
Seven Common Habits Linked to Cancer After the Age of 40

Cancer rates are increasing worldwide, and one of the main contributing factors is unhealthy lifestyle habits. Many everyday behaviors that seem harmless can accumulate over time, significantly increasing the risk of cancer. Below are seven common habits that, if maintained long-term, may contribute to the development of cancer, especially after the age of 40.
1. Chronic Late Nights and Lack of Sleep
Staying up late and insufficient sleep are among the most harmful habits for overall health. Disrupted sleep patterns interfere with the body’s biological clock and weaken the immune system. Lack of sleep also reduces the production of melatonin, a hormone with antioxidant properties that helps protect cells from damage.
When the body does not get enough rest, cells have less time to recover and repair themselves. This increases the likelihood of abnormal cell division and raises the risk of cancer, particularly liver cancer and breast cancer.
2. Frequent Consumption of Processed and Fast Foods
Processed foods, fast food, and canned products often contain high levels of preservatives, salt, sugar, and artificial additives. Over time, these substances can accumulate in the body and negatively affect internal organs.
Nitrites and nitrates commonly found in processed meats can convert into carcinogenic compounds when exposed to high temperatures. In addition, these foods are typically low in fiber, vitamins, and essential minerals, which can impair digestion and increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
3. Excessive Intake of Salty or Sugary Foods
A diet high in salt can increase the risk of high blood pressure and stomach cancer, as salt damages the stomach lining and promotes inflammation. Overly salty foods may also contribute to gastric ulcers, further raising cancer risk.
On the other hand, excessive sugar intake increases insulin levels in the blood, disrupts hormonal balance, and creates favorable conditions for cancer cell growth. High sugar consumption has been linked to an increased risk of breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and pancreatic cancer. Studies suggest that cancer cells thrive in high-sugar environments, making sugar reduction essential for prevention.
4. Physical Inactivity and a Sedentary Lifestyle
A lack of physical activity reduces mobility, contributes to weight gain, and weakens overall health. Excess body fat, especially abdominal fat, is strongly associated with an increased risk of several cancers, including breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and uterine cancer.
Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, strengthens the immune system, and improves metabolism. Physical inactivity also slows digestion, increasing the likelihood of digestive disorders and toxin buildup in the body.
5. Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Heavy alcohol consumption is a major risk factor for cancer, particularly liver cancer, stomach cancer, and esophageal cancer. Alcohol is converted into acetaldehyde in the body, a highly carcinogenic substance that damages DNA and impairs cell repair mechanisms.
Excessive drinking also leads to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and liver overload, increasing the risk of liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. Additionally, alcohol weakens the immune system, making the body more vulnerable to disease.
6. Smoking
Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer, but it is also linked to cancers of the throat, stomach, pancreas, and many other organs. Tobacco smoke contains more than 70 known carcinogens, including benzene, formaldehyde, and polonium.
These toxic substances enter the body through the respiratory system and damage not only the lungs but also other organs. Passive smoking is also dangerous, as people exposed to secondhand smoke face an increased cancer risk. Avoiding tobacco is essential for protecting both personal and family health.
7. Skipping Regular Health Checkups
Many people neglect routine health screenings and only seek medical care when symptoms appear. However, cancer often develops silently over many years without obvious signs, making early detection difficult.
Regular health checkups increase the chances of identifying cancer at an early stage, when treatment is more effective. Screening methods such as blood tests, endoscopy, and ultrasound can detect abnormal cells early and help prevent cancer progression.
Conclusion
Unhealthy habits such as staying up late, poor diet, lack of exercise, alcohol consumption, smoking, and neglecting regular health checkups significantly increase the risk of cancer. To protect long-term health, it is important to adopt a balanced diet, stay physically active, undergo regular medical screenings, and avoid harmful substances like tobacco and excessive alcohol. By making these lifestyle changes, the risk of cancer can be reduced and overall quality of life improved.
News in the same category


Vinegar Consumption and Reduced Risk of Calcium Oxalate Kidney Stones: Evidence from a Pilot Human Study

11 Health Warnings Your Fingernails May Be Sending

Bloated Stomach: 8 Common Reasons and How to Treat Them (Evidence Based)
Occupational Bromide Exposure and the Development of Multiple Cherry Angiomas: Insights from a Case Report

How to Use Castor Oil to Regrow Eyelashes and Eyebrows

Three-Dimensional Video Gaming and Hippocampal Plasticity in Older Adults

Affectionate Touch, Oxytocin, and Women’s Stress and Cardiovascular Health

Raw Cabbage Juice and Rapid Healing of Peptic Ulcers: Early Clinical Evidence from Stanford

Montmorency Tart Cherry Juice as a Supportive Dietary Intervention in Ulcerative Colitis

Anemia: A Lesser-Known Side Effect of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists?

Can Gray Hair Be a Sign That the Body Is Eliminating Cancer Cells?

A 95-Year-Old Cancer Expert with 60 Years of Research Reveals: Four Things You Must Avoid to Keep Cancer from Knocking on Your Door
Clinical Trials Show Meaningful Progress in Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
Medicinal Health Benefits of Garlic (Raw, Supplement) – Science Based
Colon Cleansing: How to Naturally Flush Your Colon at Home (Science Based)
7 Warning Signs of Lung Cancer You Shouldn’t Ignore

After a Stroke, Women Struggle With Daily Tasks for Longer Than Men
What causes night cramps and how to fix the problem
News Post

The "Freedom Ride": A New Chapter for a Shelter Survivor
The Wisdom of a Short Life: Why Dogs Leave Us So Soon

From "Death Row" to a Dignified Life: The Miracle Transformation of Clementine

The Warrior’s Wag: Celebrating a Cancer-Free Pitbull and the Truth Behind the Breed

The Power of a Hug: How One "Code Red" Dog Embraced His Way to a Second Chance

The Bright Spot in the Shadows: A Tribute to Kaydee

Five Highly Toxic Meats That Should Be Avoided

Even old, non-stick pans can be "revived" with just a few simple tips that everyone should know.
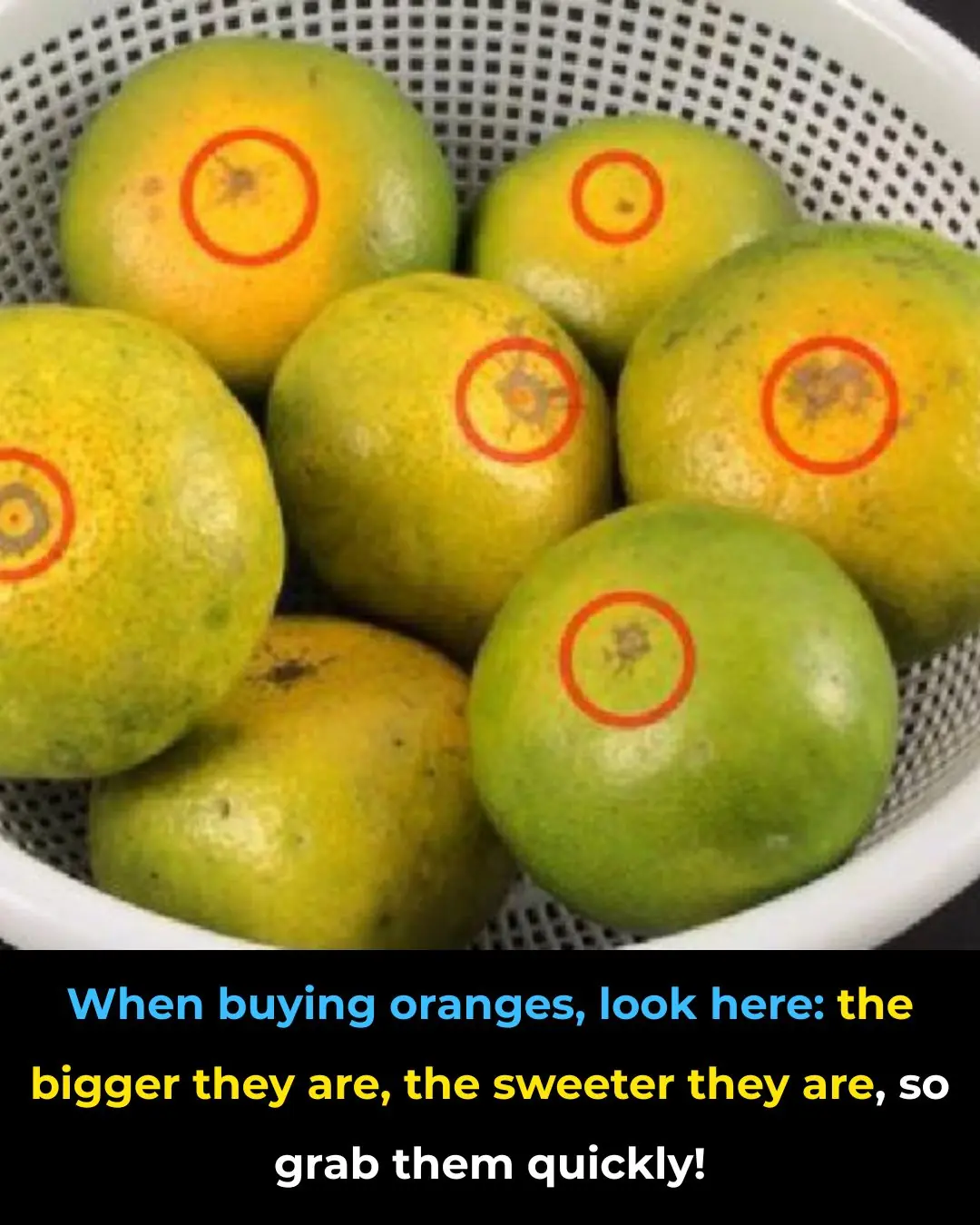

When buying oranges, look here: the bigger they are, the sweeter they are, so grab them quickly!

Tips for making sticky rice that cooks quickly without soaking the rice overnight, resulting in plump grains that remain soft and chewy even after a while.

10 signs you're not drinking enough water

Vinegar Consumption and Reduced Risk of Calcium Oxalate Kidney Stones: Evidence from a Pilot Human Study

11 Health Warnings Your Fingernails May Be Sending

Bloated Stomach: 8 Common Reasons and How to Treat Them (Evidence Based)

Occupational Bromide Exposure and the Development of Multiple Cherry Angiomas: Insights from a Case Report

How to Use Castor Oil to Regrow Eyelashes and Eyebrows

Three-Dimensional Video Gaming and Hippocampal Plasticity in Older Adults

Affectionate Touch, Oxytocin, and Women’s Stress and Cardiovascular Health
