Why the Tongue Is One of the Most Important Organs in the Human Body
Why the Tongue Is One of the Most Important Organs in the Human Body
The tongue is often overlooked, yet it is one of the most complex and hard-working organs we use every single day. Made up of a unique combination of muscles, sensory cells, and supporting structures, the tongue plays a vital role in speaking, tasting, chewing, and swallowing. Its flexibility, strength, and sensitivity make it essential not only for communication but also for nutrition, safety, and overall well-being. Below is a simple and expanded explanation of why this powerful muscular organ is so important.
1. The Tongue: A Highly Flexible and Powerful Muscular Organ
The tongue is made almost entirely of muscle, which makes it extremely flexible and capable of many precise movements. According to the Cleveland Clinic, the tongue contains both intrinsic muscles (that change its shape) and extrinsic muscles (that move it in different directions). This unique structure gives it unmatched mobility compared with other muscles in the body.
Thanks to these muscles, the tongue can:
-
Lift, lower, and retract
-
Change shape to become thin, thick, curved, or flat
-
Move food smoothly around the mouth
-
Produce clear speech sounds
This combination of strength and fine control allows us to perform delicate actions like pronouncing words, as well as powerful movements needed to swallow food safely.
2. The Tongue’s Essential Role in Speech and Communication
Speech is one of the most important human abilities, and the tongue plays a leading role in creating the sounds we use to communicate. By shifting its position and shape, the tongue helps form consonants and vowels, control airflow, and adjust the loudness of our voice.
The Mayo Clinic explains that speech depends heavily on how the tongue interacts with the teeth, lips, and palate. Without a properly functioning tongue, most speech sounds would be unclear or impossible to produce. This is why speech therapists often focus on strengthening tongue movement in patients with speaking difficulties.
3. A Key Player in Eating, Chewing, and Swallowing
During meals, the tongue works constantly—even though we hardly notice it. It helps:
-
Move food around the mouth
-
Mix food with saliva
-
Form a soft ball of food called a bolus
-
Push the bolus toward the throat for swallowing
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) notes that swallowing is a coordinated process involving more than 30 muscles, and the tongue is one of the main organs that initiate this movement. Without the tongue’s ability to control food texture and position, swallowing would be difficult and unsafe.
4. The Tongue: The Body’s Main Organ of Taste
Our eating experience would be incomplete without taste—and the tongue is the primary organ responsible for detecting flavors. It contains thousands of taste buds, each with sensory cells that react to different flavors such as:
-
Sweet
-
Salty
-
Sour
-
Bitter
-
Umami
According to Britannica, these taste buds help us identify nutrients, enjoy food, and avoid harmful substances. For example, bitterness can signal toxins, while sweetness often indicates energy-rich foods. This makes taste not only enjoyable but also crucial for survival.
5. The Hyoid Bone: A Unique Structure That Gives the Tongue Power
One of the most fascinating parts of tongue anatomy is the hyoid bone. The hyoid is located in the upper neck and is the only bone in the human body that does not attach directly to another bone. Instead, it is suspended by muscles and ligaments, giving the tongue exceptional freedom of movement.
This unusual structure supports:
-
Speech
-
Chewing
-
Swallowing
-
Breathing control
Medical anatomy references often highlight the hyoid bone as a key evolutionary feature that helps humans achieve advanced vocal communication.
6. Important Muscles That Control the Tongue
The tongue’s impressive mobility comes from several major muscles connected to surrounding areas of the mouth and throat. These include:
-
Palatoglossus – elevates the back of the tongue
-
Palatopharyngeus – helps guide food during swallowing
-
Hyoglossus – depresses and flattens the tongue
These muscles work with internal tongue muscles to enable both precise movements for speech and stronger motions for swallowing. Together, they form a complex muscular system unique to humans.
7. Why the Tongue Is Vital for Overall Health
Beyond taste and speech, the tongue also plays important roles in:
-
Detecting food temperature
-
Keeping the mouth clean
-
Supporting digestion
-
Helping maintain open airways during sleep
Doctors often examine the tongue to identify signs of dehydration, infection, nutrient deficiency, or digestive problems. This makes the tongue an important indicator of general health.
Conclusion
The tongue may seem small, but its functions are essential for daily life. Its powerful muscles, rich sensory system, and unique support from the hyoid bone allow it to perform complex tasks—from shaping speech to guiding food safely into the throat. Supported by credible medical sources such as Mayo Clinic, Cleveland Clinic, NIH, and Britannica, it is clear that the tongue is one of the most important organs for communication, nutrition, and overall well-being.
News in the same category

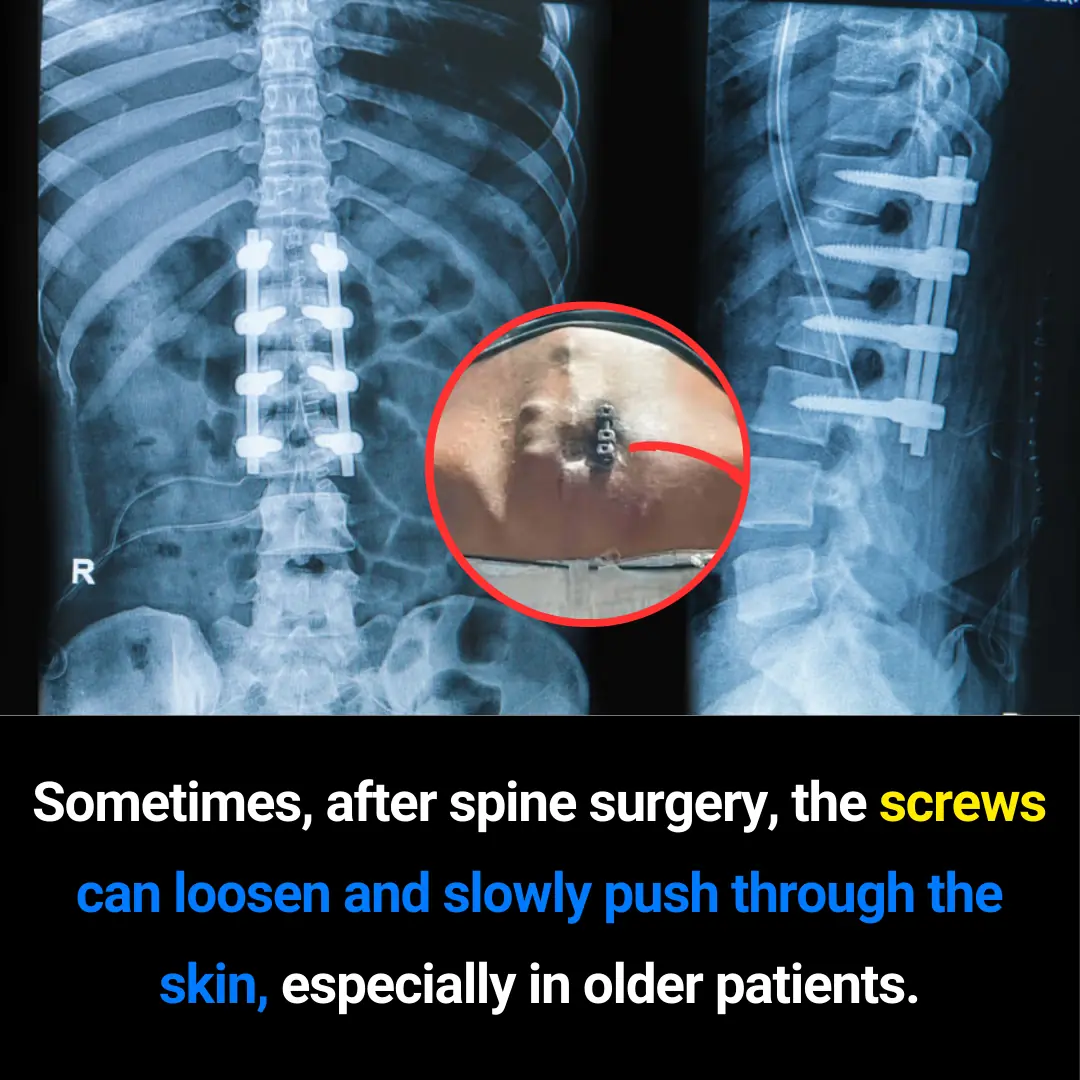
Can Spinal Screws Push Through the Skin? Understanding a Rare but Serious Post-Surgery Complication

What You Do First in This Scenario

Small Steps, Big Impact: How 4,000 Steps a Day Can Transform Your Health

Rising Concerns Over Excessive Headlight Brightness: A Growing Challenge for Nighttime Driving Safety in the UK

Unwavering Loyalty: The Stray Dog's Final Journey of Love and Devotion

Revolutionary MRI-Guided Cryoablation Offers Non-Invasive Cancer and Pain Treatment in Sydney

So this is what it does, here is the answer
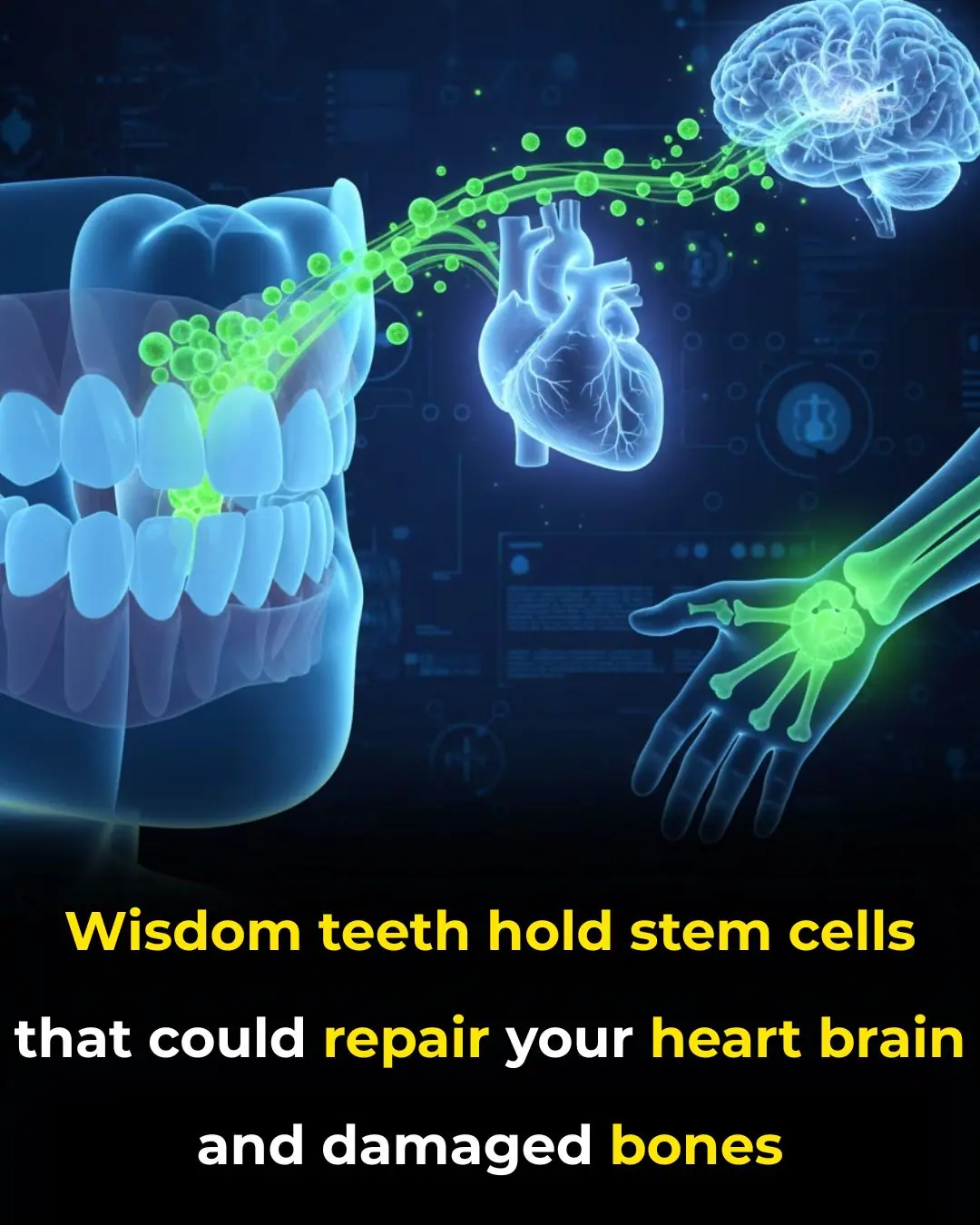
Scientists Unlock Healing Potential of Wisdom Teeth: Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine

1054 Supernova: The Cosmic Explosion That Shaped the Crab Nebula

The zodiac signs with a supernatural sixth sense… See now

Acts of Kindness Amid the Flames: A Firefighter's Reminder of His Purpose
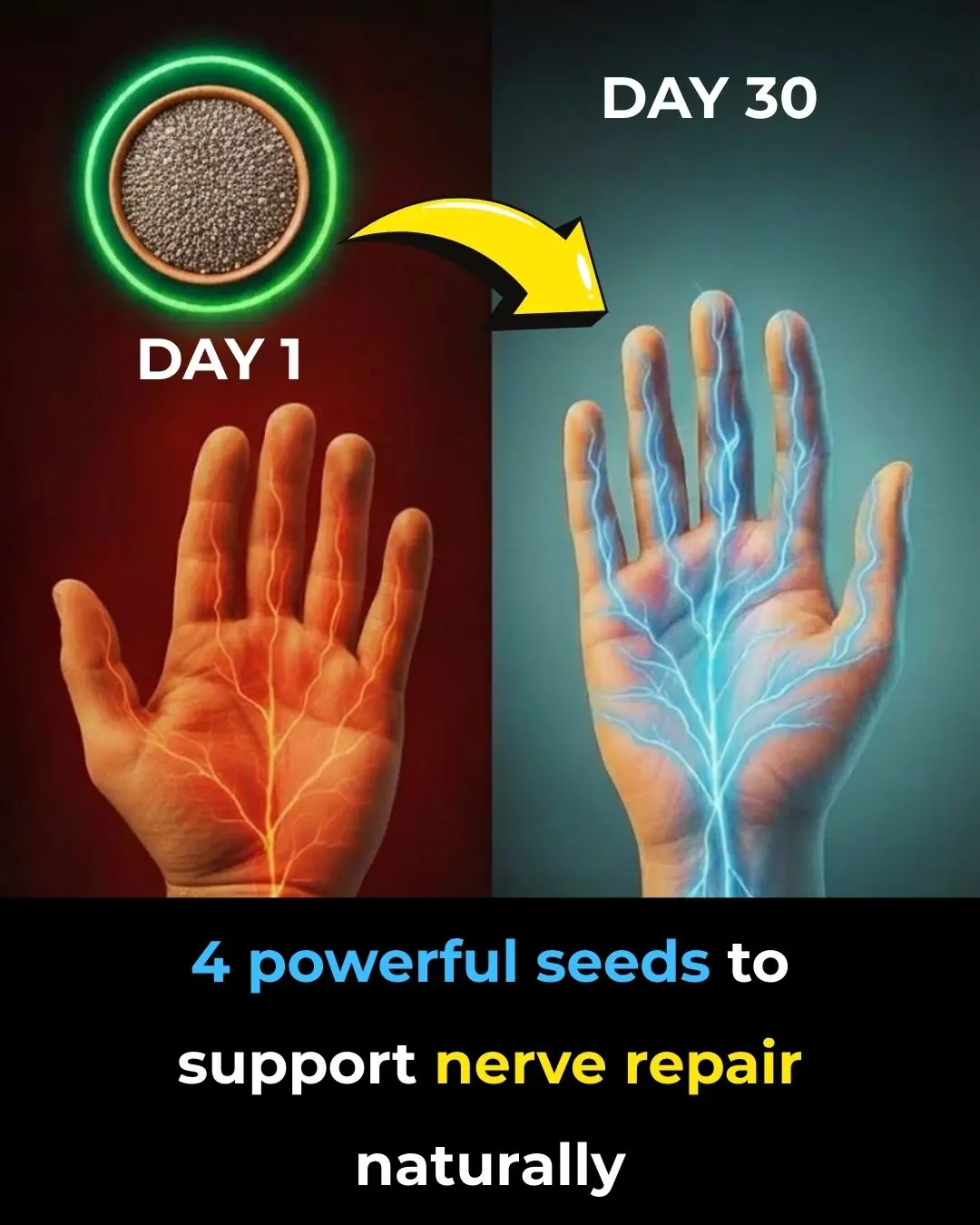
The surprising power of 4 seeds to repair your nerves naturally

Why Some Toilet Seats Have an Open-Front Design: History, Hygiene, and Practical Benefits

Swiss Scientists Develop Tiny Robots to Swim Through Bloodstream and Stop Strokes

The Odd and Enduring Tale of “Volvo Island” in Illinois

Virginia's Drunk Raccoon: The Wildest Customer to Ever Visit a Liquor Store

The Kaaba Shines From Space: A Stunning Photo Captured From the International Space Station

Scientists 3D-Print Human Corneas Using Stem Cell Bio-Ink, A Major Step Towards Restoring Sight
News Post

How an Italian Police Lamborghini Huracán Helped Save Lives by Delivering Kidneys Across Italy

Can Spinal Screws Push Through the Skin? Understanding a Rare but Serious Post-Surgery Complication

What You Do First in This Scenario

The Surprising Health Benefits of Sleeping in a Cold Room

A 4-Minute, Zero-Effort Hack to Clean Grill Gunk – The Simple Trick My Nana Taught Me
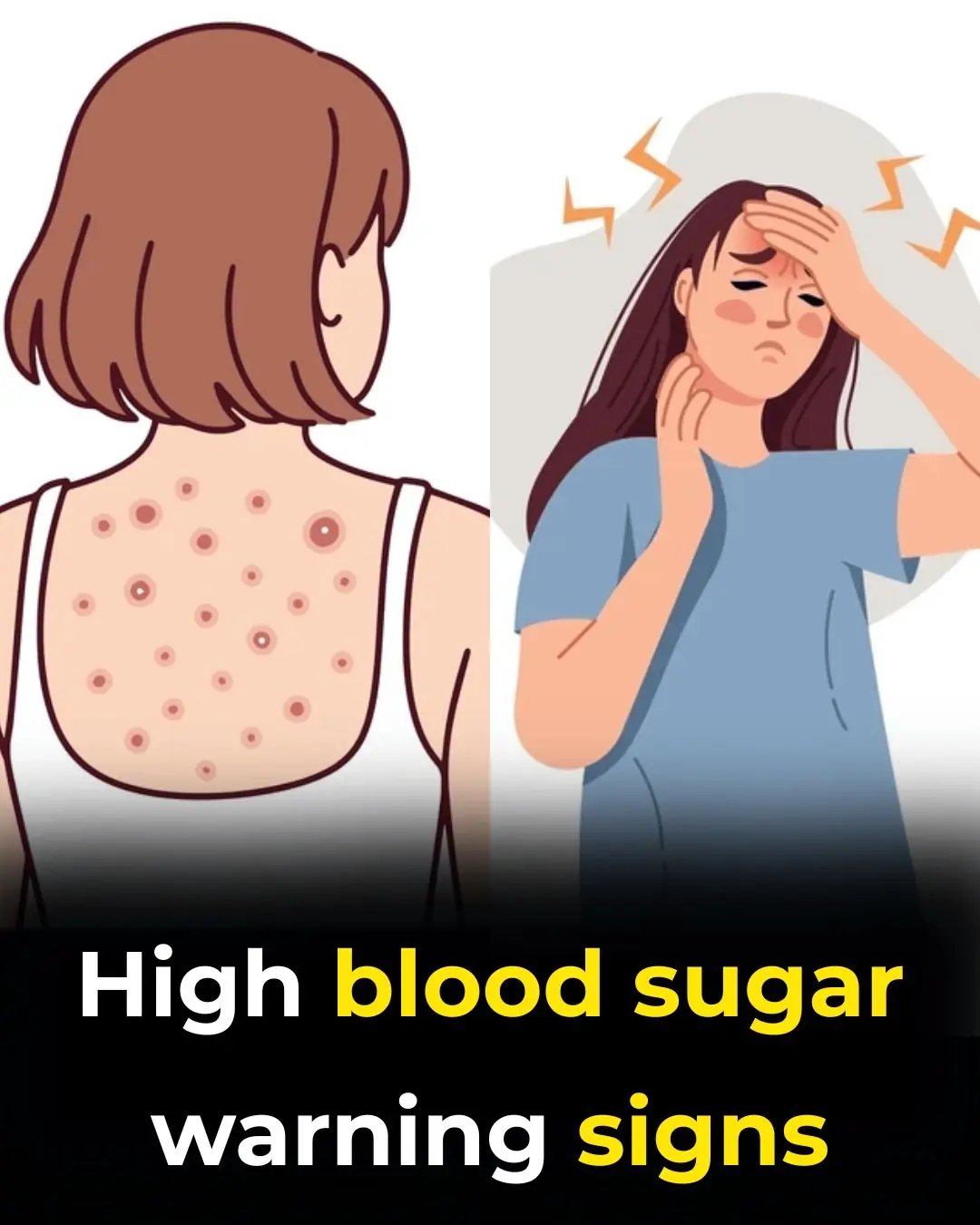
High Blood Sugar Warning Signs

🥚 A Look at How Certain Boiled Egg Habits May Affect Your Heart Health

Small Steps, Big Impact: How 4,000 Steps a Day Can Transform Your Health

🌿 Clove Water Sitz Baths for Women: A Gentle Guide to Hygiene and Comfort

What Happens to Your Body When You Eat Canned Tuna Every Day
17 Warning Signs Your Liver Is Crying for Help
How to Support Your Kidneys Naturally Using 1 Teaspoon of Baking Soda
Fish oil cuts CV risk nearly in half for dialysis patients

The hidden heart danger doctors say is more common in people with diabetes

The surprising power of 4 seeds to repair your nerves naturally

Trial: mRNA Flu Vaccines More Effective Than Quad

3 Miracle Herbs to Instantly Lower Blood Pressure & Clear Arteries Naturally

The Surprising Uses of Lemon and Charcoal: A Natural Mix That May Change Your Daily Routine
