
Hyperactive Brain Cells May Trigger Schizophrenia Symptoms—and Point to a Critical Window for Early Intervention
Overactive Brain Cells May Hold a Key to Understanding Schizophrenia
Scientists have identified a small but powerful group of brain cells that may play a crucial role in the development of schizophrenia. In a recent study, researchers found that a specific type of neuron—known as GABAergic projection neurons—became unusually overactive in cases linked to the disorder. Experiments conducted in laboratory mice carrying a genetic mutation associated with schizophrenia revealed that when these neurons went into overdrive, the animals began to show clear signs of disrupted sleep patterns and cognitive difficulties, both of which are hallmark symptoms seen in people with the condition.
GABAergic neurons normally act as the brain’s braking system. By releasing the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), they help maintain a healthy balance between excitation and inhibition in neural circuits. This balance is essential for stable thinking, emotional regulation, and normal sleep. However, in the study, the affected GABAergic projection neurons did the opposite of what might be expected: instead of calming brain activity, they became excessively active, throwing key neural networks out of balance. When researchers experimentally reduced this hyperactivity, the results were striking—sleep patterns normalized, and the mice’s behavioral and cognitive performance improved dramatically. This finding highlights just how tightly mental health depends on finely tuned brain cell activity.
One of the most surprising aspects of the discovery was timing. Although the genetic mutation linked to schizophrenia was present from early life, the neurons did not become overactive right away. The abnormal activity only emerged later, as the brain matured. This suggests that the developing brain can initially compensate for genetic risk, maintaining normal function for years. At a certain point, however, this compensatory ability appears to break down, triggering the onset of symptoms. Researchers believe this delayed shift may correspond to adolescence or early adulthood in humans—the same life stage when schizophrenia most often first appears, according to the U.S. National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH).
This idea of a “critical window” is especially important. If scientists can identify when and why the brain loses its ability to maintain balance, it could open the door to early interventions that prevent or reduce the severity of symptoms. Similar concepts have been discussed in leading neuroscience journals such as Nature Neuroscience and Science, which emphasize that schizophrenia is not a sudden illness but a progressive brain disorder with roots in early development (Nature Neuroscience; Science).
The findings also give researchers a much more precise biological target. Rather than broadly altering brain chemistry—as many current antipsychotic medications do—future treatments could aim to specifically regulate the activity of these GABAergic projection neurons. Such targeted approaches may reduce side effects and improve outcomes, especially if applied before the disorder fully manifests. This strategy aligns with a broader shift in psychiatry toward early detection and prevention, supported by organizations like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the World Health Organization.
Overall, this discovery deepens our understanding of how schizophrenia develops and why its symptoms often appear later in life, despite early genetic risk. By showing that a small population of misfiring neurons can disrupt sleep, thinking, and behavior—and that restoring balance can reverse these effects—the study offers hope for more effective and timely interventions. It underscores a powerful message from modern neuroscience: maintaining balance in brain activity is essential for mental health, and even subtle disruptions can have profound consequences if left unchecked.
News in the same category


Why Cats Leave Home and Don’t Return

7 Things A Man Only Does In Bed When He Really Loves You

Increasingly Hot Solar Flares Pose Growing Threat to Space Weather and Earth's Technology

Breakthrough RNA-Based Blood Test Shows 95% Accuracy in Early-Stage Colon Cancer Detection

Revolutionary Chip Prototype Achieves 100 Gbps Wireless Speeds, Paving the Way for 6G Networks
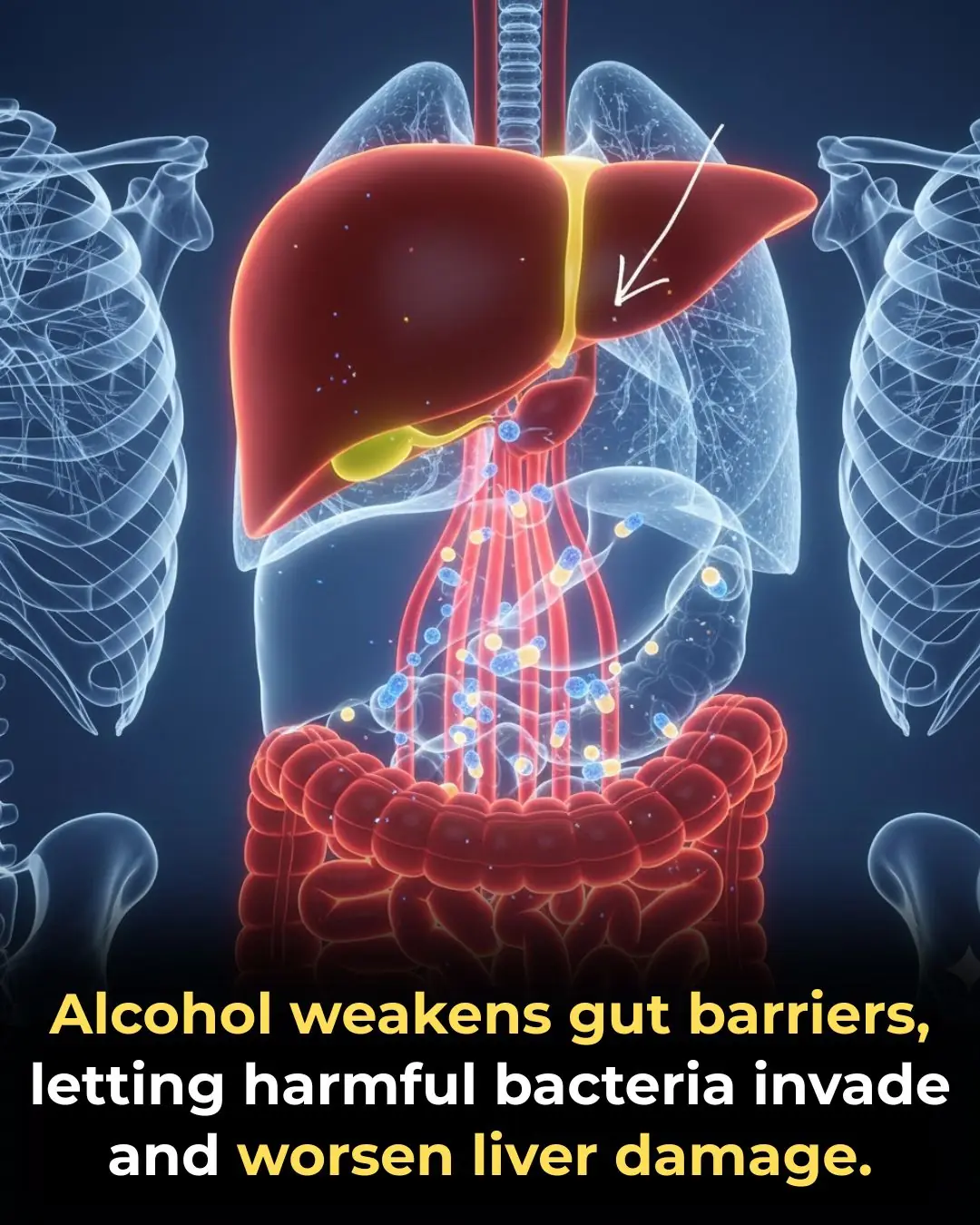
The Gut-Liver Connection: How Alcohol Impairs Immune Defenses and Exacerbates Liver Damage

Scientists Have Finally Figured Out What Causes ‘Hoarding’

Lab Study Shows Dandelion Root Kills Over 90% of Colon Cancer Cells In Just Two Days

Your Cat Might Love You More Than You Think—Here’s How to Tell

Woman Declared Dead for 8 Minutes Says She Discovered Death Is An Illusion

Reviving Italy’s Old Barns: Creative Studios Where Pottery and Bread Bring Generations Together

Sweden's Kindness Drawers: A Quiet Act of Sharing Fresh Bread with Those in Need

Urban Gardens in Italy: Transforming into Nighttime Sanctuaries for the Homeless

Modular Sleep Pods in Germany: A Subtle Solution for Refuge and Dignity in Public Spaces
A Month in Space Can Rapidly Age Human Stem Cells, Scientists Find

Even a month in space can leave your cells looking older.

Solar Flares Are Growing Hotter and More Powerful, Scientists Warn

The Brain’s Backup Plan: Neuroplasticity and Rehabilitation
News Post

Why Cats Leave Home and Don’t Return
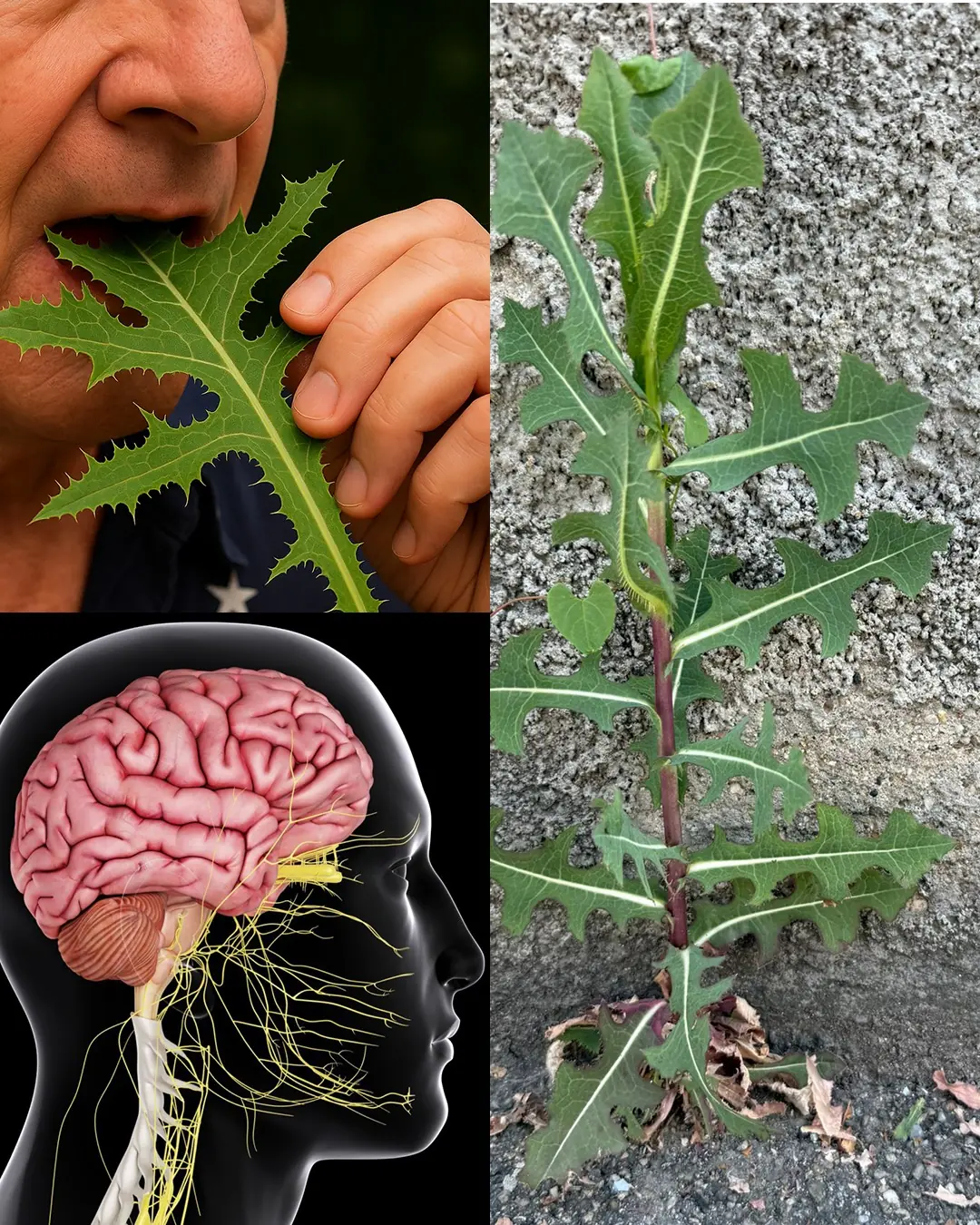

The Powerful Benefits of Eating Lactuca serriola Leaves (Prickly Lettuce)

7 Things A Man Only Does In Bed When He Really Loves You
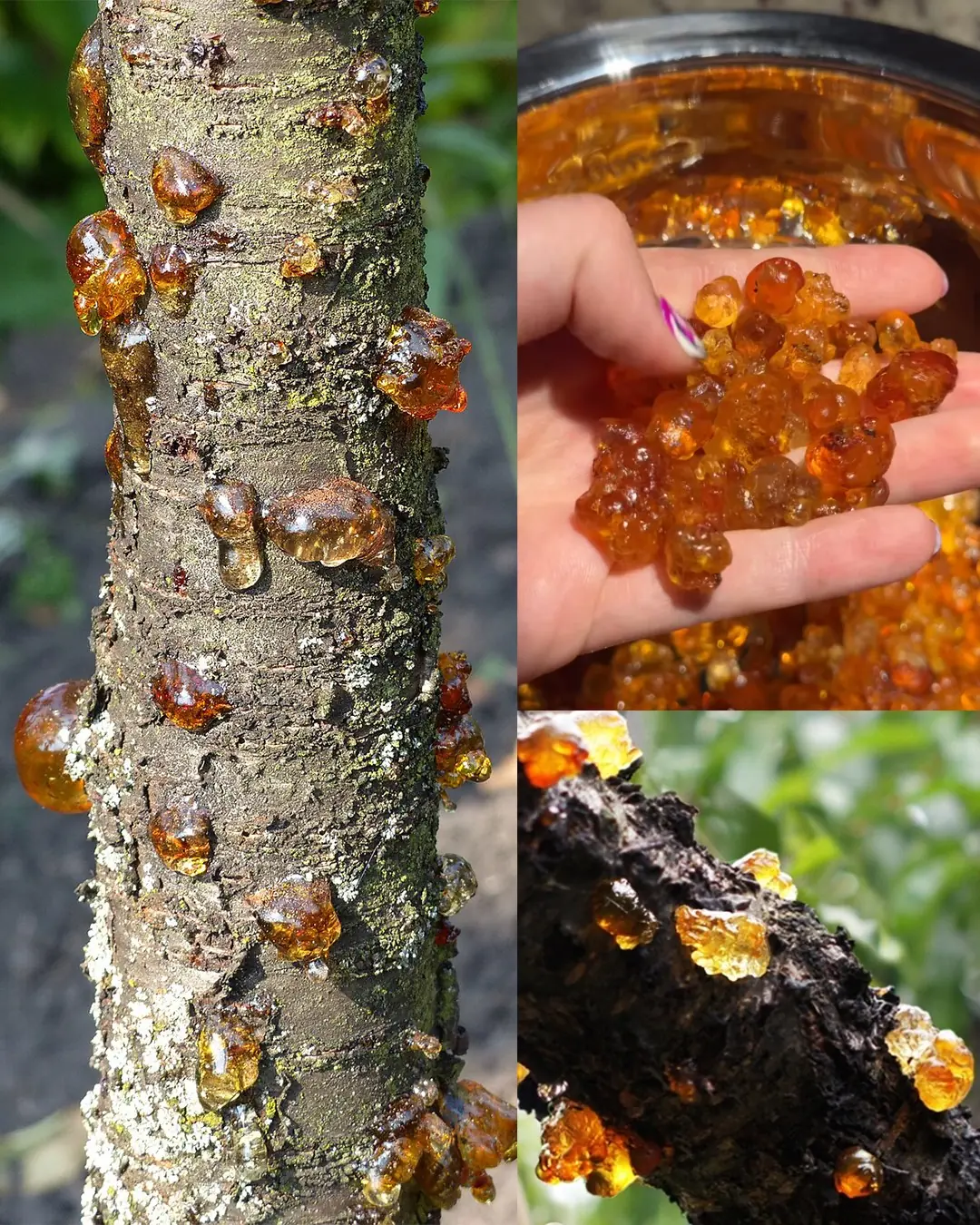

The Power of Peach Tree Resin (Tao Jiao): 15 Surprising Benefits and How to Use It at Home

4 DIY Herbal Clove Skincare Toners

Tomato Benefits for Skin – Rub Tomato Slice on Face

Treat Dark Circles, Sunken Eyes & Puffy Eyes with Home Remedies and Eye Creams

4 DIY Herbal Clove Skincare Toners

Homemade Herbal Hair Oil – Adivasi Hair Oil

Potato Toner for Face – Dark Spots, Clear Skin & Pigmentation

Why Do Women Cross Their Legs When Sitting

Clench Your Fist And Count The Palm Lines

Pokeweed (Phytolacca americana): Why You Should Keep Your Distance from This Toxic Plant

Increasingly Hot Solar Flares Pose Growing Threat to Space Weather and Earth's Technology

How to Preserve Meat and Rice in Jars: A Hearty Homemade Meal That Lasts for Months

Breakthrough RNA-Based Blood Test Shows 95% Accuracy in Early-Stage Colon Cancer Detection

Revolutionary Chip Prototype Achieves 100 Gbps Wireless Speeds, Paving the Way for 6G Networks

How to Cook Broccoli the Right Way: Simple Methods for Perfect Flavor, Color, and Nutrition

The Gut-Liver Connection: How Alcohol Impairs Immune Defenses and Exacerbates Liver Damage
