
Weird Hacks That Heal Faster Than You Think: Folk Remedies Through a Scientific Lens
Throughout history, people have relied on simple household remedies to relieve everyday health problems. While some of these methods may sound unusual, modern science has begun to explain why certain “weird hacks” can be surprisingly effective. The infographic “Weird Hacks That Heal Faster Than You Think” presents common remedies for minor ailments, many of which are supported by biological or clinical evidence.
One widely shared remedy for mosquito bites is rubbing the inside of a banana peel on the affected area. Banana peels contain natural sugars and antioxidant compounds that may help soothe itching and reduce inflammation. While clinical trials are limited, studies on plant-based anti-inflammatory compounds support the plausibility of this effect.
Scientific context: Journal of Medicinal Plants Research – Plant antioxidants and skin inflammation
For minor burns, applying raw honey after cooling the skin has long been recommended. Honey possesses antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and wound-healing properties. Clinical studies show that honey can accelerate healing and reduce infection risk in superficial burns.
Scientific source: Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews – Honey for wound and burn healing (https://www.cochranelibrary.com)
Bad breath is often linked to an imbalance of oral bacteria. Eating plain yogurt introduces beneficial probiotics that can suppress odor-causing microorganisms. Research confirms that probiotic dairy products can reduce volatile sulfur compounds responsible for halitosis.
Scientific source: Journal of Clinical Periodontology – Probiotics and oral health (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21740430/)
For hiccups, swallowing a spoonful of peanut butter may help reset diaphragm contractions. The thick texture alters breathing patterns and stimulates swallowing reflexes, which can interrupt the hiccup cycle. Though evidence is mostly anecdotal, the physiological explanation is well recognized.
Scientific context: British Medical Journal – Mechanisms of hiccups
Tension headaches may respond to diluted peppermint oil applied to the temples. Peppermint contains menthol, which produces a cooling sensation and improves local blood flow, helping relax tense muscles. Clinical studies show peppermint oil can be as effective as mild analgesics for tension-type headaches.
Scientific source: Phytomedicine – Peppermint oil for headache relief (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11243423/)
For nausea, smelling fresh lemon or ginger can provide relief. Aromatherapy studies indicate that ginger reduces nausea by acting on gastrointestinal motility and serotonin receptors.
Scientific source: American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology – Ginger and nausea (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20418184/)
A sore throat is often soothed by raw honey, which coats the throat and inhibits microbial growth. Honey has been shown to reduce coughing and throat irritation, particularly in upper respiratory infections.
Scientific source: Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine – Honey for cough relief (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18056558/)
For temporary toothache relief, placing a clove near the affected tooth is a traditional practice. Cloves contain eugenol, a compound with natural anesthetic and antibacterial properties widely used in dentistry.
Scientific source: Journal of Dentistry – Eugenol in dental pain management (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25258397/)
Unusual techniques such as pressing the tongue to the roof of the mouth for a stuffy nose may stimulate nerves connected to nasal passages, offering short-term relief. Though evidence is limited, similar nerve stimulation methods are studied in nasal congestion management.
For trouble sleeping, warm milk with nutmeg has traditionally been used to promote relaxation. Milk contains tryptophan, a precursor to serotonin and melatonin, while nutmeg has mild sedative properties in small amounts.
Scientific context: Nutrients – Diet and sleep regulation (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5452224/)
Foot odor can be reduced by soaking feet in black tea due to tannins, which have antibacterial and astringent effects that limit odor-causing bacteria.
Scientific source: Journal of Dermatological Treatment – Tannins and antimicrobial effects
Finally, dry skin benefits from coconut oil, which acts as an occlusive moisturizer and improves skin barrier function. Dermatological research confirms its effectiveness in reducing water loss from the skin.
Scientific source: International Journal of Dermatology – Coconut oil and skin hydration (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15724344/)
Conclusion
Although many of these remedies originate from traditional knowledge, science increasingly supports their practical value. While they should not replace medical treatment for serious conditions, these simple interventions can offer safe, accessible relief for minor health issues when used appropriately.
News in the same category


Right-Side Abdominal Pain in Women: Could It Be Gallstones?

It Looks Like I Had Cosmetic Surgery”: The At-Home Routine People Use to Improve the Look of Wrinkles and Dark Spots on Hands and Arms

Everything You Need To Know About Nail Pitting
🧠 8 Strange (But Real) Signs Your Body Is Begging for More Vitamin B12 – Don’t Ignore These Red Flags

How To Identify Skin Tags and When To Remove Them
14 Visible Signs of Cancer Most Women Ignore

Reducing Prostate Discomfort Naturally with a Tomato and Garlic Drink

Never Throw Away the Avocado Seed Again — Here’s Why

Guava Leaves Benefits: The Underrated Natural Remedy You Shouldn’t Ignore 🍃💪

Herbal Tea for Swollen Legs: Natural Diuretic & Anti-Inflammatory Recipe, How to Use It, and Precautions
Avocado Seed Benefits: The Overlooked Natural Remedy for Joint and Back Pain
How Garlic and Lemon Can Gently Support Your Eye Comfort and Vision Wellness

The Overlooked Tree With Powerful Health Benefits

Discover How Incorporating Fresh Parsley into Your Daily Routine Can Support Knee Joint Comfort and Mobility Naturally

Woman reveals 3 overlooked symptoms before her stage 4 cancer diagnosis at 28
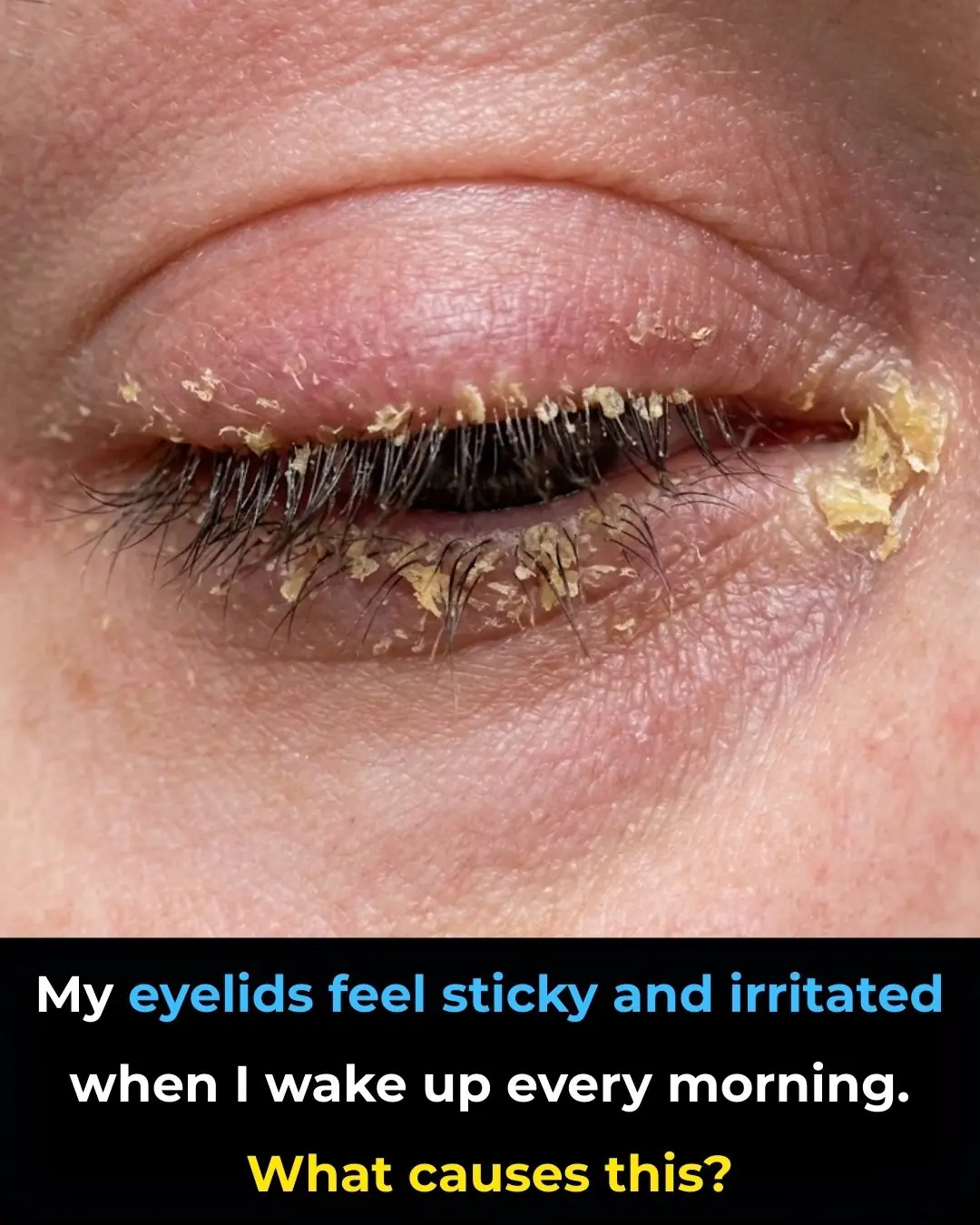
My eyelids feel sticky and irritated when I wake up every morning. What causes this?

One Spoon a Day for Stronger Vision – A Simple Daily Habit to Support Eye Comfort

A Gentle Herbal Infusion to Support Blood Sugar, Cholesterol & Circulation Naturally
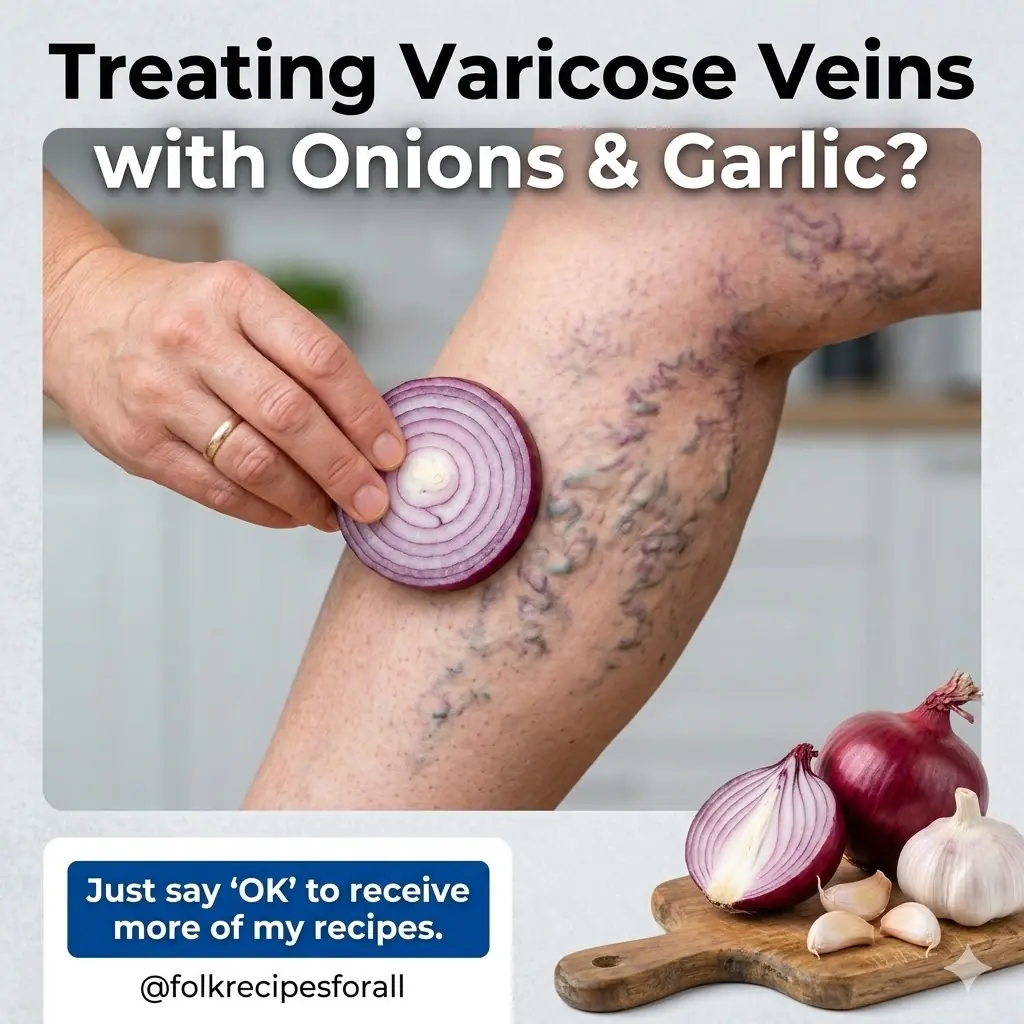
Home Remedies for Varicose Veins with Onion, Garlic, and Apple Cider Vinegar
News Post

He Crashed the Wedding With a Smile—She Raised a Shield and Ended the Nightmare

“He Smashed My Violin in Front of Everyone… Then a Black Sedan Stopped the Street.”

She Accused a Cruise Dishwasher of Stealing Her Diamond Ring — What Happened Next Froze the Entire Ship

8 Foods You Should Eat Instead of Taking a Vitamin C Supplement

Right-Side Abdominal Pain in Women: Could It Be Gallstones?

It Looks Like I Had Cosmetic Surgery”: The At-Home Routine People Use to Improve the Look of Wrinkles and Dark Spots on Hands and Arms

The Last Five Dollars

The Forgotten Backpack

Everything You Need To Know About Nail Pitting

🧠 8 Strange (But Real) Signs Your Body Is Begging for More Vitamin B12 – Don’t Ignore These Red Flags

How To Identify Skin Tags and When To Remove Them

14 Visible Signs of Cancer Most Women Ignore

Reducing Prostate Discomfort Naturally with a Tomato and Garlic Drink

Never Throw Away the Avocado Seed Again — Here’s Why

Guava Leaves Benefits: The Underrated Natural Remedy You Shouldn’t Ignore 🍃💪

Herbal Tea for Swollen Legs: Natural Diuretic & Anti-Inflammatory Recipe, How to Use It, and Precautions

Avocado Seed Benefits: The Overlooked Natural Remedy for Joint and Back Pain

How Garlic and Lemon Can Gently Support Your Eye Comfort and Vision Wellness

Was He Really Jesus?
