Why Does My Heart Hurt? Common Reasons For Heart or Chest Pain
Feeling as though your heart hurts can be frightening and may quickly lead to anxiety or panic. Chest pain is often associated with serious heart problems, but the reality is that there are many possible reasons why you might feel pain in the heart area. Not all chest pain originates from the heart itself. In fact, issues such as indigestion, emotional stress, muscle strain, or lung conditions can all create discomfort that feels like heart pain.
That said, pain in the chest or near the heart should never be ignored. Some forms of chest pain are linked to problems with the heart or blood vessels and may require immediate medical attention. Any unexplained, persistent, or squeezing chest pain should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out life-threatening conditions.
Often, heart-related pain is accompanied by additional symptoms that help identify the cause. For example, serious cardiac pain may spread to the left arm, shoulder, neck, or jaw. Digestive issues like heartburn can cause a burning sensation behind the breastbone along with upper abdominal discomfort. Sharp pain that worsens when coughing or breathing deeply may point to lung-related problems rather than the heart itself.
In this article, you will learn why your heart may hurt, how to recognize different types of chest pain, and when to seek medical care. We will also explore whether emotional distress, such as grief or heartbreak, can physically affect the heart.
Common Symptoms of Heart Ache
The heart is located behind the breastbone and slightly to the left side of the chest. As a result, pain in this area is often assumed to be heart-related, even when it originates from muscles, ribs, or nearby organs.
According to Dr. Charles Patrick Davis from MedicineNet, chest pain can present in several different ways, including:
-
Tight or squeezing pressure in the center of the chest
-
Pain that radiates to the left arm, shoulder, or jaw
-
Sharp, stabbing, or jabbing chest pain
-
A dull, constant ache in the upper chest
-
Discomfort associated with a fast or irregular heartbeat
-
Intermittent chest pain that comes and goes without warning
Understanding how the pain feels, how long it lasts, and what triggers it can help doctors determine its cause.
Reasons Why Your Heart Hurts
Chest pain should always be taken seriously. Even if the underlying cause turns out to be harmless, ruling out serious heart conditions early can prevent dangerous complications.
Heart Problems That Cause Chest Pain
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary artery disease occurs when plaque builds up inside the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart. This restriction often causes aching or squeezing pain in the center of the chest, especially during physical activity or emotional stress.
PubMed Health reports that chest pain is the most common symptom of coronary heart disease. This pain may spread to the arm or shoulder and can appear suddenly or gradually worsen over time.
Angina, the most common symptom of CAD, may also cause:
-
Chest tightness or burning
-
Shortness of breath
-
Pain triggered by exercise or stress
Because angina can signal an increased risk of heart attack, medical evaluation is essential.
Heart Attack
A heart attack may feel like intense pressure or heaviness on the chest, as though something heavy is pressing down. The pain can last for minutes or recur over several days.
Dr. Melissa Conrad Stöppler explains that heart attack pain often spreads to the arm, back, neck, or jaw and may be accompanied by:
-
Difficulty breathing
-
Nausea or indigestion
-
Cold sweats
-
Upper abdominal discomfort
Emergency services should be contacted immediately if these symptoms occur.
Other Heart Conditions
-
Myocarditis: Inflammation of the heart muscle, often caused by viral infections, leading to sharp chest pain, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
-
Pericarditis: Inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart, causing sharp pain that worsens over time.
-
Aortic dissection: A medical emergency involving a tear in the aorta, producing sudden, severe chest and back pain.
Stress and Emotional Causes of Heart Pain
Stress
Chronic or intense stress can significantly affect the heart. Stress raises blood pressure, increases heart rate, and tightens chest muscles, often resulting in chest pain or discomfort.
In addition to heart pain, stress may cause:
-
Digestive problems
-
Headaches
-
Sleep disturbances
-
Frequent infections
Panic Attacks
Panic attacks can closely mimic heart attacks. Chest pain during a panic attack is often caused by muscle tension, rapid breathing, or increased blood pressure.
Symptoms may include:
-
Dizziness or faintness
-
Tingling in the hands or feet
-
Shaking or chills
-
Fear of losing control or dying
Can a “Broken Heart” Really Hurt?
Yes. Severe emotional distress, such as grief after losing a loved one, can lead to physical heart symptoms. Research published in Open Heart shows that intense stress can trigger irregular heart rhythms, heart attacks, or a condition known as stress-induced cardiomyopathy.
Muscles, Ribs, and Chest Wall Pain
Pain from the chest wall or ribcage can easily be mistaken for heart pain.
Muscle Strain
Strained intercostal muscles between the ribs can cause sharp or aching pain that worsens with movement or deep breathing.
Rib or Sternum Pain
Conditions such as costochondritis (inflammation of rib cartilage) can cause pain similar to a heart attack. The pain often worsens when pressing on the chest or breathing deeply.
Lung Conditions That Cause Heart-Like Pain
Lung-related issues can produce chest pain that feels cardiac in origin.
-
Pneumonia: Causes stabbing chest pain that worsens with coughing or breathing.
-
Pleurisy: Inflammation of the lung lining, causing sharp pain with breathing.
-
Asthma: Tightened airways and chest muscles may result in aching chest pain.
-
Pulmonary embolism: A blood clot in the lungs causing severe chest pain and shortness of breath.
-
Collapsed lung: Sudden sharp pain due to pressure changes in the chest.
Digestive Problems That Mimic Heart Pain
Heartburn and Acid Reflux (GERD)
Acid reflux can cause burning chest pain that closely resembles a heart attack. However, heartburn usually feels like burning, while heart attack pain is more often described as squeezing or pressure-like.
Because symptoms overlap, medical evaluation is crucial if chest pain is severe or unfamiliar.
When to See a Doctor
You should seek immediate medical care if you experience:
-
Persistent or severe chest pain
-
Pressure spreading to the arm, jaw, or back
-
Shortness of breath
-
Nausea or cold sweats
-
Chest pain triggered by physical activity
Even mild or occasional chest pain should be evaluated if it is new or worsening.
Final Note
While many causes of heart pain are not life-threatening, chest pain should never be ignored. Identifying the cause early ensures proper treatment and peace of mind, and in some cases, it can be life-saving.
News in the same category


Chia Seeds: Health Benefits & Nutrition Facts Based on Science

Proven Health Benefits of Celery & Nutrition Facts (Evidence Based)

The Benefits of Placing a Ginger Root Under Your Pillow Before Sleeping

The Benefits of Eleusine Indica in Traditional Medicine

Is “California Sober” a Viable Strategy to Reduce Alcohol Use? New Evidence Offers Support

Cannabis Extract Eases Chronic Low Back Pain and Improves Sleep and Mobility: Promising Phase 3 Evidence

When Cannabis Triggers Hyperemesis in Youth: Understanding a Growing Emergency

Physician-Led Medical Cannabis Clinics in Geriatric Care: A Promising Model for Senior Health
A 65-Year-Old Man Collapses at Midnight: Doctors Warn Against Four Drinks Not to Consume Before Sleeping
Everything You Need to Know About Eczema on the Ears
Tips for Dealing With Nail Psoriasis

Two Family Habits That Increase the Risk of Cancer for Everyone – Avoid Them Now to Prevent Regret
Your legs are screaming ‘HELP!:’ 5 warning signs from your liver

Nighttime Olfactory Enrichment and Cognitive Enhancement in Older Adults
Sodium Bicarbonate and Immune Regulation: Evidence for an Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism
Oleocanthal from Extra-Virgin Olive Oil: A Multi-Targeted Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Cancer Compound

Fenbendazole and Unexpected Cancer Remission: Insights from a 2024 Case Report
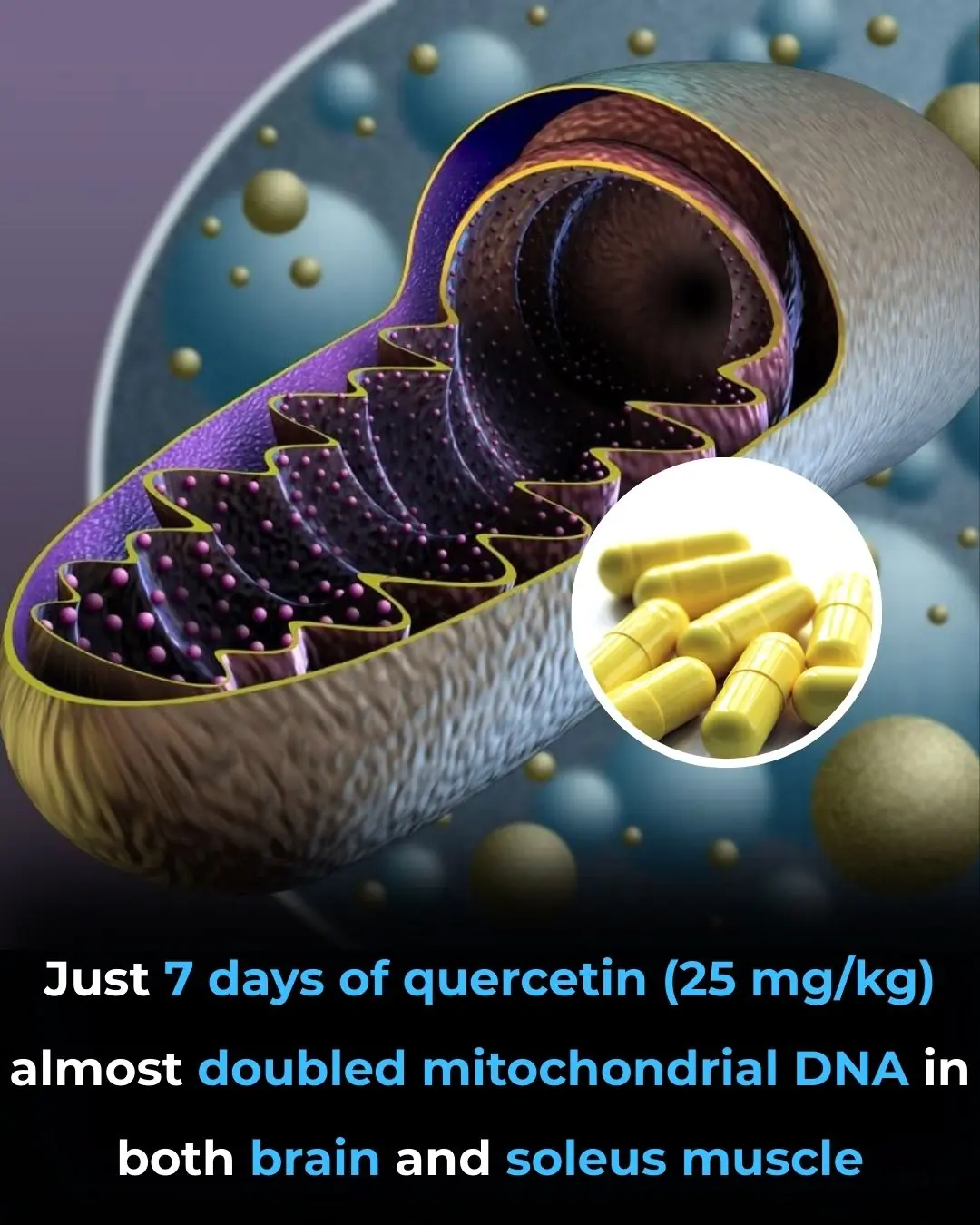
Quercetin as an Exercise Mimetic: Enhancing Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Physical Performance
News Post

To preserve tofu, don't put it directly in the refrigerator. Remember these two tips and your tofu will stay fresh for 10 days.

Don't throw away fruit netting; use it for these 12 things and save a considerable amount of money.

This liquid helps clean mold stains on walls and ceilings; it's easy to find but not many people know about it.

Rice Water Uses for Skin

15 Best Skin Gels for Glowing Skin & Wrinkles
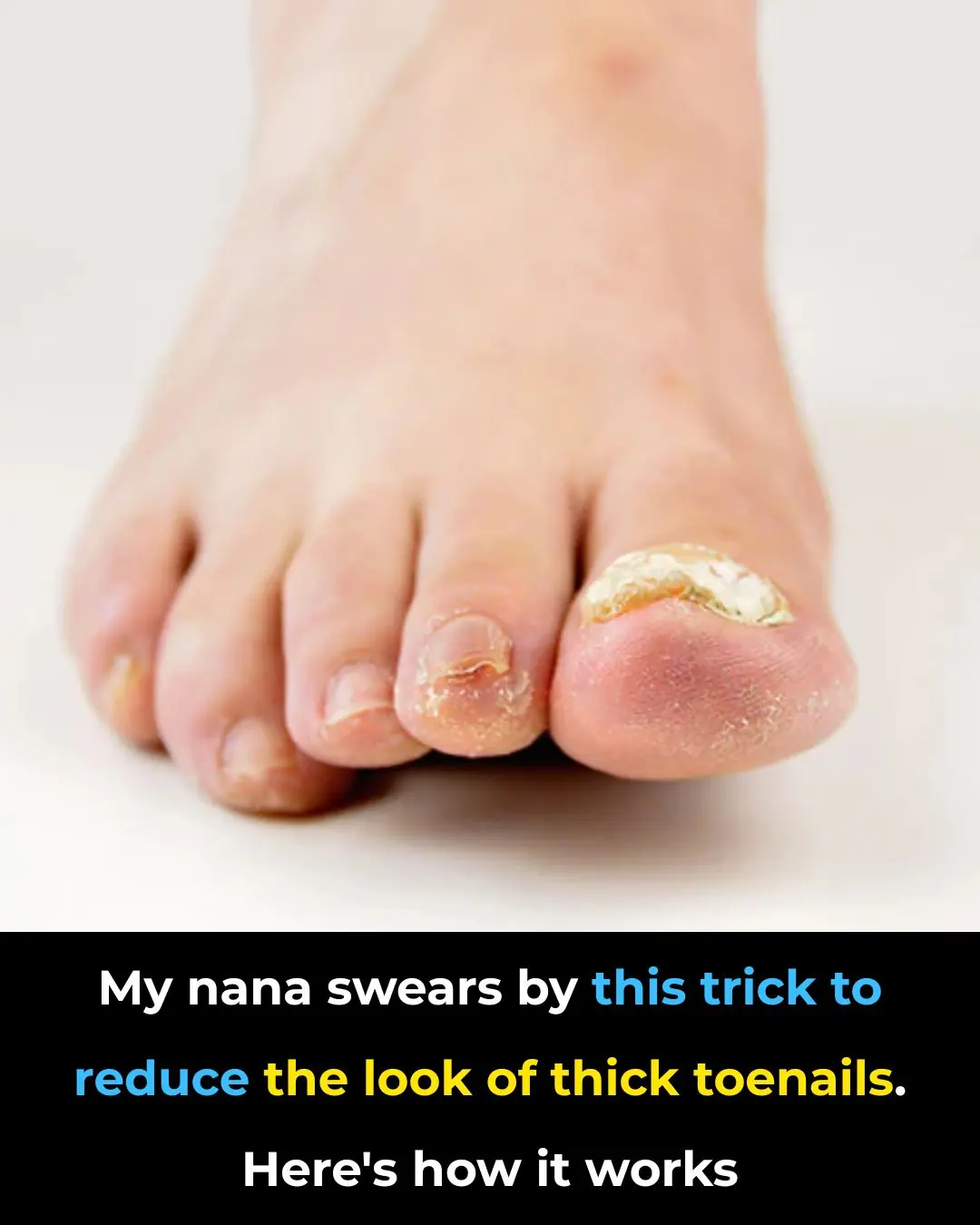
So good! Thanks nana!

Coconut Oil for Hair Growth – Add this in your Hair Oil

Red Spots on Skin: Causes, Treatments and More (Extensive Guide)

Chia Seeds: Health Benefits & Nutrition Facts Based on Science

Clove benefits for Skin – Clove Oil, Clove Gel & Clove ice cubes

Proven Health Benefits of Celery & Nutrition Facts (Evidence Based)

The Benefits of Placing a Ginger Root Under Your Pillow Before Sleeping

The Benefits of Eleusine Indica in Traditional Medicine

Is “California Sober” a Viable Strategy to Reduce Alcohol Use? New Evidence Offers Support

Cannabis Extract Eases Chronic Low Back Pain and Improves Sleep and Mobility: Promising Phase 3 Evidence

When Cannabis Triggers Hyperemesis in Youth: Understanding a Growing Emergency

Physician-Led Medical Cannabis Clinics in Geriatric Care: A Promising Model for Senior Health

A 65-Year-Old Man Collapses at Midnight: Doctors Warn Against Four Drinks Not to Consume Before Sleeping

