Regularly using these three types of cooking oil can lead to liver cancer without you even realizing it.

Many people still use one of these three types of cooking oil without realizing that they are extremely harmful to health and can even cause liver cancer.
There are many types of cooking oils such as soybean oil, peanut oil, rapeseed oil, avocado oil, etc. These oils offer various health benefits and are considered healthy foods in a balanced diet. However, if cooking oil is used incorrectly, it can pose many health risks, including cancer.
Three Types of Cooking Oil That Are Harmful to Health
If your household uses cooking oil frequently, avoid the following three types to protect the health of your entire family:
1. Reused Cooking Oil
Many families reuse cooking oil to avoid waste. However, this practice unknowingly “invites disease” into the body. Oil that has been heated repeatedly at high temperatures not only loses most of its nutrients but also produces large amounts of trans fats and carcinogenic compounds.
Some aggressive cancers associated with the use of reused cooking oil include lung cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, and prostate cancer.
[Advertisement]
In particular, using oil at high temperatures can disrupt the liver’s lipid metabolism process, potentially leading to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and accelerating liver diseases caused by oxidative stress from free radicals—most dangerously, liver cancer.
Regularly using these three cooking oils can lead to liver cancer without you even realizing it.
Reusing cooking oil increases the risk of cancer (Photo: ST).
2. Oil Made from Low-Quality Raw Materials
[Advertisement]
Cooking oil should be made from high-quality plant ingredients. Otherwise, instead of benefits, it only brings harm.
For example, with peanut oil: if it is produced from peanuts that are not properly dried or stored, the peanuts can easily become moldy and generate large amounts of toxins such as aflatoxin. Aflatoxin is a substance known to cause liver cancer.
In addition, if oil production facilities lack proper equipment and processes to remove impurities from plant materials, the oil may contain dust, coloring substances, and even toxic heavy metals or pesticide residues.
3. Hydrogenated Vegetable Oils
Hydrogenated vegetable oil is produced by adding hydrogen to the unsaturated double bonds of fatty acids in vegetable oils. This process creates partially or fully saturated oils (depending on the degree of hydrogenation), making the oil more stable, extending shelf life, and improving physical properties such as remaining solid at room temperature.
However, the hydrogenation process also produces a large amount of trans fats. These fats are harmful to health, especially increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Trans fats also increase inflammation and oxidative stress in the body, which can raise the risk of various cancers.
Four Harmful Cooking Oil Practices That Should Be Stopped Immediately
1. Waiting Until the Oil Smokes Before Cooking
Many people wait until the oil is smoking before cooking, believing this makes food tastier or simply out of habit. However, studies show that when oil reaches smoking point, fatty acids begin to break down and produce toxic substances such as acrylamide and benzopyrene. These compounds have been warned by the WHO as carcinogenic.
Illustration image
Moreover, this habit causes food to absorb more oil, making it harder to digest and irritating the stomach. To protect your health, heat oil only until it is hot enough and lightly shimmering before adding food.
2. Storing Cooking Oil Near the Stove or in Direct Sunlight
If you store cooking oil near the stove or expose it to sunlight—especially near gas stoves or open flames—it can be very dangerous.
Exposure to high temperatures causes oil to deteriorate easily. In particular, oil stored in plastic bottles may cause the plastic to melt and release toxic substances into the oil when heated. Using degraded oil can seriously affect health, especially increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease and cancer. Therefore, cooking oil should be kept away from heat sources and high temperatures.
Illustration image
3. Reusing Cooking Oil Multiple Times
Reusing cooking oil multiple times may seem economical but is extremely harmful and can lead to cancer. Research from the University of Illinois (USA) shows that oil heated repeatedly breaks down neutral fats and releases carcinogenic substances such as PAHs and HCAs. These not only affect the digestive system but also increase the risk of metabolic disorders and other cancers.
Furthermore, reused frying oil loses its nutritional value and contains toxic burnt residues. Ideally, oil should only be reused once. It should be filtered carefully, stored tightly sealed in the refrigerator, used within a few days, and discarded immediately if it smells burnt or changes color.
4. Using Cooking Oil That Has Been Stored Too Long or Has Expired
For tasty food and good health, do not use expired cooking oil. Expired oil can degrade, oxidize, produce toxic substances, and lose nutritional value. Even if it has not expired, oil that has been opened for more than three months should not be used. Once oil is exposed to air, it generates harmful peroxides and may even develop mold that produces aflatoxin—a powerful carcinogen.
Illustration image
In addition, avoid using homemade or small-scale manually pressed oils, as they often contain impurities, bacteria, mold, and oxidize easily due to inadequate processing and storage. Prioritize oils from reputable brands with safety certifications to protect your health and preserve the nutritional value of your meals.
How to Use Cooking Oil Safely
Below are some tips for using cooking oil to maintain good health:
-
Choose the right oil: Prioritize oils high in unsaturated fats such as olive oil, sunflower oil, and fish oil; avoid palm oil or heavily processed vegetable oils.
-
Control temperature: Do not heat oil at excessively high temperatures, as this can generate toxic substances.
-
Avoid repeated reuse: Limit reuse to no more than two times. Oils that contain food debris, turn dark, or have an unusual smell should be discarded immediately.
-
Store oil properly: Cooking oil should be stored in a cool, well-ventilated place and protected from direct light to prevent oxidation and quality loss.
News in the same category


6 tips for using beer as a hair mask or shampoo to make hair shiny, dark, and reduce hair loss

When rendering pork fat, don't just put it directly into the pan. Adding this extra step ensures that every batch of pork fat is perfectly white and won't mold even after a long time.

Using an electric kettle to boil water: 9 out of 10 households make this mistake, so remind your family members to correct it soon

4 "cancer culprits" lurking in your home, many people are exposed to daily without knowing it
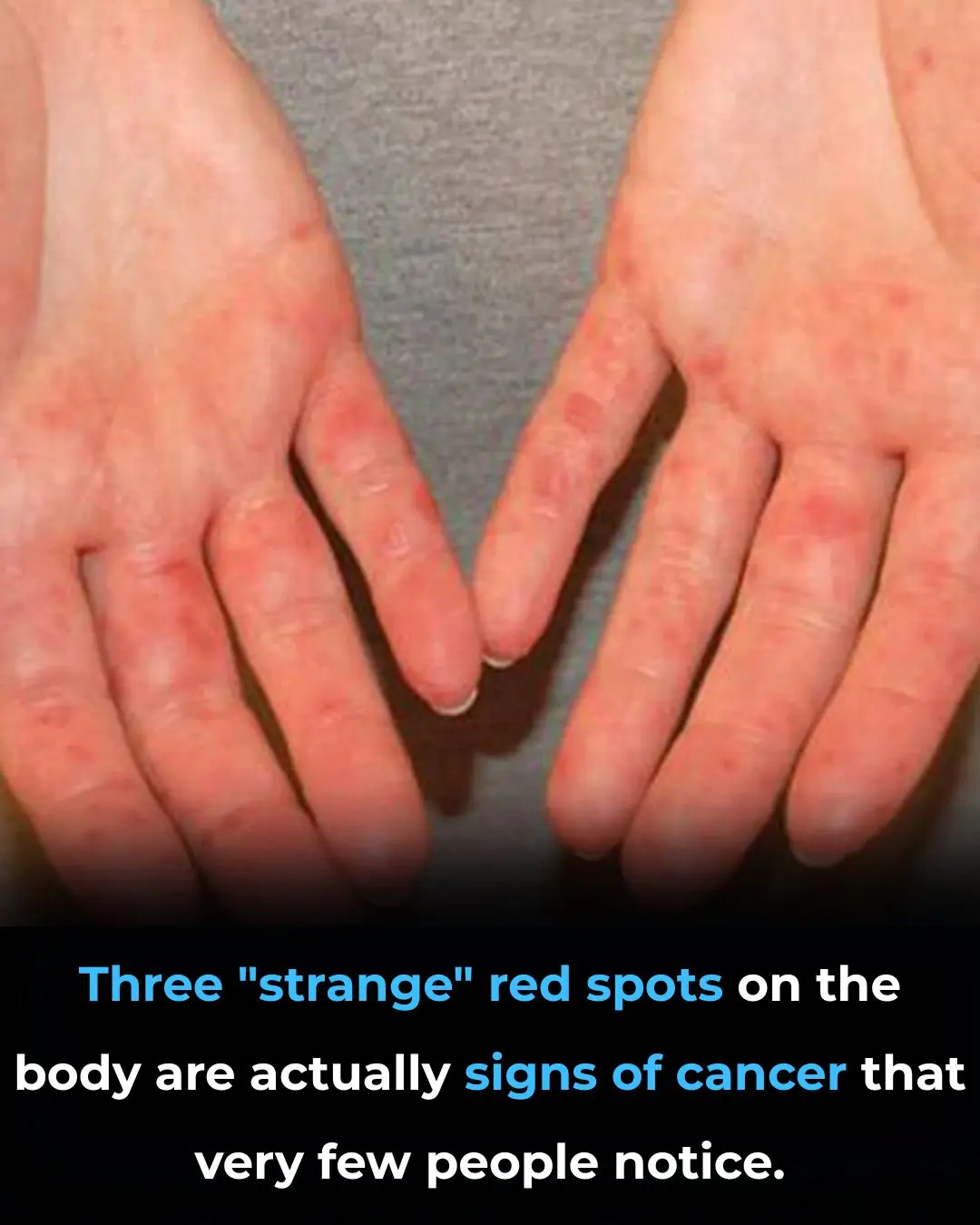
Three "strange" red spots on the body are actually signs of cancer that very few people notice
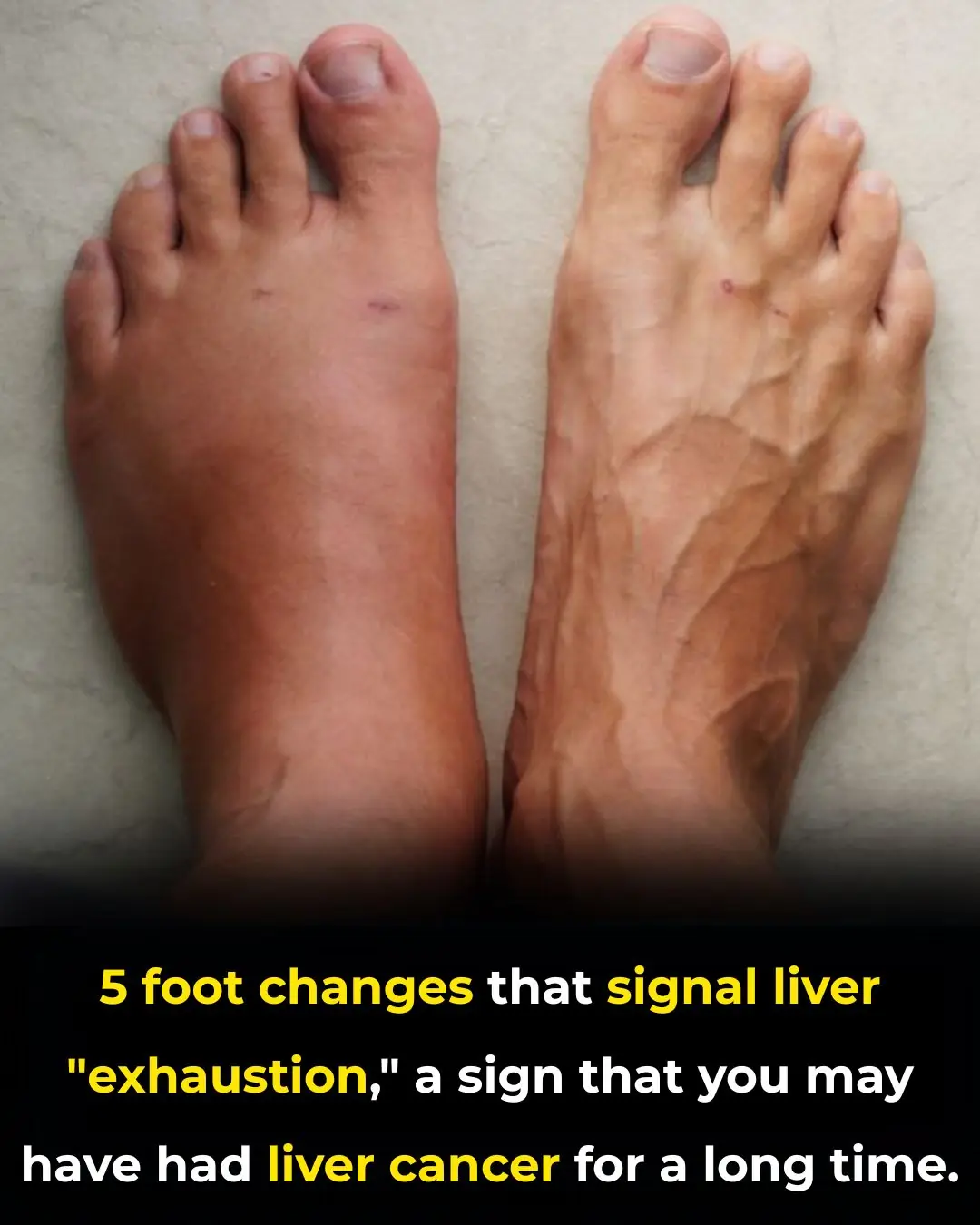
5 foot changes that signal liver "exhaustion," a sign that you may have had liver cancer for a long time.

10 types of fruits and vegetables you should never put in the refrigerator; many people don't know this and end up doing it wrong, ruining the taste and causing them to spoil quickly.

It turns out mosquitoes fear "this" the most. Put this on a lemon and leave it in a corner of the house, and the mosquitoes will be gone forever

6 seemingly harmless items in the bedroom but can silently damage the pancreas

Place ginger under your pillow before bed and receive 5 amazing benefits.

4 places in the house where you absolutely should not place a mirror

When thawing pork, don't soak it in water. These two methods are extremely quick and help the meat retain its fresh flavor

Is your pan losing its non-stick coating? Add a few drops of this, and your old pan will be like new again.

Smart people always turn on the bathroom light when staying overnight at a hotel

Fry the fish with these two ingredients, the fish will be crispy and fragrant, not sticking to the pan

5 tips for making crispy, golden-brown spring rolls.

Moved into new place, and toilet seat underside has gross yellow/brown pee stains. Plastic/melamine feel. Any miracle cleaners or tricks before I replace whole seat? Thanks!

2 tips for boiling pig ears to keep them white, crispy, and odorless.
News Post

Raw Carrots and Their Impact on Cholesterol and Colon Function

Breakthrough in Pancreatic Cancer Immunotherapy

How to grow lemons in pots for abundant fruit all year round, more than enough for the whole family to eat

6 tips for using beer as a hair mask or shampoo to make hair shiny, dark, and reduce hair loss

When rendering pork fat, don't just put it directly into the pan. Adding this extra step ensures that every batch of pork fat is perfectly white and won't mold even after a long time.
Scientists Crack an “Impossible” Cancer Target With a Promising New Drug

Blue Blood in the Ocean: How Horseshoe Crabs Help Protect Human Health

Using an electric kettle to boil water: 9 out of 10 households make this mistake, so remind your family members to correct it soon

4 "cancer culprits" lurking in your home, many people are exposed to daily without knowing it

Three "strange" red spots on the body are actually signs of cancer that very few people notice

5 foot changes that signal liver "exhaustion," a sign that you may have had liver cancer for a long time.

10 types of fruits and vegetables you should never put in the refrigerator; many people don't know this and end up doing it wrong, ruining the taste and causing them to spoil quickly.

You were raised by emotionally manipulative parents if you heard these 8 phrases as a child

The reason some seniors decline after moving to nursing homes

If You Love Being Alone, You Probably Have These 10 Qualities Others Envy

People Who Were Raised By Strict Parents Often Develop These 10 Quiet Habits

Sauna Bathing and Long-Term Cardiovascular Health: Evidence from a Finnish Cohort Study

The Role of Dietary Cysteine in Intestinal Repair and Regeneration