Deadly Nightshade Atropa Belladonna The Mysterious and Toxic Plant with a Dark History
Deadly Nightshade Atropa Belladonna is one of history’s most infamous toxic plants known for its beauty mystery and medicinal uses Despite its deadly nature it has been used in traditional medicine cosmetics and even poisons But what makes it so dangerous Can it be used safely or should it be avoided Let’s explore its history effects and risks
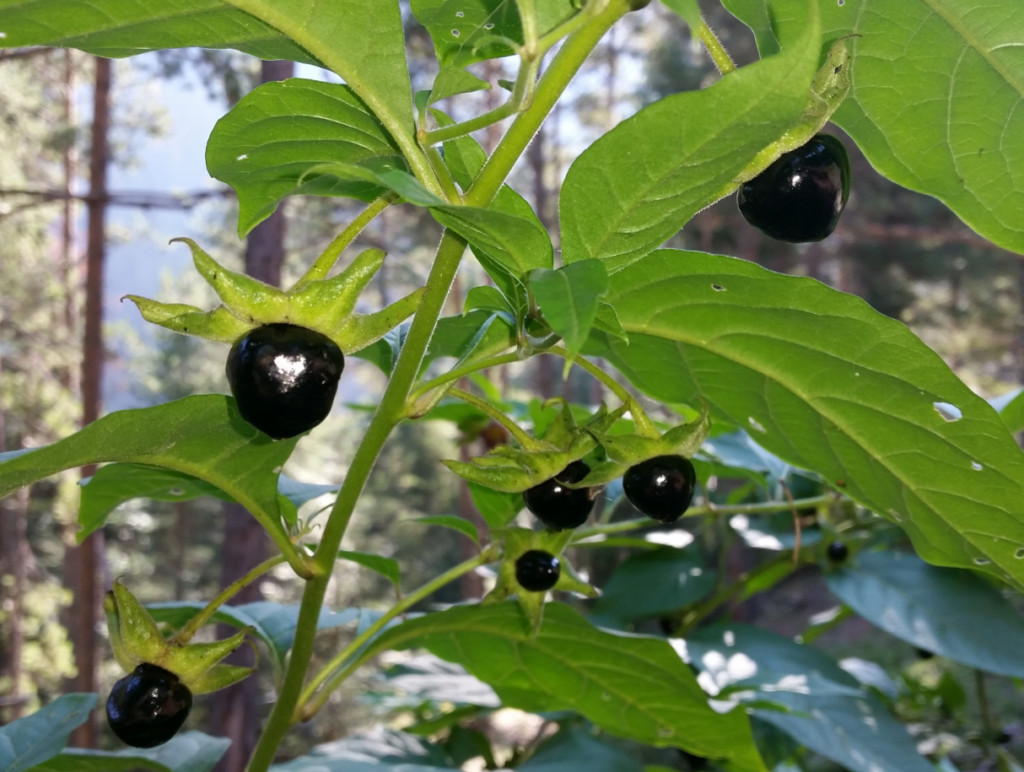

What is Deadly Nightshade
Deadly Nightshade Atropa Belladonna is a perennial plant from the nightshade family native to Europe North Africa and Western Asia With its dark purple berries and bell shaped flowers it looks beautiful but is extremely toxic every part of the plant contains deadly alkaloids
Toxic Components of Deadly Nightshade
Atropine Affects the nervous system causing hallucinations rapid heartbeat and paralysis
Scopolamine Known for its mind altering effects used historically in poisons and sedatives
Hyoscyamine Disrupts neurological functions leading to severe poisoning or death in high doses
These alkaloids block neurotransmitters in the body leading to a variety of toxic effects from blurred vision and dry mouth to respiratory failure in severe cases
The History and Folklore of Deadly Nightshade

Deadly Nightshade has been used medicinally magically and lethally throughout history Here are some fascinating historical uses
Ancient Rome and Greece


Medieval Witchcraft and Sorcery


Renaissance Beauty


Symptoms and Effects of Deadly Nightshade Poisoning
Even small doses of Deadly Nightshade can cause severe poisoning Here’s what happens when someone ingests or comes into contact with the plant
Mild Symptoms




Severe Symptoms




Who is Most at Risk




Is There a Safe Way to Use Deadly Nightshade
Despite its deadly reputation Atropa Belladonna has been used in controlled medical settings Modern pharmaceuticals extract atropine and scopolamine from the plant for legitimate medical purposes
Medical Uses of Belladonna Extracts





How to Identify and Avoid Deadly Nightshade
Since Deadly Nightshade resembles edible berries it’s essential to know how to identify and avoid it in the wild
How to Identify Atropa Belladonna




Safe Foraging Practices



Should You Grow or Avoid Deadly Nightshade



While Deadly Nightshade is fascinating from a historical and medicinal perspective its toxic nature makes it a plant to admire from a distance rather than cultivate or consume
Key Takeaways




News in the same category

How to treat nerve pain in the foot, toes & legs
Why your legs cramp at night and how to stop it from happening
1 teaspoon a day melts away fatty liver naturally

What Causes Pain Under Your Left Rib Cage?

What Causes Your Toenail To Turn Black?

Doctor Warns Popular Medication May Lead to Organ Failure

The military sleep method that can help you fall asleep in just two minutes
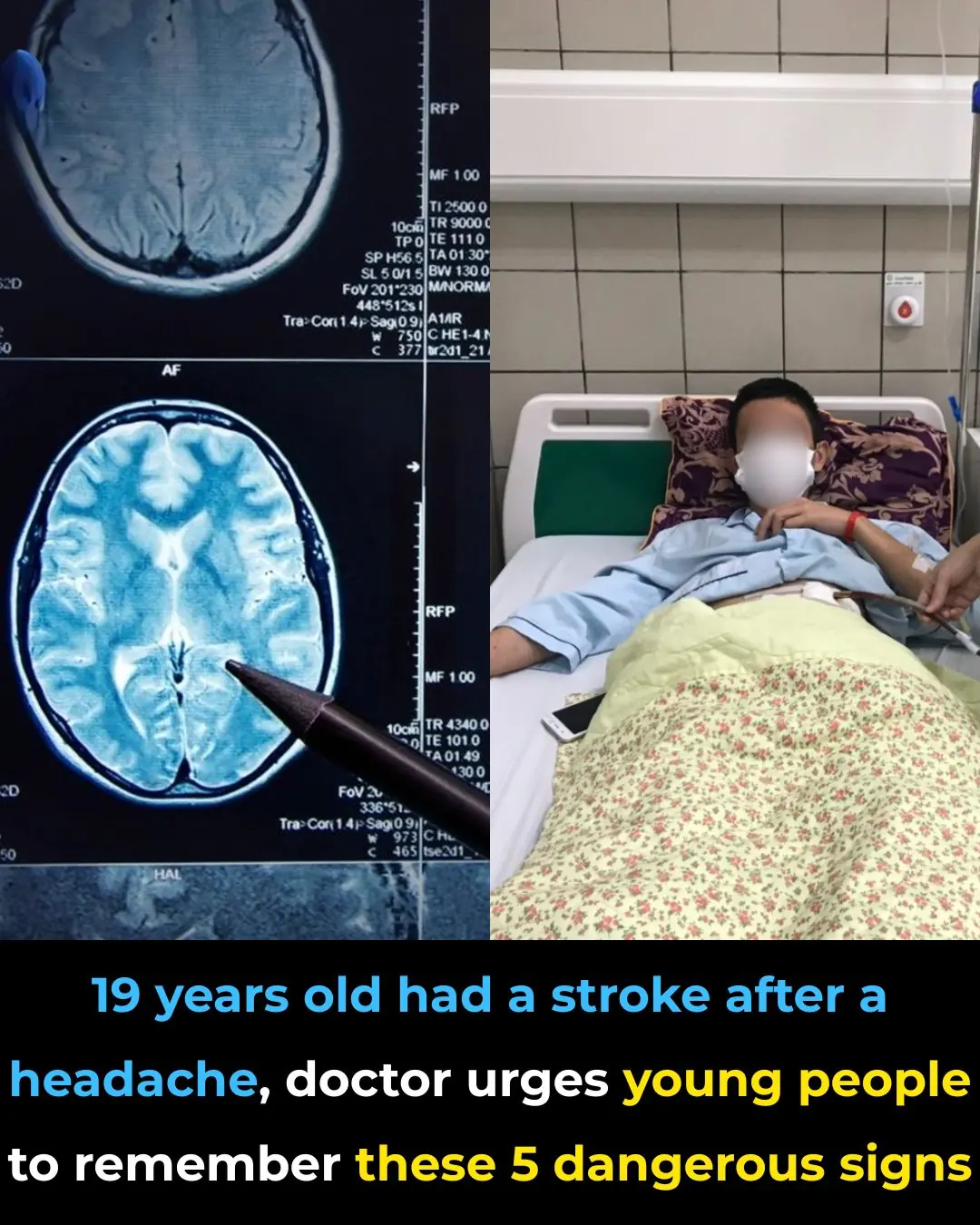
5 warning signs of stroke in young adults

20 Early Signs Your Body is Fighting Cancer

9-year-old dies after dental procedure
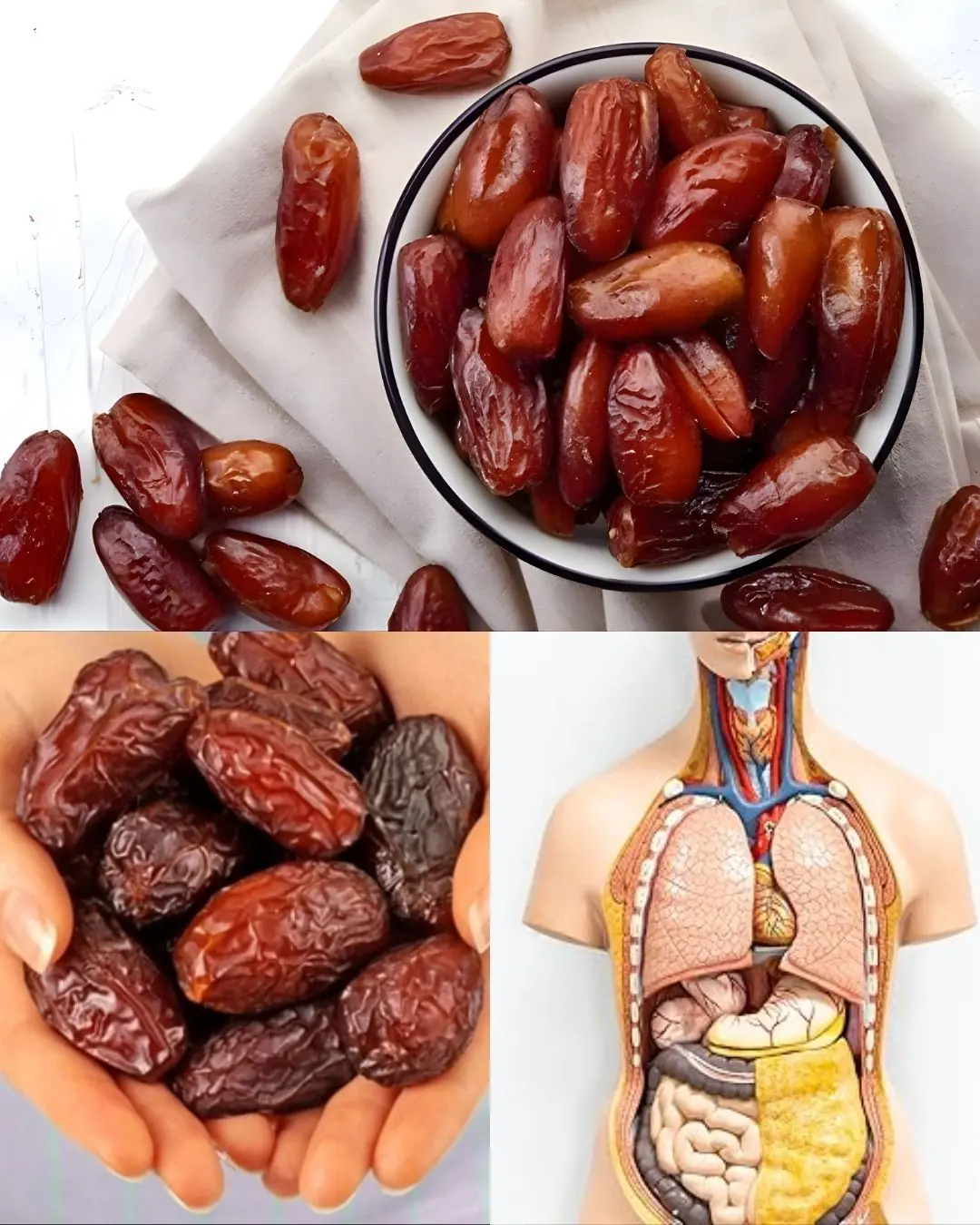
The HEALTHIEST FRUIT on Earth: what happens to your body if you eat just 3 a day

Garlic & Cloves: The Timeless Duo for Stronger Veins and Better Circulation

Taro: The Tropical Treasure Your Kitchen — and Your Body — Will Love
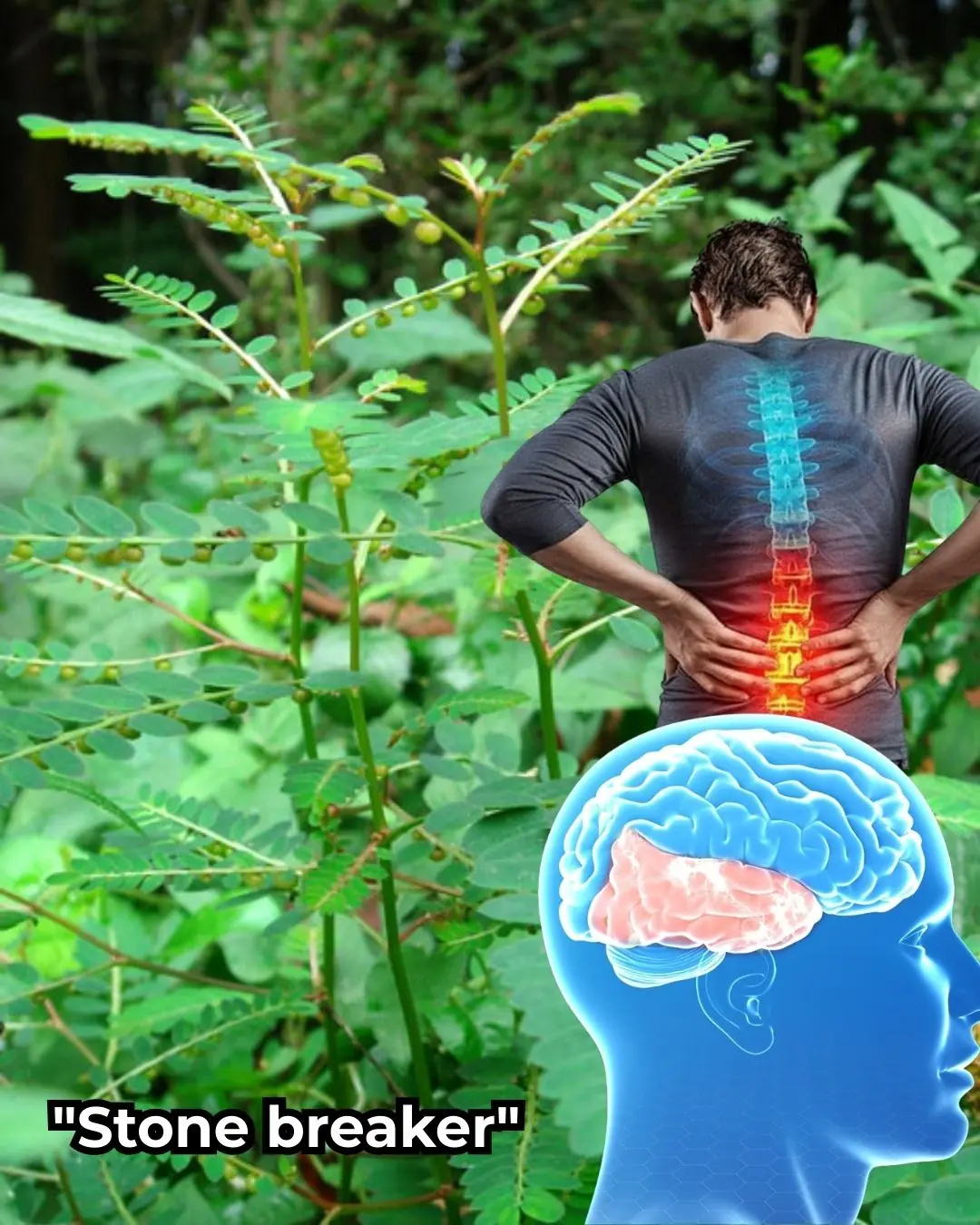
Benefits and How to Use This Powerful Herb
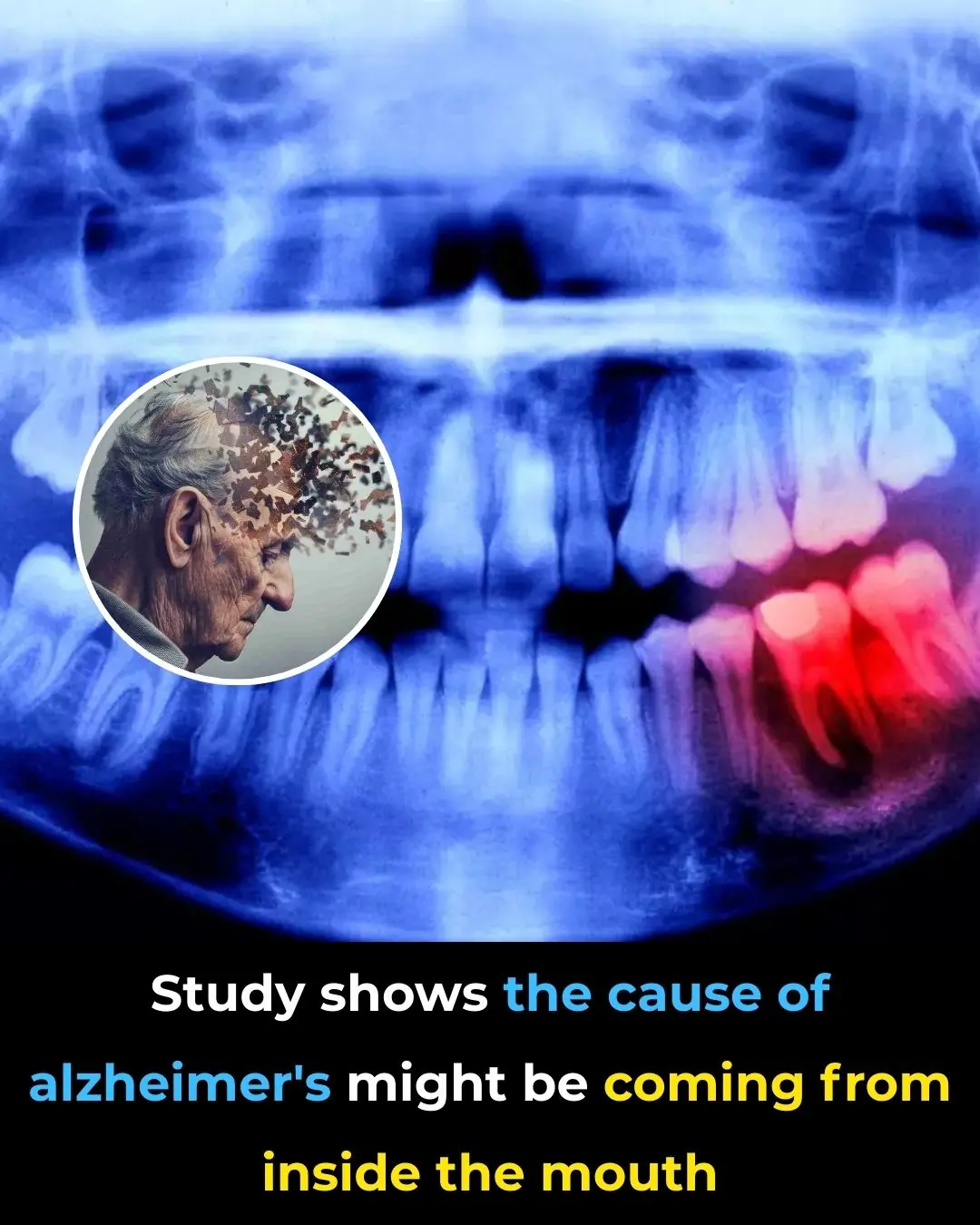
The cause of Alzheimer’s may lie within your mouth

5 Most Common Deathbed Regrets, According to Palliative Care Nurse
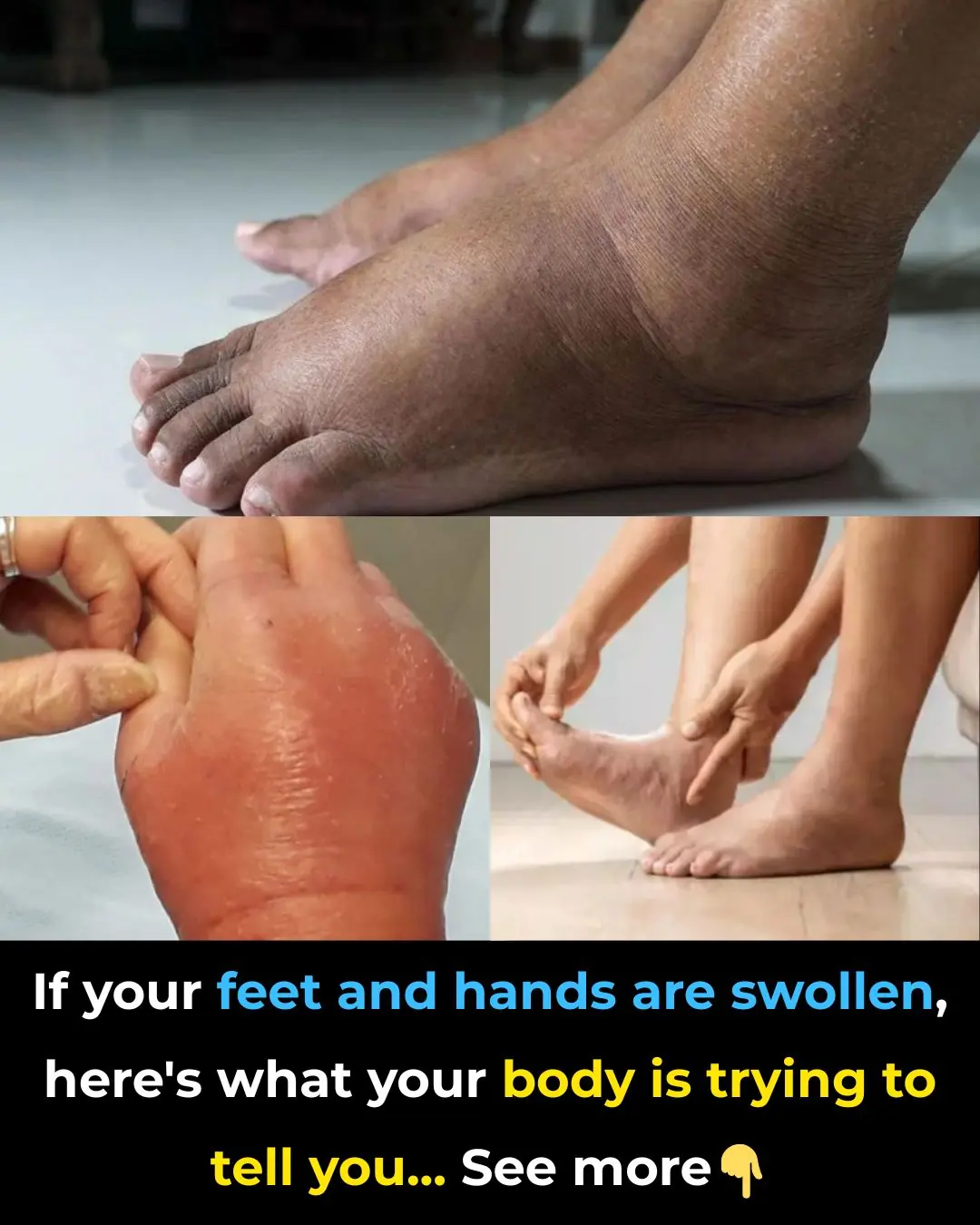
Foods that can ease swelling in hands and feet

Canadian researchers discover new evidence that vitamin D shuts down cancer cells

The Benefits of Holy Basil (Tulsi) for Better Oral Health
News Post
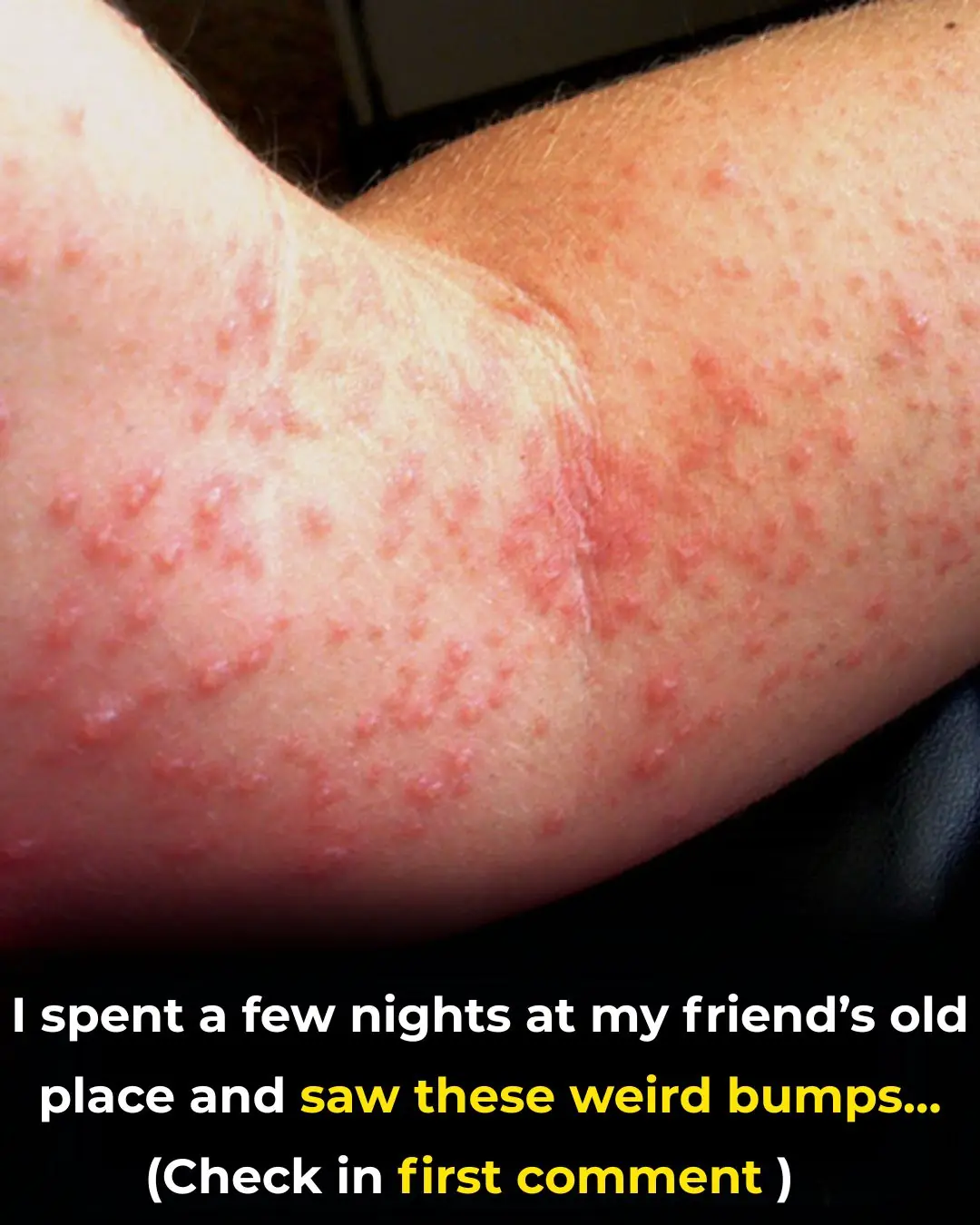
I spent a couple of nights at my friend’s previous apartment and saw these unusual bumps
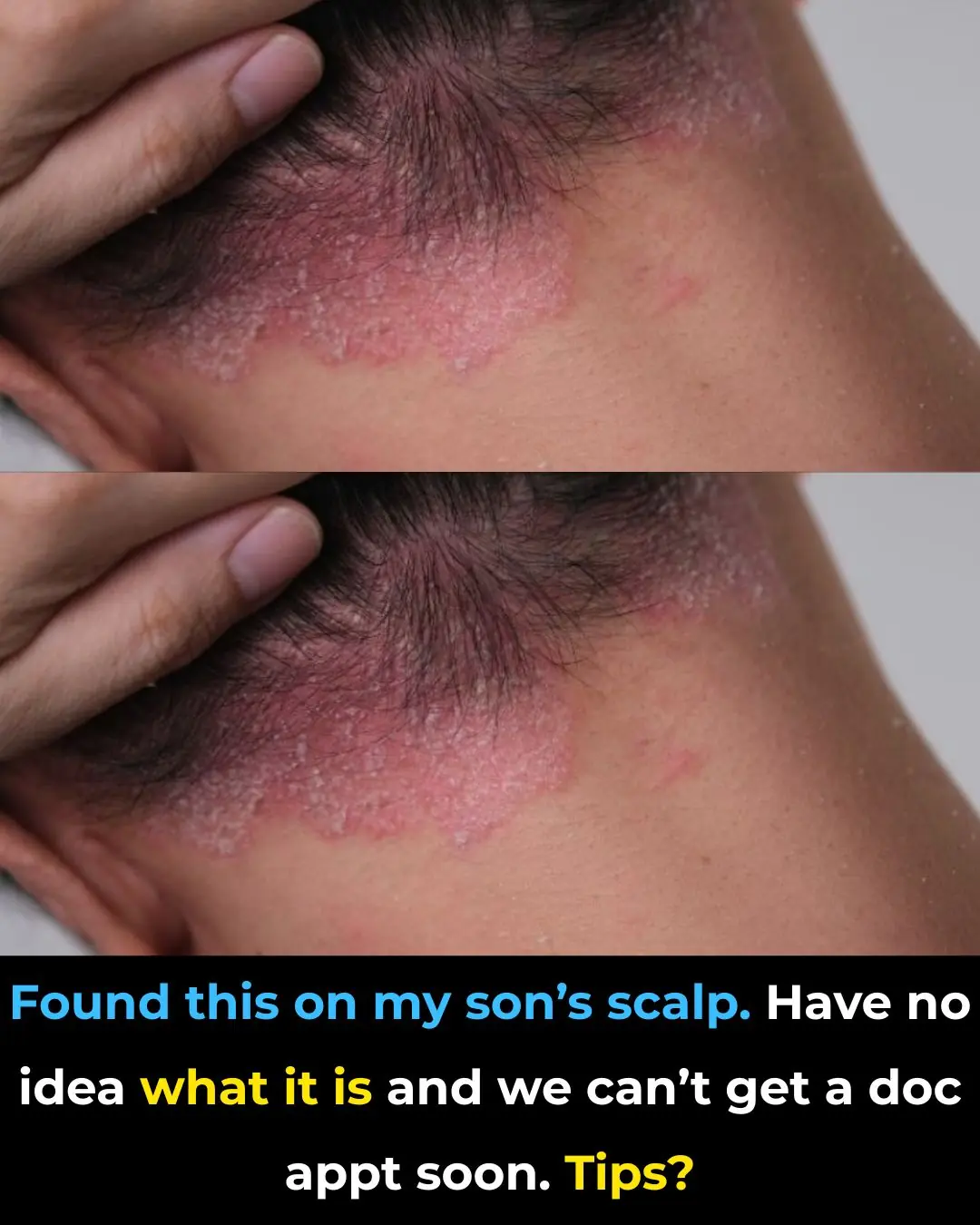
Found this on my son’s scalp. Have no idea what it is and we can’t get a doc appt soon. Tips?

Top 10 signs of a gallbladder attack

How to treat nerve pain in the foot, toes & legs

Why your legs cramp at night and how to stop it from happening

1 teaspoon a day melts away fatty liver naturally

Are You the One?

The Secret She Was Never Meant to See
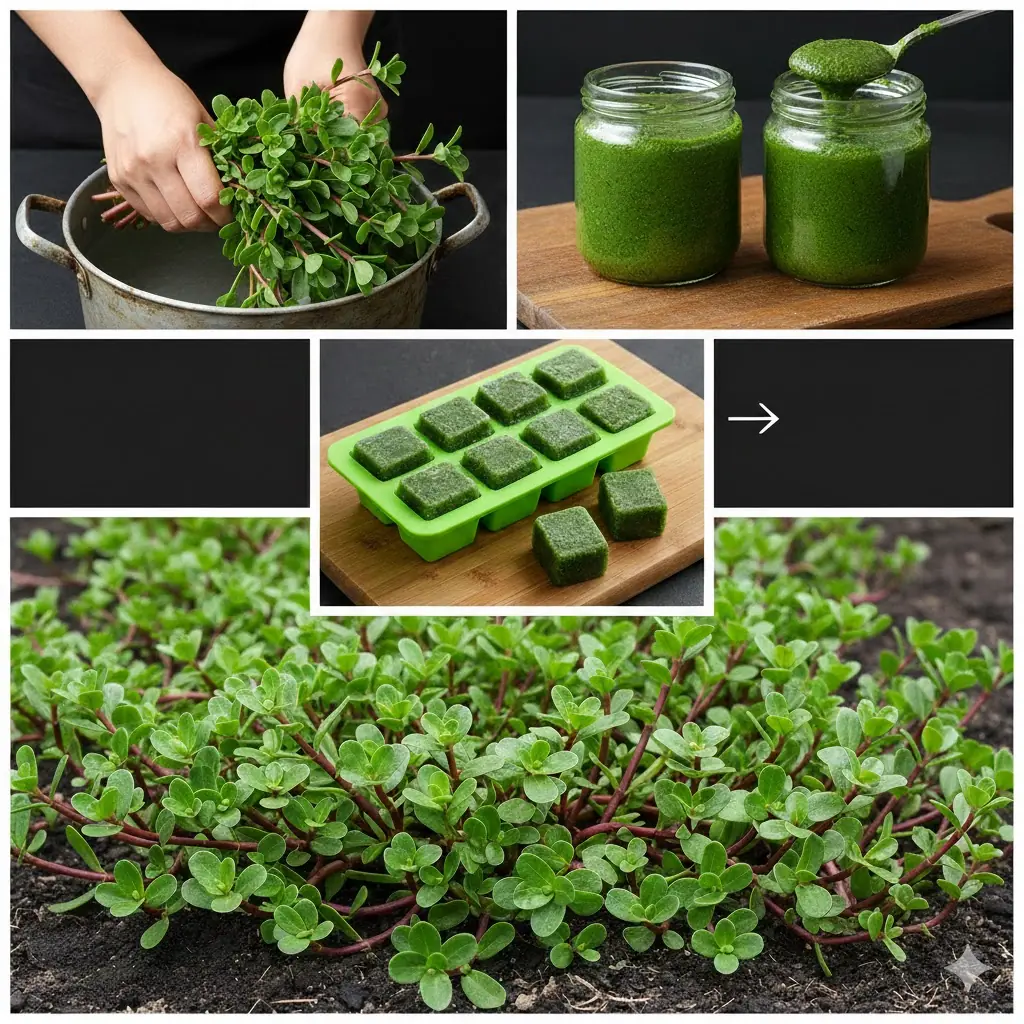

Purslane: The Superfood That Tastes Better Than Meat – 7 Reasons to Grow It in Your Garden
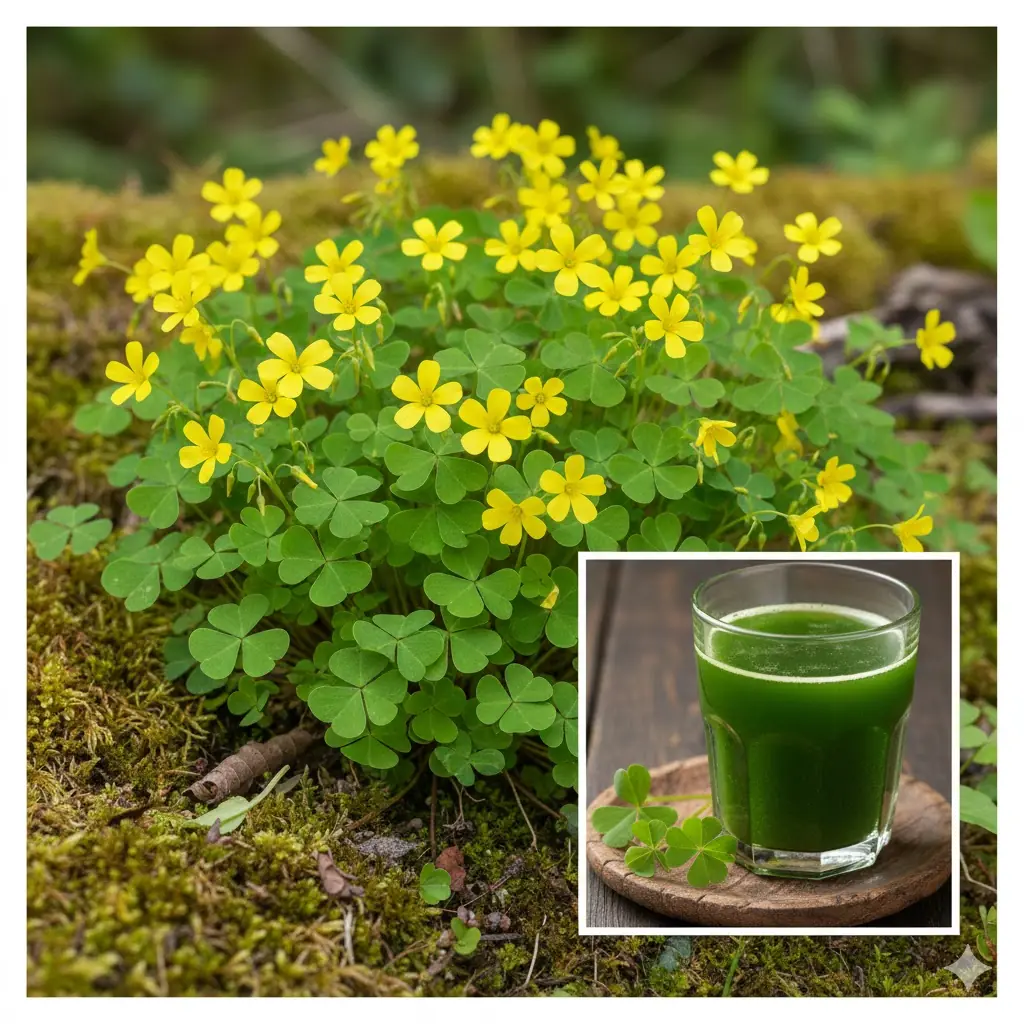

Wood Sorrel Benefits and Uses
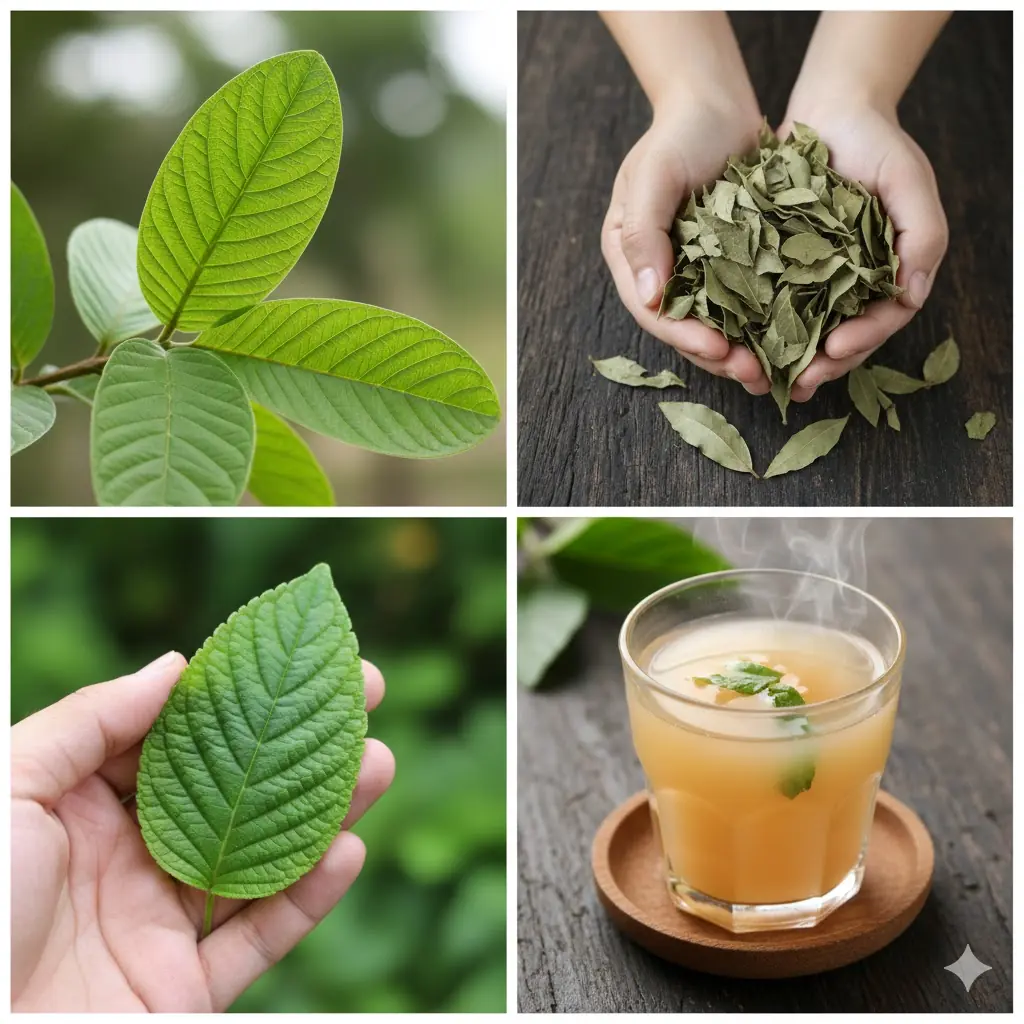

Guava, Oregano, and Bay Leaves: The Healing Leaves used in traditional medicine for centuries

🌿 Yarrow: A Timeless Herbal Ally with Amazing Health Benefits – Unlock Nature’s Ancient Healing Power!

✅ Thyme: The Tiny Herb with Big Healing Power in 2025 🌿✨
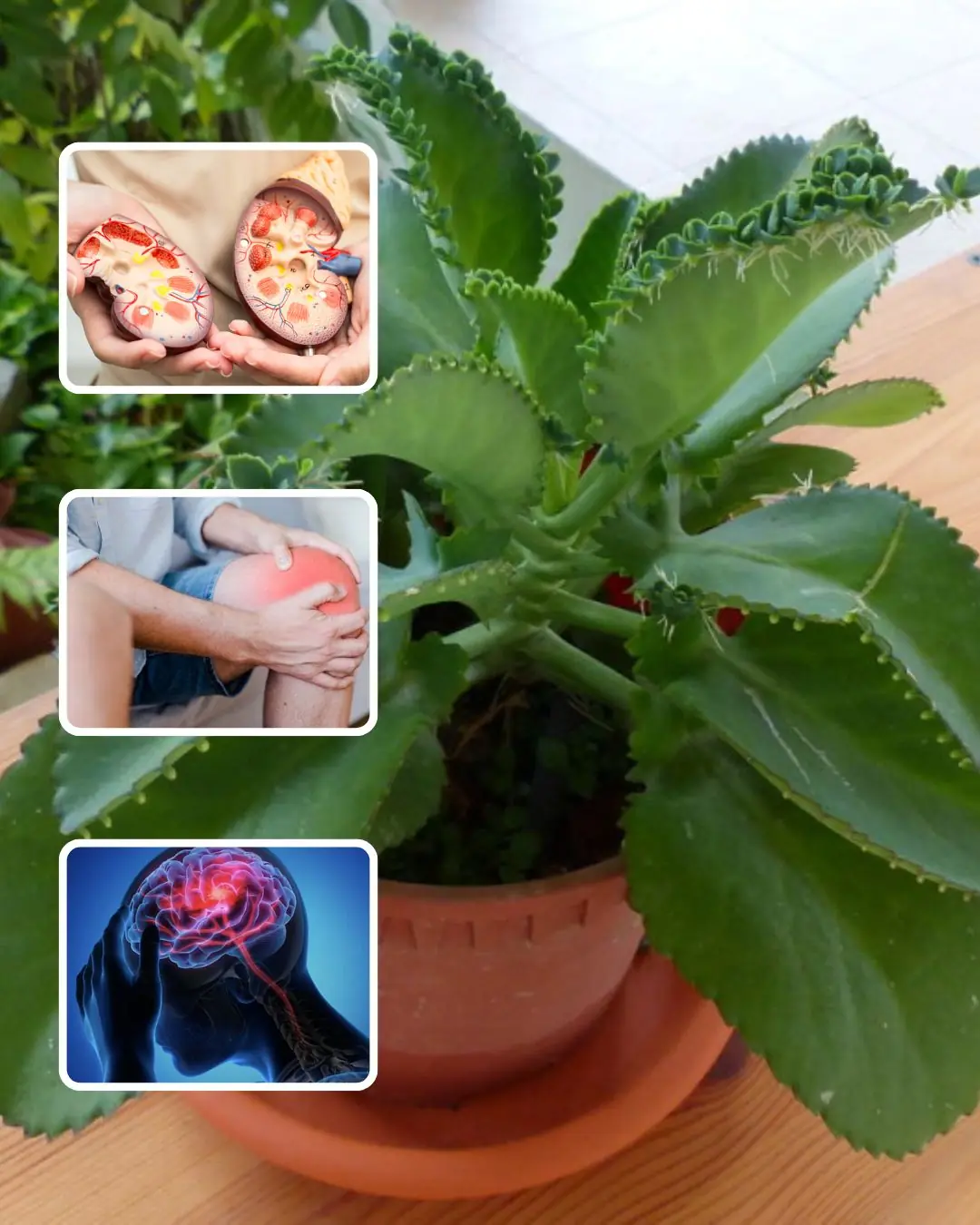

🌿 Bryophyllum Calycinum (Kalanchoe Pinnata): The "Miracle Leaf" with Powerful Healing Benefits

Love vs. Blood

What Causes Pain Under Your Left Rib Cage?

What Causes Your Toenail To Turn Black?

Doctor Warns Popular Medication May Lead to Organ Failure
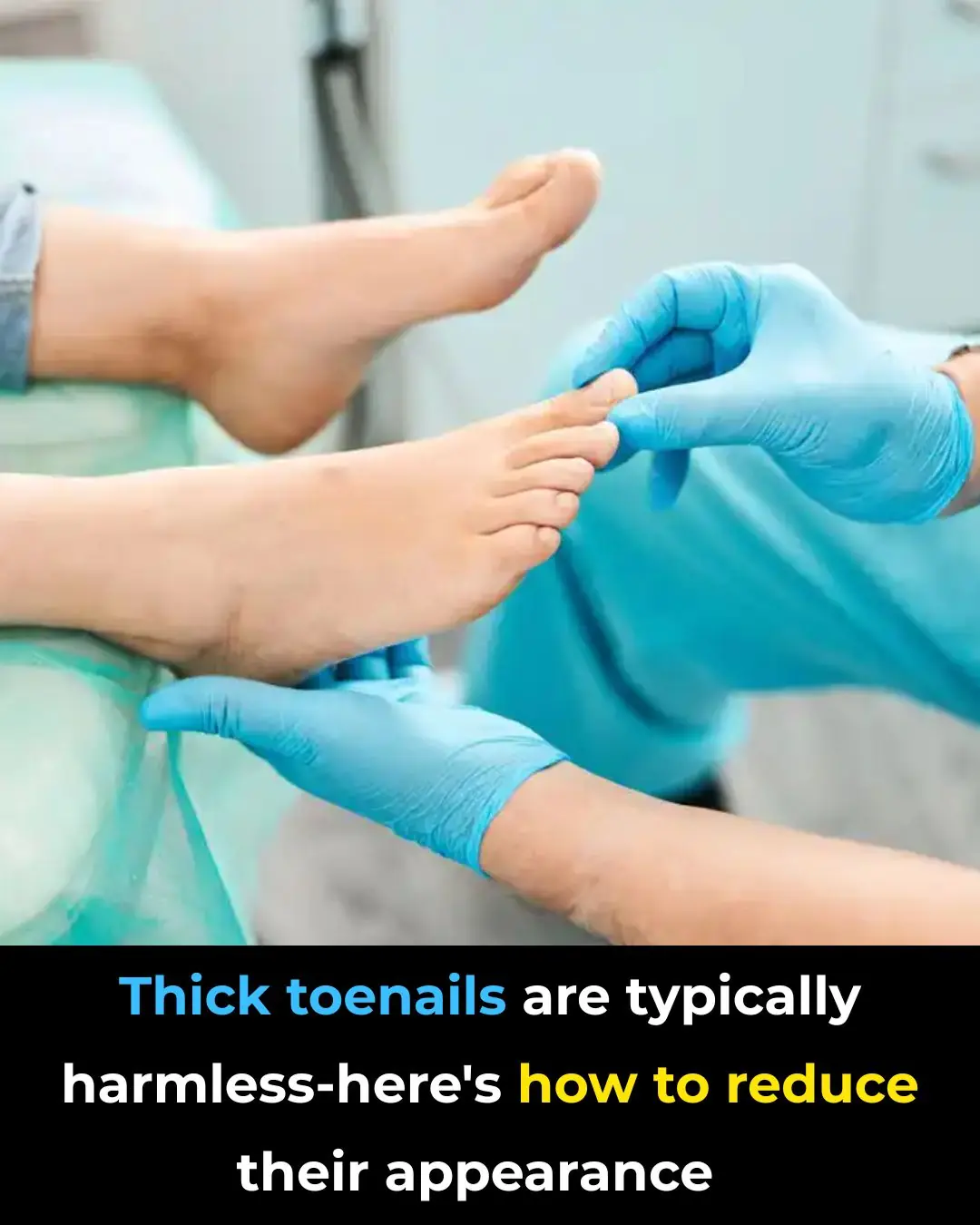
Why Do You Get Thick Toenails?
