
Five US States Brace for Deadly Airborne Fungus That Destroys Human Tissue

America’s Invisible Killer: The Fungal Threat Growing Across the Nation
Something invisible is drifting through the warm air over America right now. You can’t see it, smell it, or feel it—but with every breath, it can slip into your lungs. For hundreds of thousands of people, these microscopic invaders could spell disaster. Five U.S. states have become ground zero for a threat that sounds like it belongs in a Hollywood horror script—but scientists say this is no work of fiction.
While TV audiences might think of zombie fungi from HBO’s The Last of Us, reality has delivered something potentially more dangerous. Instead of Cordyceps turning people into mushroom-covered monsters, we face Aspergillus fumigatus—a very real fungus that doesn’t need to control your mind to kill you. It attacks silently, consuming tissue from the inside out.
When Fiction Meets Reality
In the The Last of Us video game and TV series, the Cordyceps fungus triggers a devastating pandemic, transforming humans into terrifying hybrids. Scientists reassure us that Cordyceps can’t yet infect humans in that way. But they point to a far more immediate danger—Aspergillus fumigatus—already floating in our air, already infecting people, and already claiming lives.
Unlike its fictional counterpart, this fungus doesn’t create dramatic outward signs. Its spores—so small that millions could sit on a single pinhead—enter the lungs undetected. Once inside, they can grow quietly, causing infections that are easily mistaken for common respiratory illnesses.
Meet the Real Enemy
We all inhale Aspergillus fumigatus spores daily, especially in areas where the fungus thrives: soil, compost heaps, agricultural fields, and even air conditioning systems. Most healthy people’s immune systems stop the invader before it causes harm. But for those with weakened immunity—cancer patients, transplant recipients, people with HIV—the fungus can establish itself and launch a full-scale attack.
Its arsenal is deadly. The fungus produces aflatoxin, one of the most potent naturally occurring carcinogens known to science. This toxin doesn’t just target a single organ—it can damage the lungs, liver, spleen, stomach, colon, and kidneys, often simultaneously. Once it has a foothold, the fungus can also travel through the bloodstream, infecting the brain and heart.
The danger is compounded by its resilience: even temperatures above 120°F won’t reliably kill it. This makes traditional sterilization ineffective, especially in hot, humid regions where the fungus thrives year-round.
Five States Under Siege

Florida, Texas, Louisiana, California, and Georgia are currently the highest-risk states. Their hot, damp climates provide the perfect breeding ground for Aspergillus fumigatus. Agricultural activities—plowing fields, harvesting crops, and clearing land—send plumes of spores into the air.
In big cities like New York, Houston, and Los Angeles, the risk is amplified by aging infrastructure. Old ventilation systems can become spore reservoirs, slowly circulating contamination among millions of residents.
Farming communities are especially vulnerable. Without adequate protective gear, workers are repeatedly exposed. Over time, this repeated inhalation can lead to chronic infections that permanently scar the lungs.
How the Infection Turns Deadly
The disease it causes—aspergillosis—often begins with vague symptoms: coughing, fever, fatigue. Patients and even doctors may initially mistake it for bronchitis or pneumonia. By the time the true cause is identified, the fungus may already have spread beyond the lungs.
The most lethal form, invasive aspergillosis, has survival rates as low as 25% for certain patient groups, such as those recovering from stem cell transplants. Once the fungus reaches the bloodstream, it can rapidly colonize vital organs.
The Numbers Behind the Crisis

-
400,000 new cases of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis occur globally each year.
-
In U.S. hospitals, aspergillosis admissions rose 3% annually between 2000 and 2013.
-
By 2014, nearly 15,000 hospital stays cost an estimated $1.2 billion—and the number is still climbing.
-
ICU autopsies rank aspergillosis among the top four most deadly infections.
Drug resistance is making matters worse. Overuse of agricultural antifungal sprays—especially azoles—has created strains that are immune to standard treatments. These resistant strains are now showing up in both farm soil and human patients.
Climate Change: The Silent Accelerator
As global temperatures rise, Aspergillus fumigatus is expanding into new territory. Warmer, wetter conditions help it survive in places it previously could not. Research suggests its range could grow by more than 75% by 2100 if fossil fuel emissions continue unchecked.
Southern states already show what’s coming: relentless humidity, violent storms that spread spores far and wide, and a year-round breeding season for the fungus. These same conditions are predicted to appear in more northern regions over the coming decades.
Why the Threat Was Overlooked

Unlike many infectious diseases, aspergillosis is not “reportable” in the U.S. That means cases aren’t systematically tracked. Without official data, the true scale remains hidden. Many infections go undiagnosed or are misdiagnosed, and healthcare systems lack the resources to respond to a sudden surge.
Dr. Vyas of Columbia University warns:
“This isn’t science fiction. These infections are real, and we’re not ready.”
Fighting Back

Hospitals are stepping up defenses—upgrading air filtration, increasing mold inspections, and tightening antifungal treatment protocols. The World Health Organization has listed Aspergillus fumigatus as a “critical priority” due to its rising drug resistance. Experts are pushing for:
-
Faster, more accurate diagnostic tools
-
Development of new antifungal drugs
-
Inclusion of children in treatment trials, as pediatric cases remain under-researched
How You Can Protect Yourself
If you are at high risk, you can take specific steps:
-
Avoid gardening, soil handling, or dusty environments.
-
Wear an N95 mask if working in construction zones or on farms.
-
Use HEPA filters at home and change HVAC filters regularly.
-
Stay alert for persistent respiratory symptoms and seek testing early.
The spores may be invisible, but the threat is real—and growing. As climate shifts and drug resistance builds, this airborne killer could become one of the defining public health challenges of the century. Awareness, early detection, and preventive action are our best defenses against the silent danger drifting through American skies.
News in the same category


This is why you should keep the bathroom light on when sleeping in a hotel
Leaving your hotel bathroom light on at night might seem unnecessary, but it could be a small habit that makes a big difference for your comfort and safety. From preventing nighttime accidents to deterring intruders, experts say this simple tip can protec
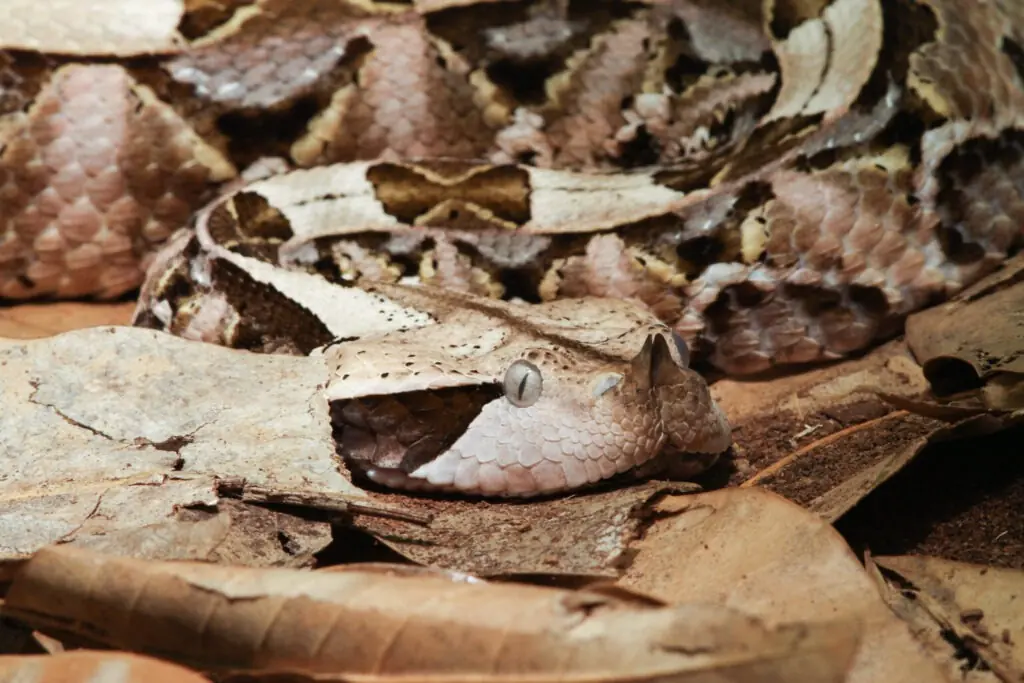

The Mystical Gaboon Viper, Master Of Disguise And Deadly Accuracy

If You See Square Waves Forming In The Ocean, Get Out Of The Water Immediately

A Greenland Shark Born in 1620 is Still Alive Four Centuries Later

15 Things You Should Never Plug Into A Power Strip

China is Developing a Levitating Train That Could Travel From New York to Chicago in Just Two Hours

The world’s oldest woman, who lived to 117, ate the same meal every day throughout her life
Emma Martina Luigia Morano, the world’s oldest woman at the time of her passing, credited her extraordinary 117 years of life to a mix of genetics, resilience, and one very peculiar daily diet. Her remarkable story spans two World Wars, personal tragedy
TikTok’s ‘Vabbing’ Trend Sparks Debate: Does It Attract Partners?

In Sweden, You’re Not Allowed to Leave Your Dog Alone for More Than Six Hours, Here’s the Reason

A A tendon raises up when you touch your pinky to your thumbraises up when you touch your pinky to your thumb

The Hidden Meaning Behind Leg-crossing — It’s More Than Just Comfort

The Sh0cking Truth Behind Your Ankle Bracelet And What It Reveals About You — It’s More Than Just Jewelry
For many, an ankle bracelet is just a delicate, eye-catching piece of jewelry. But behind its shimmer lies a rich tapestry of history, tradition, and hidden symbolism that stretches across cultures and centuries.

Lost Underwater City Near Noah’s Ark Site Could Rewrite Biblical History Forever
The discovery of an underwater city found by the 'resting place of Noah's Ark' is a revelation that may lead to the Bible story being re-written.

11 Heartbreaking Yet Essential Signs Your Dog May Be Nearing the End — And How to Give Them Comfort Until the Last Moment
When you notice these signs, your role transforms from caregiver to emotional anchor. This is the time to be fully present — offering touch, reassurance, and unconditional love.
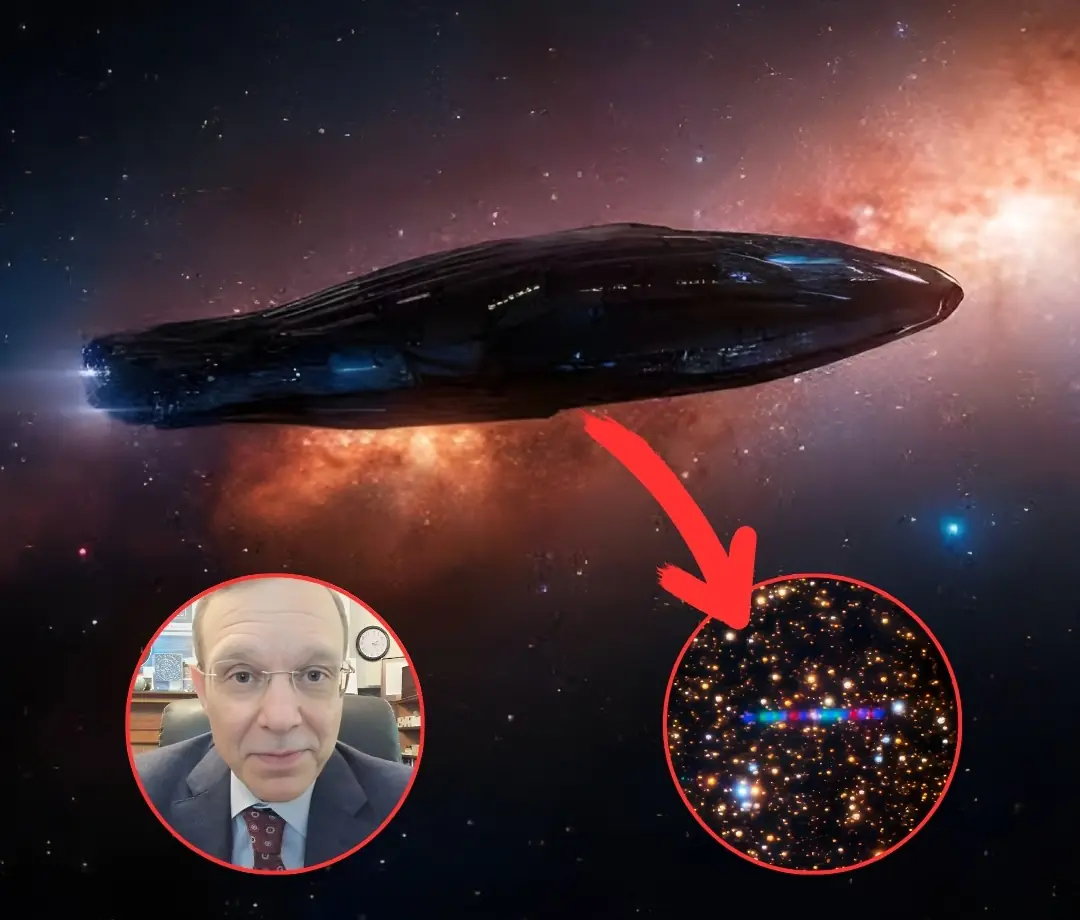

Harvard Professor Warns: Object Heading Toward Earth Could Be Something Beyond Nature
A massive interstellar object, 3I/ATLAS, is racing toward Earth, and one Harvard astrophysicist believes it may not be natural. With missing comet features and a suspicious trajectory, experts are now debating whether it could be an engineered spacecraft.

Mass Panic as ‘New Baba Vanga’ Predicts Majo Disasters Striking in Just One Month
A chilling prophecy from Japan’s so-called “New Baba Vanga” has triggered widespread fear and mass trip cancellations. Tourists are now abandoning travel plans as the forecast warns of a catastrophic natural disaster hitting in early July 2025.

What Is SPAM Meat? History, Origin, Ingredients, and How It Became a Global Food Icon
SPAM — the world-famous canned meat — has been sold over 8 billion times and is loved in more than 40 countries. From its humble beginnings during the Great Depression to its role in World War II, here’s the complete story of SPAM’s origin, ingred

Scientists Reverse Aging of a 53-Year-Old’s Skin Cells to That of a 23

Mom Stepped on an Ant Hill and Died Instantly
News Post

Poor Postcancer Surgery Outcomes Tied to 3 Factors

Teamwork Boosts Primary Care Doc Job Satisfaction, Cuts Stress
HIV Was Successfully Eliminated from Human Immune Cells Using CRISPR Gene Editing in Landmark Study
Scientists Discover An “Off Switch” For Cholesterol—And It Could Save Millions Of Lives

How to Treat Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Naturally According to Science
4 Common Causes of Body Pain on the Right Side

The Truth About Eating the Black Vein in Shrimp Tails

12 Subtle Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms That Most People Ignore

What Your Heart Experiences When You Drink Energy Drinks

How to Eat Right for Your Blood Type

Eyes Full of Hope, Heart Full of Trust.
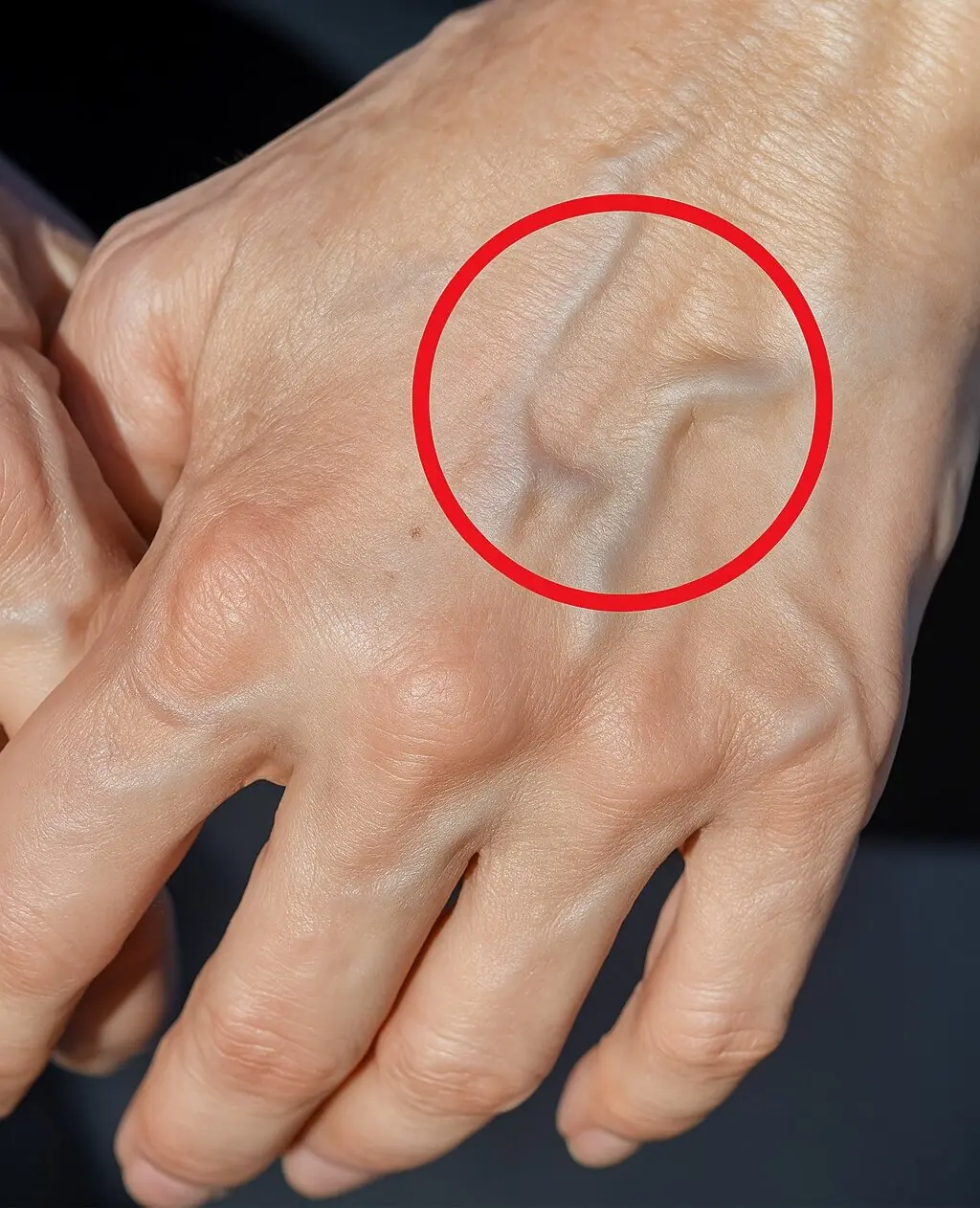
When to Worry About Veins That Appear Out of Nowhere
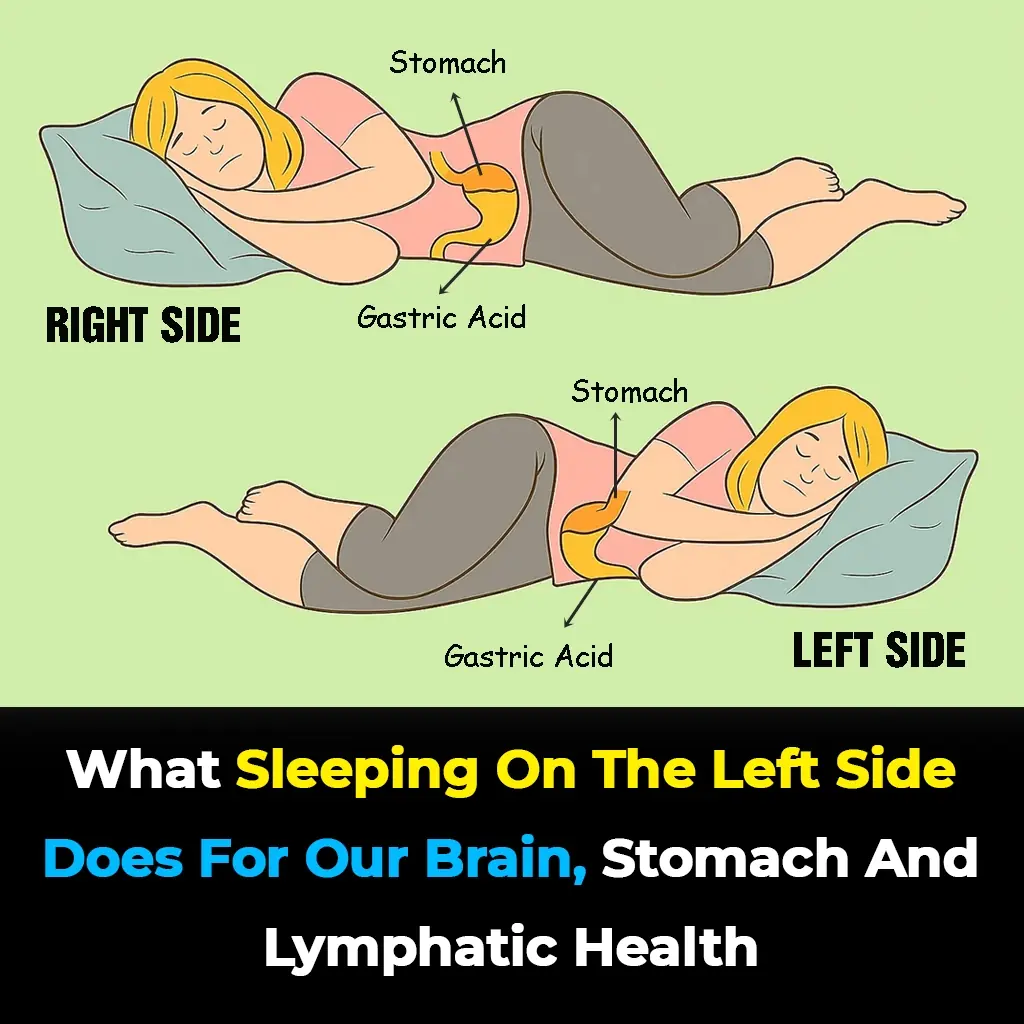
This is what sleeping on the left side does for our brain, stomach & glymphatic health
Sleeping position might be the last thing you think about before bed, but it can have a powerful impact on your health. Experts say that lying on your left side could improve digestion, support brain detox, ease back pain, and even enhance circulation.

I Haven’t Seen My Daughter in 13 Years — Then a Letter Arrived from a Grandson I Never Knew

This is why you should keep the bathroom light on when sleeping in a hotel
Leaving your hotel bathroom light on at night might seem unnecessary, but it could be a small habit that makes a big difference for your comfort and safety. From preventing nighttime accidents to deterring intruders, experts say this simple tip can protec

Wife Left Husband to Raise Their Baby Alone — 20 Years Later, She Reached Out to Their Daughter

My Stepmom Crashed My Birthday and Made the Most Ridiculous Demand

The Mystical Gaboon Viper, Master Of Disguise And Deadly Accuracy
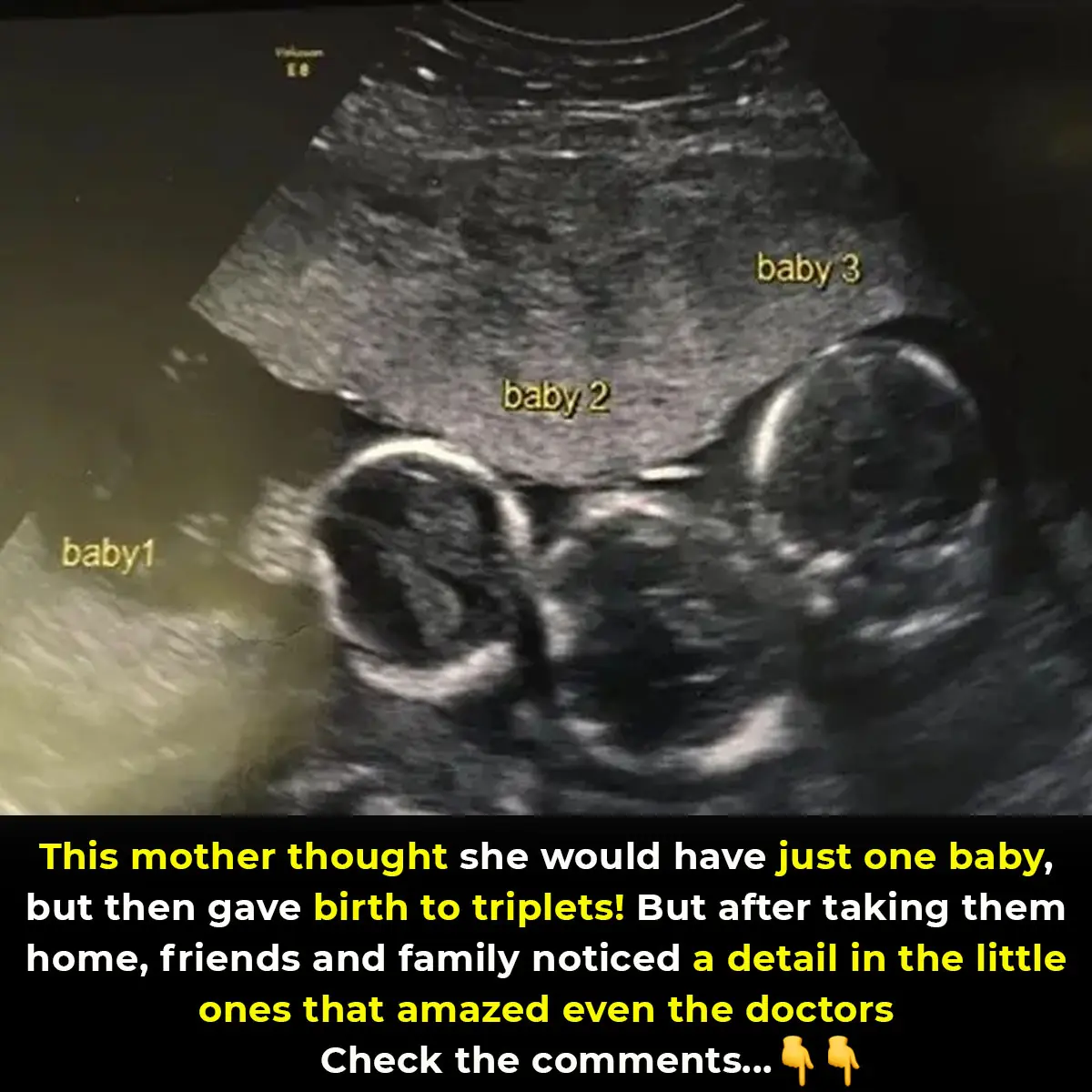
Mother Rushes To Emergency Room To Deliver Triplets: Then Nurses Look Closer At Their Faces And Freeze
