What you should know when your urine is foamy.
Noticing foam or bubbles in your urine can be unsettling.
Many people experience it at least once and immediately wonder whether it’s a harmless occurrence or a warning sign of something serious.
The truth is that foamy urine can range from completely normal to a possible indicator of an underlying health condition.
Understanding why it happens, what it smells like, and
when it matters can help you respond calmly and appropriately.What Does Foamy Urine Mean?
Foamy urine refers to urine that appears bubbly, frothy, or forms a layer of foam on the surface after urination.
Unlike a few bubbles that disappear quickly, foamy urine tends to linger for a longer time, sometimes resembling soap suds.
While this can look alarming, it is not always dangerous.
In many cases, foamy urine is temporary and harmless.
However, if it happens frequently or is accompanied by other symptoms, it may point to a medical issue that deserves attention.

Common Harmless Reasons for Foamy Urine
-
Strong or Fast Urine Stream
One of the most common reasons for foam is simply the force of urination. When urine hits the toilet water quickly, it can trap air and create bubbles—similar to how water foams when poured rapidly into a bowl. This is especially common when your bladder is very full. -
Dehydration
When your body lacks enough fluids, urine becomes more concentrated. Concentrated urine contains higher levels of waste products, making it thicker and more likely to foam. In this case, increasing your water intake often resolves the issue quickly. -
Residual Cleaning Agents
Sometimes, foam isn’t caused by your urine at all. Leftover soap, detergent, or cleaning chemicals in the toilet bowl can react with urine and create bubbles. This is often overlooked but very common.
When Foamy Urine Can Signal a Health Problem
If foamy urine occurs regularly and is not explained by dehydration or urine flow, it may be related to protein in the urine
, a condition called proteinuria.Protein in Urine (Proteinuria)
Healthy kidneys filter waste from the blood while keeping important substances—like protein—inside the body.
When the kidneys are damaged or stressed, protein can leak into the urine.
Protein lowers surface tension, which causes urine to foam more easily.
Proteinuria can be associated with:
-
Kidney disease
-
Diabetes
-
High blood pressure
-
Autoimmune disorders
-
Infections affecting the kidneys
Occasional protein in urine can occur after intense exercise, stress, fever, or pregnancy.
Persistent proteinuria, however, requires medical evaluation.
What About Strong or Foul-Smelling Urine?
Foamy urine combined with a strong or unusual odor can provide additional clues.
Common Causes of Strong-Smelling Urine
-
Dehydration
When urine is concentrated, ammonia becomes more noticeable, resulting in a sharp or strong smell. This is one of the most common and least concerning causes. -
Dietary Factors
Certain foods—such as asparagus, garlic, onions, coffee, or spices—can alter urine odor. Supplements and vitamins, especially B vitamins, may also produce a strong smell. -
Medications and Supplements
Antibiotics and some medications can temporarily change urine odor without indicating harm.
When Odor May Signal a Medical Issue
If urine smells unusually strong, sweet, rotten, or fishy
, and especially if combined with foam, it may indicate a medical condition.-
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
UTIs often cause foul-smelling urine, cloudiness, burning during urination, urgency, or lower abdominal discomfort. -
Diabetes
Sweet- or fruity-smelling urine may be linked to excess glucose or ketones in the urine, especially in poorly controlled diabetes. -
Liver or Metabolic Disorders
Rare metabolic conditions can cause distinctive odors due to the buildup of certain chemicals. -
Kidney Infection
Strong-smelling urine with foam, fever, back pain, or fatigue may indicate an infection that requires prompt treatment.

Should You Be Worried If You See Foam Once?
Occasional foamy urine
is usually not a cause for concern, especially if:-
It happens only once or infrequently
-
It disappears when you drink more water
-
There are no other symptoms such as pain, swelling, fatigue, or changes in urination
However, you should pay closer attention if:
-
Foamy urine occurs regularly
-
The foam is thick and persistent
-
You notice swelling in your hands, feet, face, or ankles
-
You feel unusually tired
-
Your urine smells very strong or abnormal for days
-
You have a history of kidney disease, diabetes, or high blood pressure
What Should You Do If It Keeps Happening?
If foamy urine persists, a healthcare provider may recommend:
-
Urine tests to check for protein, infection, or glucose
-
Blood tests to assess kidney function
-
Blood pressure monitoring
-
Further imaging or specialist referral if needed
Early detection of kidney-related issues can make a significant difference.
Many kidney problems progress silently, and urine changes are sometimes one of the first visible signs.
How to Reduce the Risk
While not all causes are preventable, you can lower your risk by:
-
Staying well hydrated
-
Managing blood pressure and blood sugar levels
-
Eating a balanced diet
-
Avoiding excessive use of painkillers without medical advice
-
Getting regular health checkups if you have risk factors
Final Thoughts
Foamy urine is not automatically dangerous, and in many cases, it is a normal and temporary occurrence.
However, when it becomes persistent—especially alongside strong odor or other symptoms—it can be your body’s way of signaling that something needs attention. Listening to these subtle signs and responding early is one of the simplest yet most powerful ways to protect your long-term health.
News in the same category


Discover the miracle drink that helps seniors rebuild knee cartilage quickly
This drink helps reduce gastroesophageal reflux and heartburn effectively
Simple Ways to Improve Circulation

Small but Mighty: The Magic of Clove and Goron Tula Water

Old Doctor’s Secret: Combine Dates and Papaya to Tackle These 10 Health Problems

Why So Many People Are Choosing Natural Ingredients for Skincare

The Breuss 42-Day Juice Therapy: An Evidence-Based Look at a Controversial Regimen
That Nagging Symptom You Keep Ignoring? Your Body Is Trying to Tell You Something.
10 Bizarre Home Remedies

See if you fall into this group!

Heart Surgeon’s Hidden Secret: Eat This Daily to Boost Cardiac Health!
More people are dying from heart failure, doctors warn: give up these 4 habits now
Claim: a juice regimen reportedly cleared can:cer cells in 42 days

FDA-Approved Eye Drops Offer a Non-Surgical Alternative for Age-Related Vision Loss

Recognizing a Stroke Fast
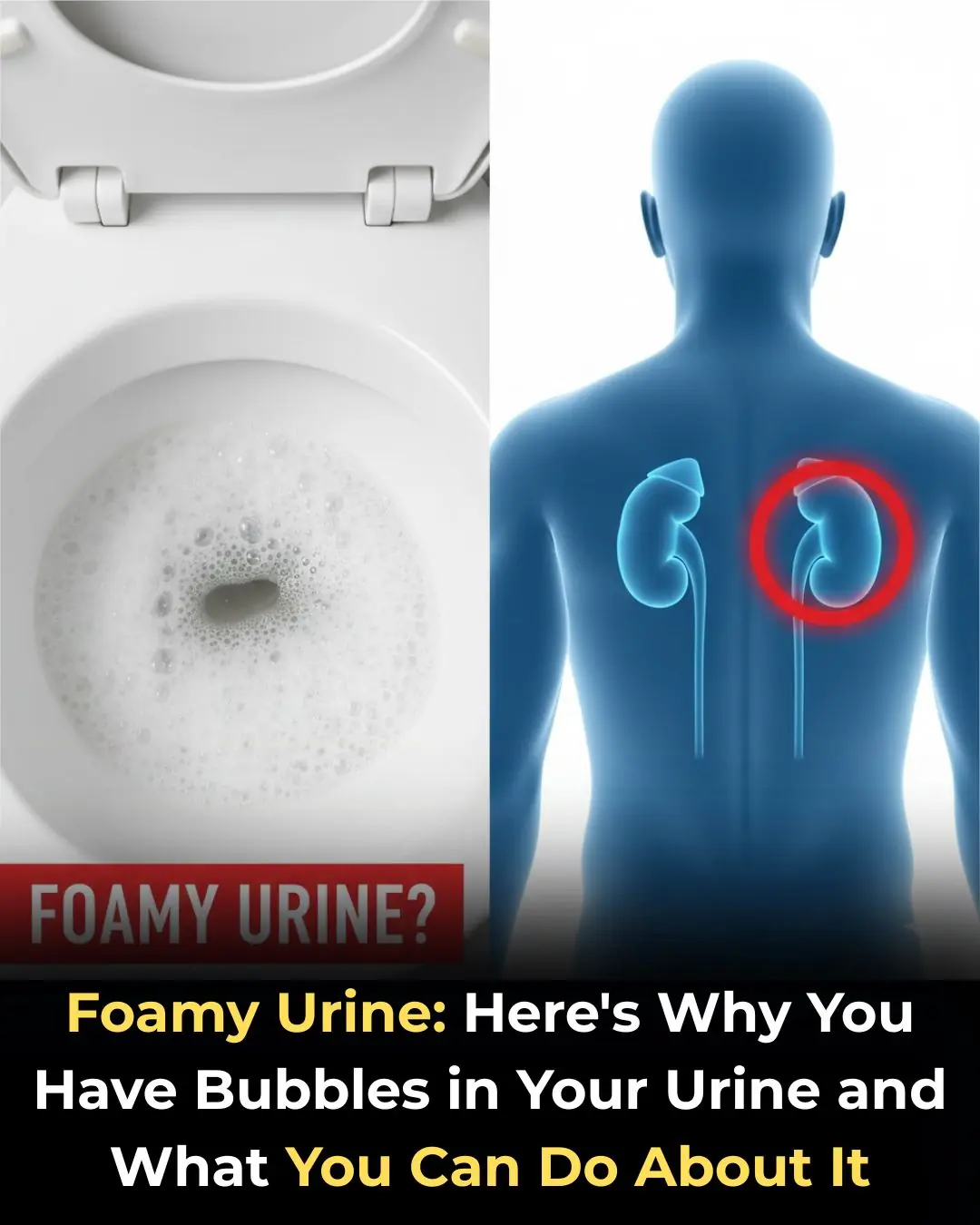
Foamy Urine: Here’s Why You Have Bubbles in Your Urine

Why Almonds Are So Good for You: Health Benefits of Almonds Backed by Science

How to Naturally Increase Estrogen Levels
News Post

Influencers Mock “Fat Woman” On Stream—She’s An Olympic Coach

The Real Purpose of the Aluminum Ring on Sausage Bars

Over 60? Struggling to Sleep Through the Night? Try This Simple Bedtime Drink for Deeper Rest

Discover a Simple Daily Habit: How to Incorporate Lemon and Nopal into Your Wellness Routine

Top 5 Veggies to Detox Your Arteries and Prevent Heart Attacks!

Discover the miracle drink that helps seniors rebuild knee cartilage quickly

This drink helps reduce gastroesophageal reflux and heartburn effectively

Simple Ways to Improve Circulation

The Power of Castor Leaves: Nature’s Hidden Gift for Joint Pain, Detox, and Glowing Skin (The Ancient Remedy Science Is Rediscovering)

Kalanchoe Wellness Guide: Gentle Habits and Everyday Tips for Using This Traditional Succulent Plant Safely

12 Practical Benefits of Bull Thistle Root and Simple Natural Ways to Use It at Home

Mother-In-Law Strips Bride Naked—Then Learns Who Her Father Really Is

Small but Mighty: The Magic of Clove and Goron Tula Water

Karen Throws Coffee At Teen Barista—Then Her Dad Walks Out

Old Doctor’s Secret: Combine Dates and Papaya to Tackle These 10 Health Problems

Why So Many People Are Choosing Natural Ingredients for Skincare

Blogs Is He a Foe… or an Ally

Bully Hits Girl at Lunch—Cafeteria Lady’s Response Shocks Everyone
