both ears even though no external noise is present. These phantom sounds can vary from a faint background hum to a loud, constant ringing. About 15–20% of adults experience tinnitus at some point, making it a widespread issue.
While tinnitus typically isn’t dangerous, it can be incredibly frustrating. Some people adjust quickly, while others find that the constant noise leads to irritability, anxiety, or sleep disturbances.
Why Is Tinnitus So Challenging to Treat?
Treating tinnitus is often difficult because it can have many different causes, and in some cases, the exact source isn’t clear. If doctors can’t pinpoint what’s triggering the symptoms, choosing the right treatment becomes complicated.
Tinnitus can gradually worsen over time, especially if underlying issues go untreated. However, once the root cause is identified—whether it’s hearing loss, medication, circulation issues, or something else—treatment becomes much more effective.
Key Points to Remember
-
Tinnitus is a symptom, not a standalone illness.
-
It affects a large portion of adults—around 15–20%.
-
Identifying the underlying cause is the most important and often the hardest step.
Common Causes of Tinnitus
Tinnitus can stem from the ears, brain, blood vessels, or even the spine. Below are some of the most frequent contributors:
1. Inner Ear Damage
Inside your ear are tiny hair cells responsible for detecting sound waves and sending signals to the brain. When these cells become damaged—due to aging, illness, or noise exposure—they may misfire and cause tinnitus.
2. Neck and Spine Issues
Problems in the cervical spine can affect nerves connected to the auditory system. This form, known as somatic tinnitus, is more common than people realize.
3. Circulation Problems
High blood pressure, poor blood flow, or vascular disease can distort the sounds your ears pick up. In some cases, people even hear a pulsing sound in sync with their heartbeat.
4. Age-Related Hearing Loss
As hearing ability declines with age, the auditory system becomes more sensitive, sometimes resulting in tinnitus.
5. Loud Noise Exposure
Long-term exposure to loud environments—such as concerts, construction sites, or headphones at high volume—can damage inner ear hair cells. Even a single loud blast (like fireworks) can trigger symptoms.
6. Ear Conditions
Issues such as otosclerosis (abnormal bone growth in the middle ear), chronic ear infections, or excess earwax may contribute to tinnitus.
7. Other Medical Conditions
Conditions like anemia, thyroid disorders, or vitamin deficiencies can also create or worsen tinnitus.
8. Medications
Several medications are known to cause tinnitus as a side effect, including:
-
Certain antibiotics
-
Chemotherapy drugs
-
Diuretics
-
High-dose aspirin
-
Some antidepressants
Always consult your healthcare provider if you suspect your medication might be contributing to symptoms.
9. Stress and Mental Health
Emotional stress, anxiety, and depression don’t directly cause tinnitus, but they can intensify it. Many people notice their symptoms worsen during periods of high stress.
Vitamins That May Help With Tinnitus
While vitamins are not a cure, some research shows that certain nutrient deficiencies appear more frequently in people with tinnitus. Supporting overall health through proper nutrition may help reduce symptoms or prevent them from worsening.
1. Vitamin A
Vitamin A supports ear and immune health. It helps protect tissues from inflammation and infection.
-
Suggested intake: Many supplements provide 10,000–15,000 IU daily, though it’s best to use Vitamin A combined with beta-carotene, which helps regulate absorption.
-
Sources: Carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, liver, fortified dairy products
2. B Vitamins (Especially B12)
B vitamins play a vital role in nerve function and can help regulate pressure within the ear. Deficiencies—particularly in Vitamin B12—have been linked to tinnitus in some studies.
-
Common approach: A B-complex supplement taken throughout the day
-
For B12: Higher doses around 1000 mcg daily may be recommended temporarily
-
Food sources: Eggs, milk, organ meats like liver and kidney, fish, poultry
Low B vitamin levels are fairly common, especially in older adults or those with digestive issues.
3. Vitamin E
Vitamin E acts as a powerful antioxidant and helps support healthy blood flow—something that’s essential for proper ear function.
-
Typical supplement amount: 150–200 IU daily
-
Best form: Alpha-tocopherol
-
Food sources: Wheat germ, almonds, sunflower seeds, avocado, red peppers
Improved circulation may help reduce tinnitus symptoms caused by vascular issues.
Additional Ways to Manage Tinnitus
Beyond vitamins, lifestyle changes can also influence how often or how intensely you experience tinnitus.
Helpful Foods
-
Pineapple (contains bromelain, which may reduce inflammation)
-
Garlic (supports circulation)
-
Sea vegetables like kelp (rich in minerals)
Things to Avoid
-
Excess sugar
-
Alcohol
-
Cigarettes
-
High caffeine intake
These can trigger or worsen tinnitus in many individuals.
Finding Long-Term Relief
Achieving lasting relief from tinnitus depends on one key step: identifying and addressing the root cause. For some people, the solution may be as simple as treating an ear infection or adjusting medication. For others, managing stress, improving nutrition, or treating circulation problems may make a significant difference.
While the journey can be challenging, paying attention to your overall health—sleep, stress levels, diet, and vitamin intake—can help support your ears and nervous system. Over time, these small actions can contribute to better comfort and fewer symptoms.
Important Note
This article is for general information only and not a substitute for medical advice. If you have persistent or worsening tinnitus, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
News in the same category


🦵 The 5 Best Nutrients to Reduce Swelling in the Feet and Legs
How Ginger Targets Prostate, Ovarian and Colon Cancer Stem Cells Better Than Chemo

Top 13 Inflammatory Foods You Should Avoid (Replace with These)

Common Habits to Avoid for Better Heart Health
Cardiomyopathy: Causes, Risks, and Treatment Approaches
Understanding Phlegm: Why It Builds Up and How to Naturally Reduce It
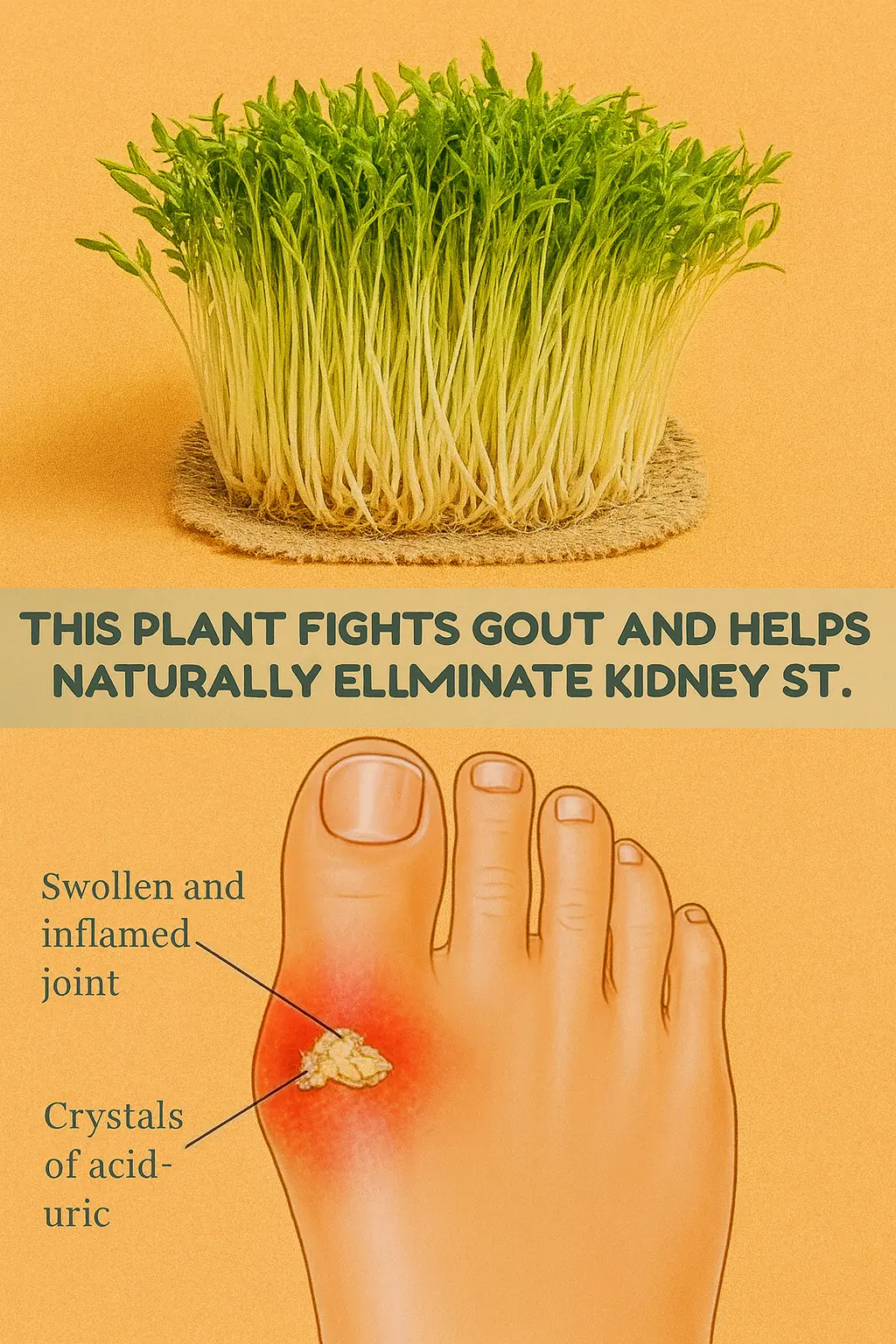
Alfalfa for Kidneys and Gout: A Natural Support for Cleansing and Balance

Sulfur Power: Onion Juice for Hair Regrowth—Science-Backed Tips & How to Use It

Unlock the Hidden Power of Sessile Joyweed: 30 Life-Changing Benefits for Seniors
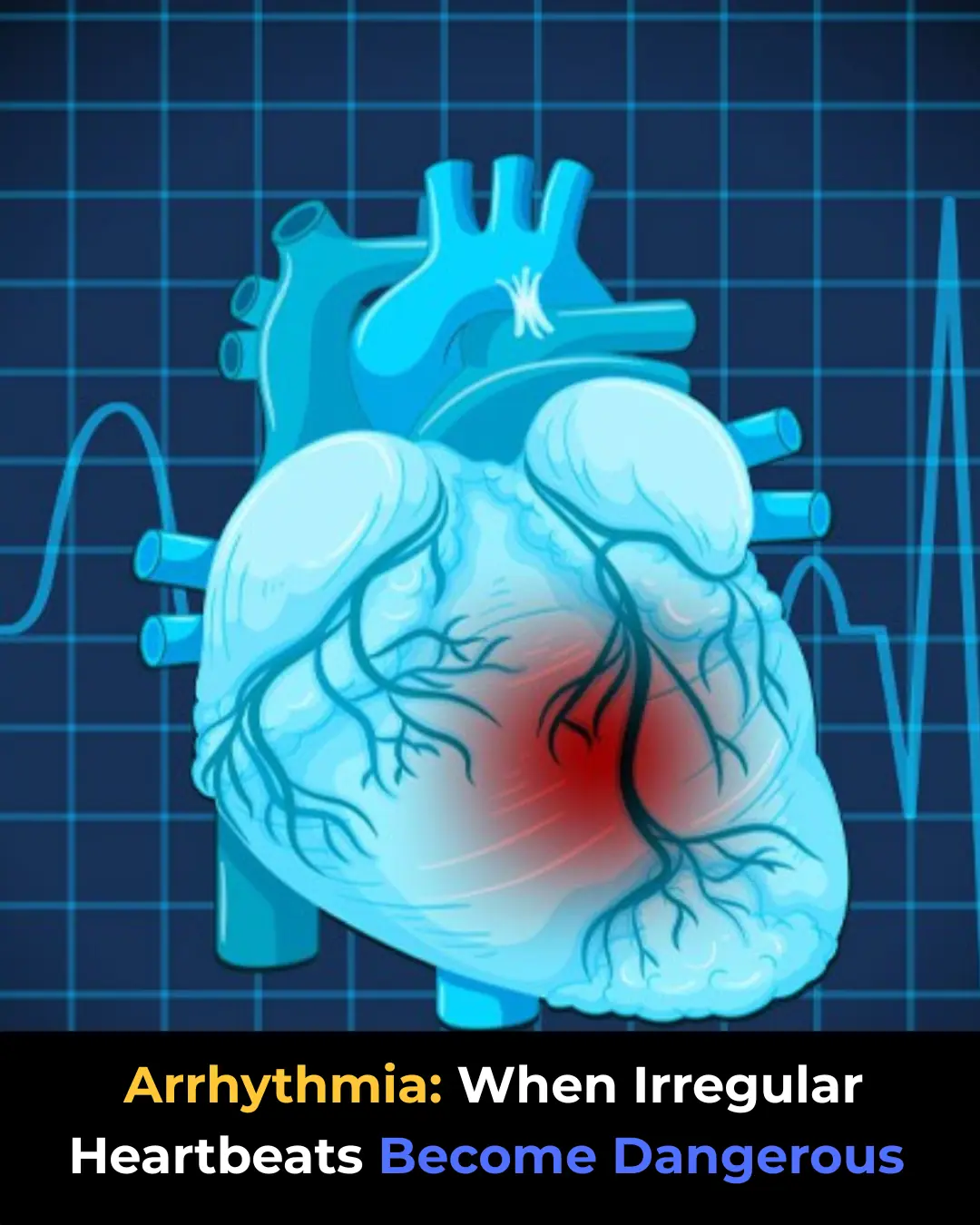
Arrhythmia: When Irregular Heartbeats Become Dangerous
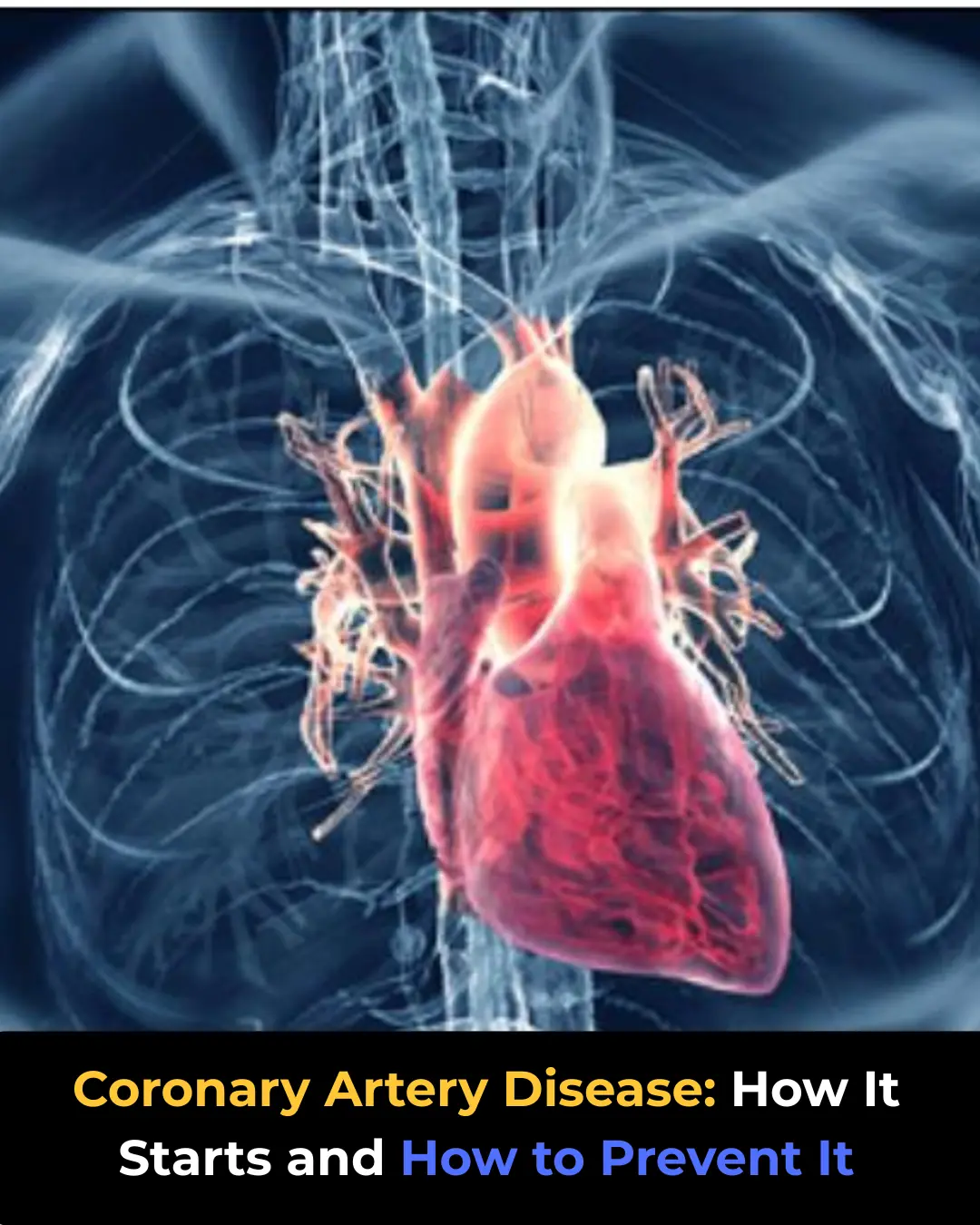
Coronary Artery Disease: How It Starts and How to Prevent It

Tension Headaches: Causes and Long-Term Management

Brain Tumor Symptoms: The Red Flags You Must Not Ignore
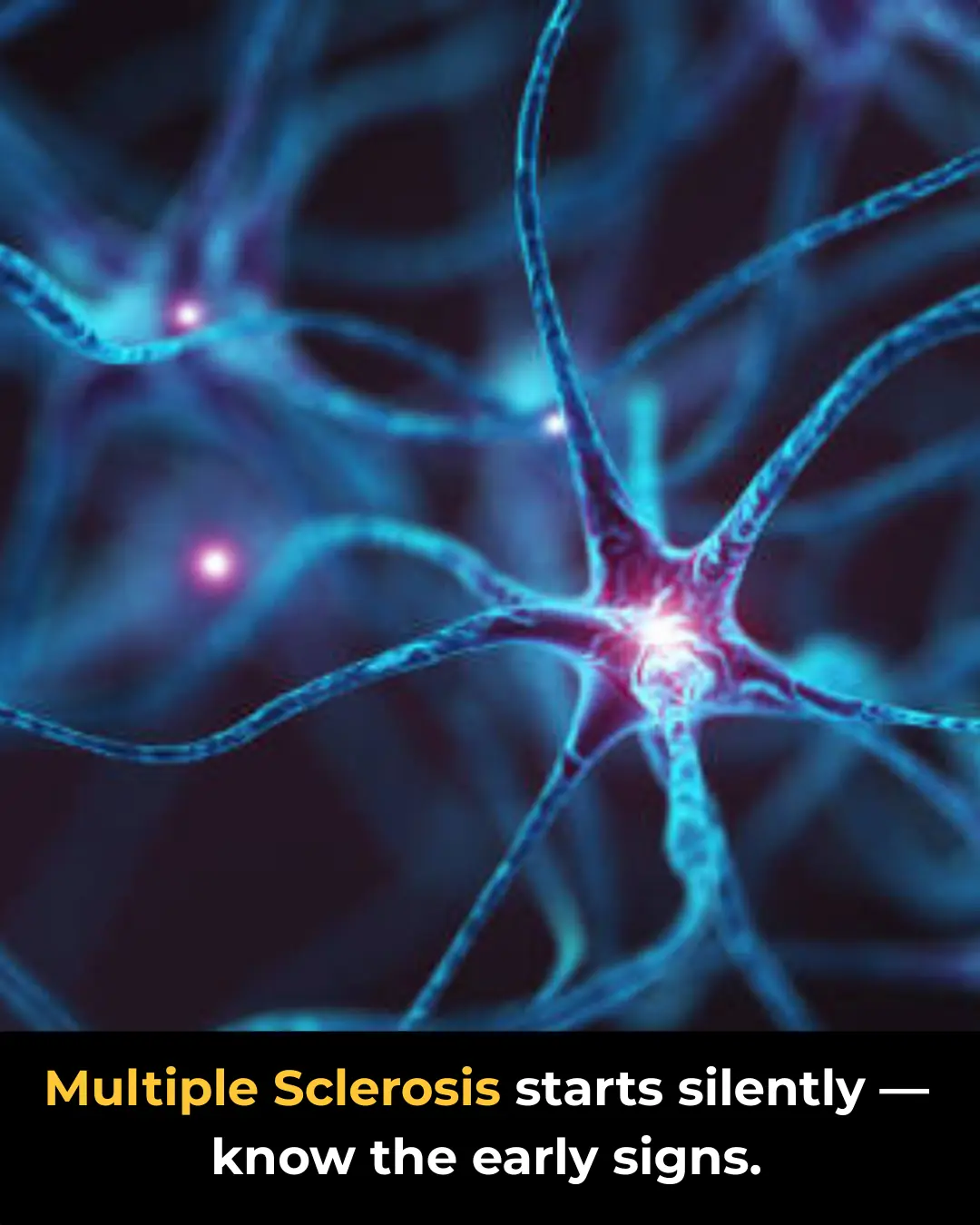
Multiple Sclerosis: First Symptoms You Should Notice

1 shot to open arteries instantly (prevent heart attack & stroke)

These 5 foods reverse type 2 diabetes—no meds needed
Proven Foods, Supplements and Vitamins That Act as Powerful Natural Blood Thinners

Why Not Having A Himalayan Salt Lamp In Your Home Might Be The Biggest Mistake You Are Making Right Now
News Post

Hello Kitty's Harmonyland Transforms into "Park in the Sky" Luxury Resort in Japan

UK’s Military Readiness Under Scrutiny: Could It Survive a Major Conflict with Russia?

New US Travel Rules Require Social Media Accounts: A Step Towards Security or Invasion of Privacy?

Disney’s Live-Action Tangled: McKenna Grace and Mason Thames in the Spotlight for Rapunzel and Flynn Rider Roles

Sour Candy: A Surprising Ally in Managing Panic Attacks and Anxiety

Science-Backed Herbs That Cleanse and Protect Your Body

Two Lungs, One Earth: Protecting Our Planet’s Vital Ecosystems for a Sustainable Future

2,000 Years Later: The Enduring Strength of Roman Concrete and Its Self-Healing Secrets

No need for mosquito repellent, use this readily available household item to drive away mosquitoes, it's both cheap and safe.

14 Vegetables That Work Like Vitamins: The Science Behind Nature’s Most Powerful Foods

The Kidney’s Role in Muscle Health
Doctor Warns of Mesotherapy’s Risky Side, Causing Reptile-Like Skin

Objects People Were Confused About Their Purpose
Here's The Truth Behind This Scar On People's Upper Left Arm

🦵 The 5 Best Nutrients to Reduce Swelling in the Feet and Legs

How Ginger Targets Prostate, Ovarian and Colon Cancer Stem Cells Better Than Chemo

Top 13 Inflammatory Foods You Should Avoid (Replace with These)

Simple way to get rid of cockroaches: Use only one ingredient readily available in your home.

Soaking orange and grapefruit peels in vinegar produces a special liquid that can save you a considerable amount of money.
