Bamboo and Hemp: Sustainable Solutions for a Greener, Plastic-Free Future
Bamboo and Hemp: Sustainable Resources for a Greener Future
Bamboo and hemp are steadily gaining global recognition for their immense environmental and economic potential as highly sustainable resources. These two plants are not only versatile and rapidly renewable, but they also hold promise as key players in mitigating environmental issues, such as deforestation and plastic pollution. As the world increasingly looks for sustainable alternatives to conventional materials, bamboo and hemp offer solutions that align with both ecological conservation and economic growth.
Remarkable Growth Rates and Sustainability
Both bamboo and hemp are lauded for their impressive growth rates, making them ideal candidates for sustainable resource management. Unlike traditional timber, which requires decades to reach maturity, these plants can be harvested frequently, with minimal environmental impact. Bamboo, a type of perennial grass, is particularly notable for its extraordinary speed of growth. Some species of bamboo have been recorded as the fastest-growing plants on Earth, capable of growing several feet in a single day. This incredible speed allows for repeated harvests within just a few years, and the root system remains intact, which helps prevent soil erosion—a significant environmental concern in many parts of the world.
Similarly, hemp, an annual crop, matures within a single growing season, typically around four to six months. Its rapid growth cycle allows for efficient harvesting of cellulose and fiber, which are used in a wide range of applications. This fast turnaround makes hemp a valuable crop for meeting the growing demand for eco-friendly materials.
Versatile and Durable Fibers
The strong fibers of both bamboo and hemp are exceptionally versatile, with applications across various industries. Bamboo’s fibers are used to produce a wide range of products, including furniture, textiles, and paper. Hemp fibers are similarly diverse, finding their way into clothing, bioplastics, and even building materials. One of the most promising uses for both plants is in the creation of bioplastics. Unlike traditional plastics made from petroleum, bioplastics made from bamboo or hemp decompose much faster and require significantly less energy to produce. These biodegradable materials offer a viable solution to the growing plastic pollution crisis, providing an environmentally friendly alternative that can help reduce plastic waste in landfills and oceans.
In addition to their application in bioplastics, both bamboo and hemp are used to create durable and long-lasting products, contributing to a circular economy that emphasizes the reuse and recycling of materials.
Combating Deforestation and Protecting Ecosystems
The adoption of bamboo and hemp products directly supports efforts to combat deforestation. As demand for sustainable building materials increases, these crops offer an alternative to wood-based products such as paper, construction materials, and furniture. By substituting bamboo and hemp for timber, the pressure on old-growth forests and slower-growing tree species is reduced. Bamboo, in particular, is a renewable resource that grows quickly and can be harvested in just a few years without the need for replanting, unlike trees, which can take decades to reach maturity.
The ecological benefits of cultivating bamboo and hemp extend beyond just providing alternative materials. Both plants are highly effective at sequestering atmospheric carbon dioxide, helping to mitigate the effects of climate change. Bamboo forests, in particular, are renowned for their ability to absorb carbon at a faster rate than many tree species. Hemp cultivation also offers ecological benefits through a process known as phytoremediation, where the plants help clean and restore soil by absorbing contaminants and improving soil health.
A Sustainable Future
As the demand for sustainable materials continues to rise, bamboo and hemp provide practical, scalable solutions to some of the world’s most pressing environmental challenges. Their rapid growth cycles, combined with their ability to replace wood-based materials and reduce plastic pollution, make them vital to building a more sustainable global economy. Moreover, the economic benefits of cultivating these plants extend beyond their environmental contributions, as they provide income opportunities for farmers and create jobs in green industries.
According to the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), the global push for sustainable materials is essential for achieving long-term environmental goals, such as reducing deforestation and promoting a circular economy. The rise of bamboo and hemp as renewable resources aligns with these objectives, offering a path to a greener, more sustainable future.
Bamboo and hemp are not just the future of sustainable materials—they are the present. By embracing these extraordinary plants, we can address the challenges of plastic pollution, deforestation, and soil degradation, all while building a more resilient and sustainable economy for generations to come.
Sources:
-
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP): The role of sustainable materials in achieving environmental goals. UNEP
-
National Hemp Association: The environmental benefits of hemp cultivation and its potential as a sustainable resource. National Hemp Association
-
World Wildlife Fund (WWF): Bamboo and its role in combating deforestation. WWF
News in the same category


How This Traditional Korean Dish Helped Immune Cells Spot Viruses Without Overreacting

How Siblings Can Grow Up in the Same Home but Live Completely Different Childhoods
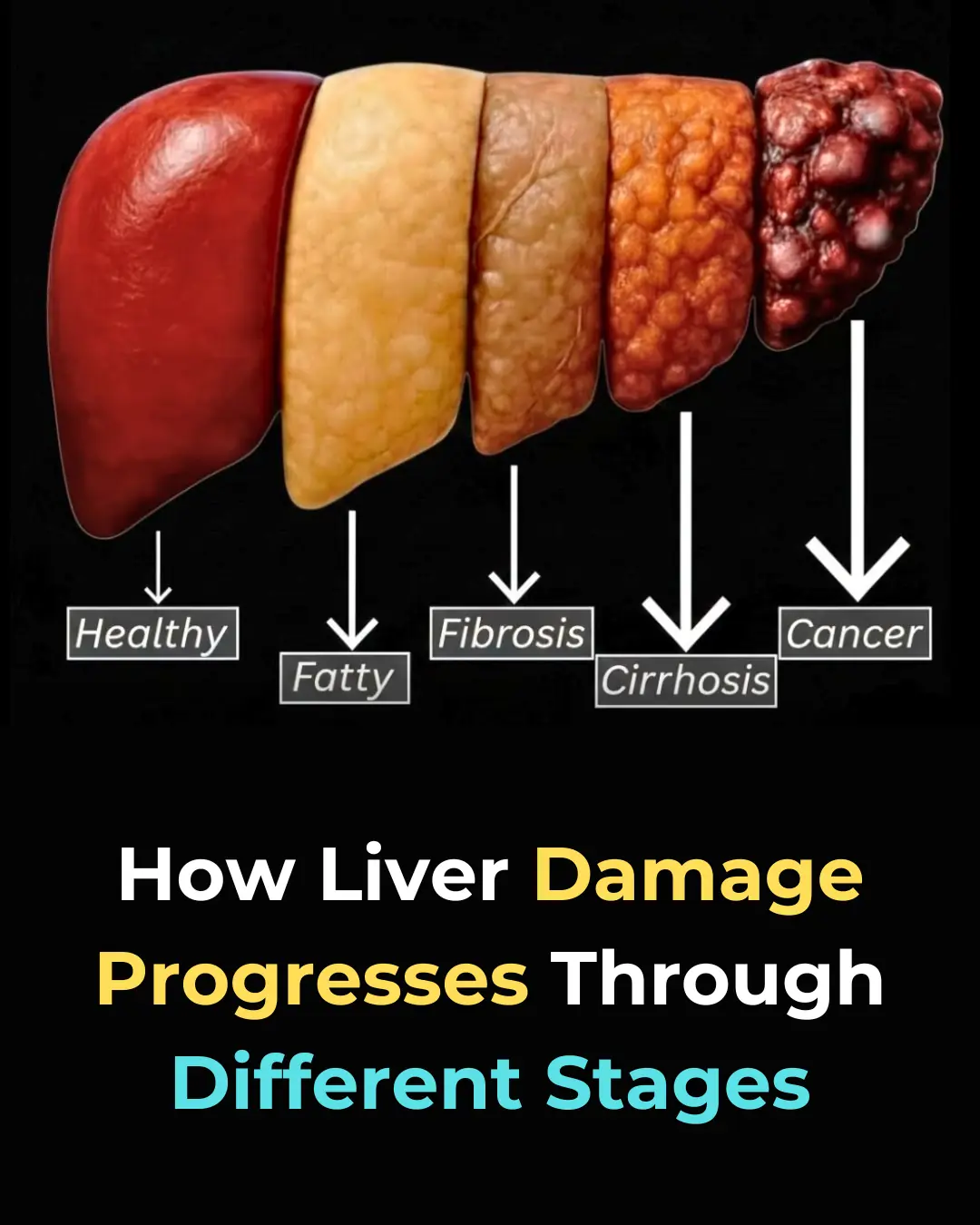
Understanding Liver Damage: Stages, Causes, and How to Prevent It

Kaaba’s Radiant Glow Seen from Space: A Celestial Spotlight on Islam’s Holiest Site

Scientific Breakthroughs in Women's Health: How Research is Finally Addressing Gender Gaps

Monkeys, Money, and Unexpected Behavior: Insights from a 2005 Yale Study on Capuchin Monkeys and Economic Decision-Making

How Europe's Skin Pigmentation Evolved: Dark to Light Over Millennia

The Myth of “Safe” Smoking Debunked: How Minimal Tobacco Use Still Damages the Body

The Regal Cat on the Beer Box: A Quiet Reminder of the Power of Stillness and Simplicity

Johan Eliasch's Impact on Amazon Conservation: A Commitment to Sustainable Practices and Empowering Indigenous Communities

The Science Behind Cats’ Calming Influence on Stress and Heart Health

12 Phrases That Reveal Someone Is Struggling More Than They Want To Admit

For the first time in 40 years, Panama’s Ocean lifeline has vanished

The Meaning Behind the WC Toilet Sign

Why Zohran Mamdani may not be sworn in as New York's 111th

'Living Nostradamus' makes truly terrifying prediction for 2026 - here's what he said

Cosmic Double Feature Tonight: Taurid Fireball Meteor Shower & Strong Solar Storm
News Post
Silent Kidney Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention Tips

When boiling duck, don't add ginger and cold water: Add this and the meat will lose all its stench, and you won't get tired of eating it.

How to make steamed chicken with lemongrass, golden brown chicken, soft and delicious, irresistible

Simple tips to help reduce itching extremely quickly when bitten by mosquitoes and insects
10 Warning Signs of Heart Disease Most People Ignore

How to wash and condition hair with rice water to reduce hair loss and help new hair grow continuously

A Medical Miracle From Japan: How Stem Cells Helped a Paralyzed Man Walk Again

Shocking Truth About How Crabsticks Are Made

The Fungus That Eats Radiation — And May Help Humans Survive in Space

How This Traditional Korean Dish Helped Immune Cells Spot Viruses Without Overreacting

How Siblings Can Grow Up in the Same Home but Live Completely Different Childhoods

Doctors reveal that eating beets causes...

Understanding Liver Damage: Stages, Causes, and How to Prevent It

Kaaba’s Radiant Glow Seen from Space: A Celestial Spotlight on Islam’s Holiest Site

Scientific Breakthroughs in Women's Health: How Research is Finally Addressing Gender Gaps

Monkeys, Money, and Unexpected Behavior: Insights from a 2005 Yale Study on Capuchin Monkeys and Economic Decision-Making

How Europe's Skin Pigmentation Evolved: Dark to Light Over Millennia

People with heart problems should avoid these 4 things to reduce stimulation to the heart