Nobel-Winning Discovery Reveals How to Stop the Immune System From Attacking the Body
Scientists have unlocked one of the most important secrets of the human body: how to stop the immune system from attacking itself — a discovery that permanently changed modern medicine. For decades, researchers faced a troubling paradox. The very system designed to protect us from infections and cancer could, under certain conditions, turn against the body and destroy healthy tissues. Autoimmune diseases arise from this internal misdirection, where the immune system mistakes normal cells for dangerous invaders and launches relentless attacks against them.
Conditions such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, and type 1 diabetes all share this central mechanism: immune confusion. Traditional treatments relied on broadly suppressing immune function with steroids or chemotherapy-like drugs. Although these therapies sometimes reduced symptoms, they also weakened the body’s natural defenses, increasing susceptibility to severe infections and certain cancers. Doctors were forced to balance disease control with serious side effects, and the underlying problem remained unsolved.
The turning point came when scientists identified the biological “brakes” that regulate immune activity. They discovered that immune cells are not automatically aggressive; instead, their behavior is fine-tuned by special checkpoint proteins that signal when to activate, slow down, or stop attacking. These checkpoints — including proteins such as CTLA-4 and PD-1 — act as regulatory switches. They protect the body from excessive inflammation and prevent immune cells from mistakenly targeting self-tissues.
By understanding how these immune brakes operate, researchers learned how to manipulate them. In autoimmune disease, turning on these brakes can calm destructive immune responses and reduce tissue damage. In cancer, doing the opposite — releasing the brakes — allows immune cells to recognize and attack tumor cells more effectively. This insight demonstrated that immunity is not a simple on-off switch but a highly calibrated system more like a volume dial, capable of subtle adjustments.
The discovery of immune checkpoint regulation earned the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine and reshaped the landscape of immunology, rheumatology, and oncology. It led to the development of checkpoint-based therapies that are now used worldwide in cancer treatment and are being explored for autoimmune conditions and transplant tolerance. Beyond medication, it transformed how scientists conceptualize immune balance, tolerance, and self-recognition.
The implications are profound. Instead of shutting down immunity across the entire body, future therapies aim to retrain it — selectively correcting cells that misbehave while preserving normal protection against infections. This precision approach paves the way for personalized treatments based on genetic background, immune signatures, and disease subtype. Patients may one day receive therapies tailored to how their own immune system fails to regulate itself.
Equally important is the shift in perspective. Autoimmune disease is no longer seen merely as the immune system “going crazy,” but as a breakdown in regulation — a failure of the checkpoints meant to maintain peace within the body. Science has revealed that this failure can be understood, measured, and in some cases corrected. Instead of fearing the immune system, researchers are learning how to guide and modulate it with increasing accuracy.
This breakthrough did more than win a Nobel Prize; it offered millions of patients genuine hope. It showed that the immune system is not a reckless force but a sophisticated network that, when properly regulated, can distinguish friend from foe with remarkable precision. The discovery of immune checkpoints opened the door to treatments that are smarter, safer, and more effective than blanket immune suppression.
References:
– Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine: Immune Checkpoint Regulation Research (Nobel Committee)
– National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Immunology and Autoimmune Disease Research
– American Autoimmune Related Diseases Association (AARDA)
– The New England Journal of Medicine – Immune Checkpoint Therapy Reviews
– Nature Immunology – Mechanisms of Immune Regulation
News in the same category

Diagnosed with terminal cancer that had metastasized to the brain, the woman went for a check-up and burst into tears upon learning that her husband and son were the culprits
Doctors warn: 4 types of inflammation can easily turn into cancer in just one year if treatment is delayed
Triple Therapy Linked to Lower Lung Clearance Index in Children With Cystic Fibrosis

Drink Water First: Hydration on Waking May Sharpen the Brain More Than Your Morning Coffee

Why Sugar Matters More Than Cholesterol in Heart Disease Risk
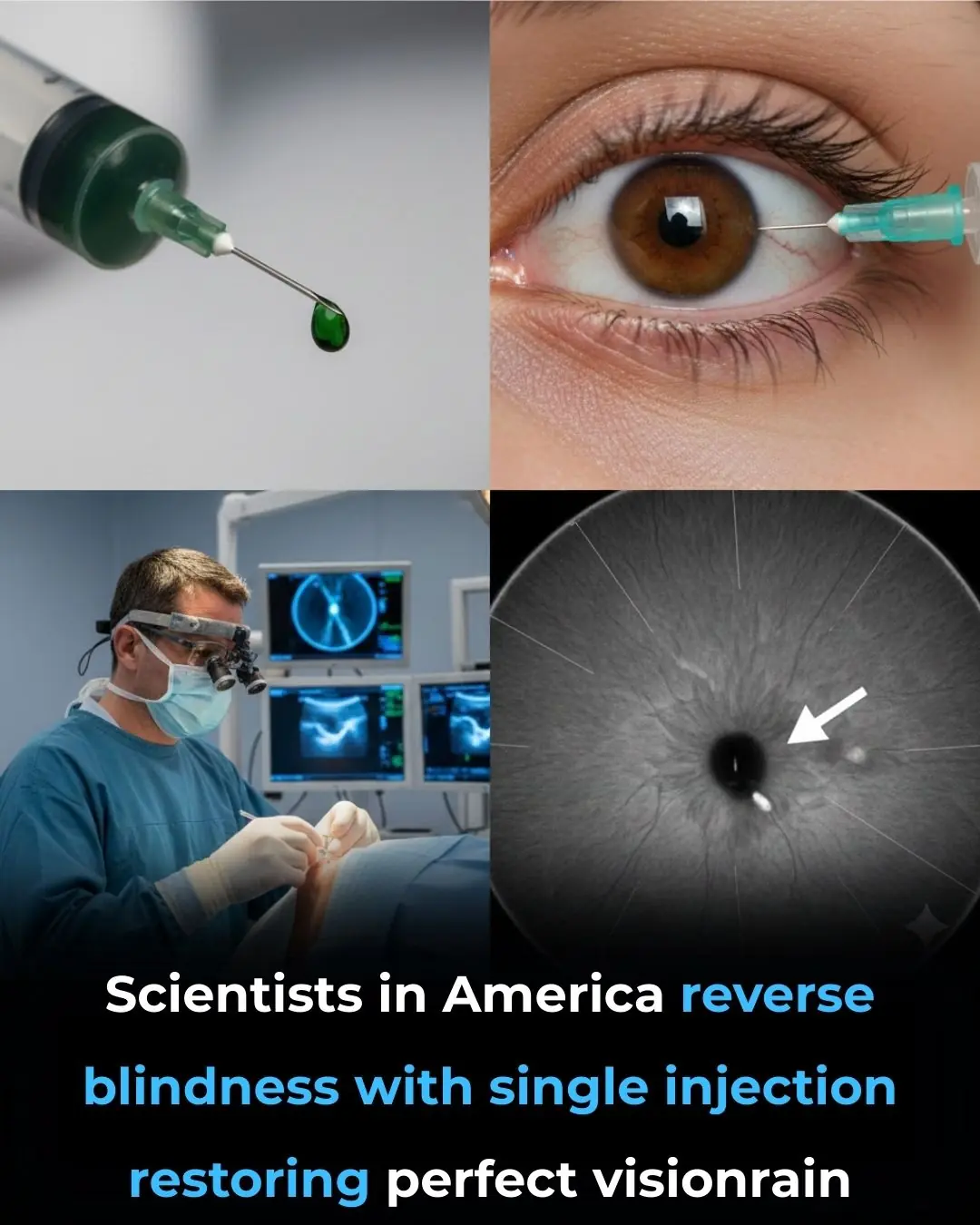
Single-Injection Gene Therapy Restores Vision in Patients With Inherited Blindness

Smelly but Smart? Weird Study Claims Your Own Gas Could Benefit Brain Health
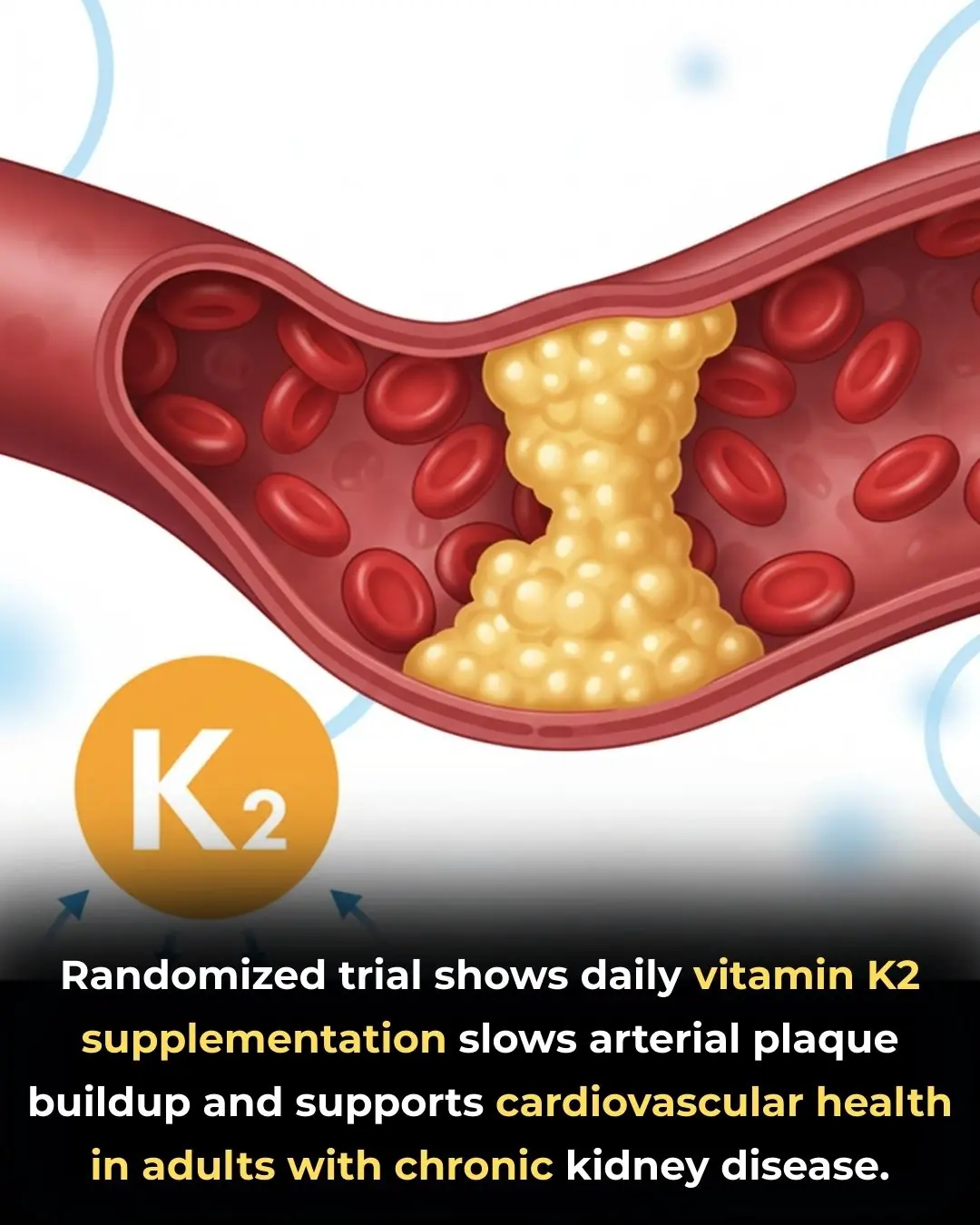
Vitamin K2 Supplementation Slows Arterial Plaque Progression in Chronic Kidney Disease

Everyone Fears Diabetes, but Diabetes “Fears” These 5 Foods

A Hard-Earned Lesson for Middle-Aged Parents: Let Go of These Habits, and Your Children Will Naturally Grow Closer
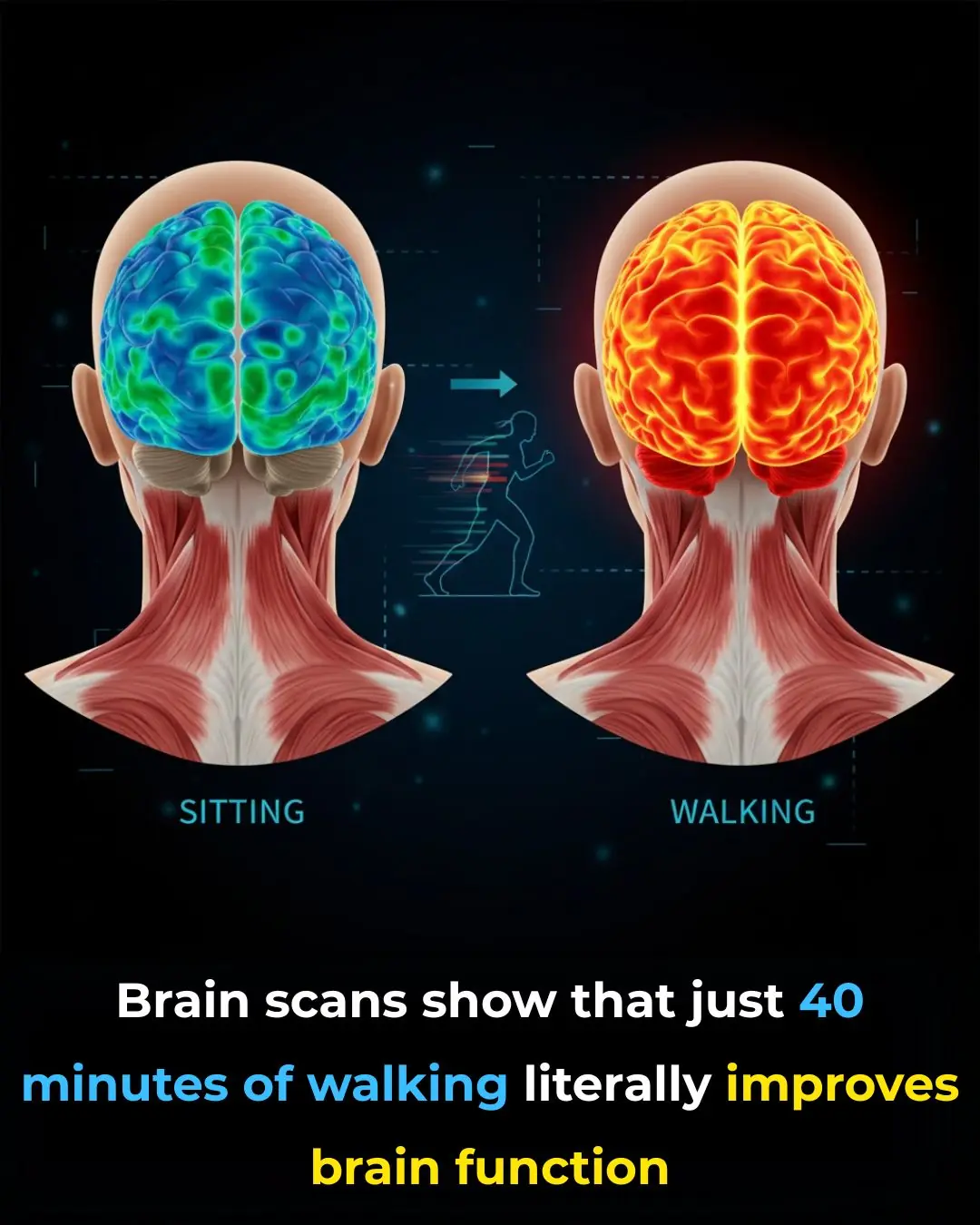
How Walking Activates the Brain: The Hidden Link Between Movement, Focus, and Mental Clarity

It’s Time to Protect Your Stomach: Remove These 5 Popular Vietnamese Breakfast Foods from Your Morning Menu
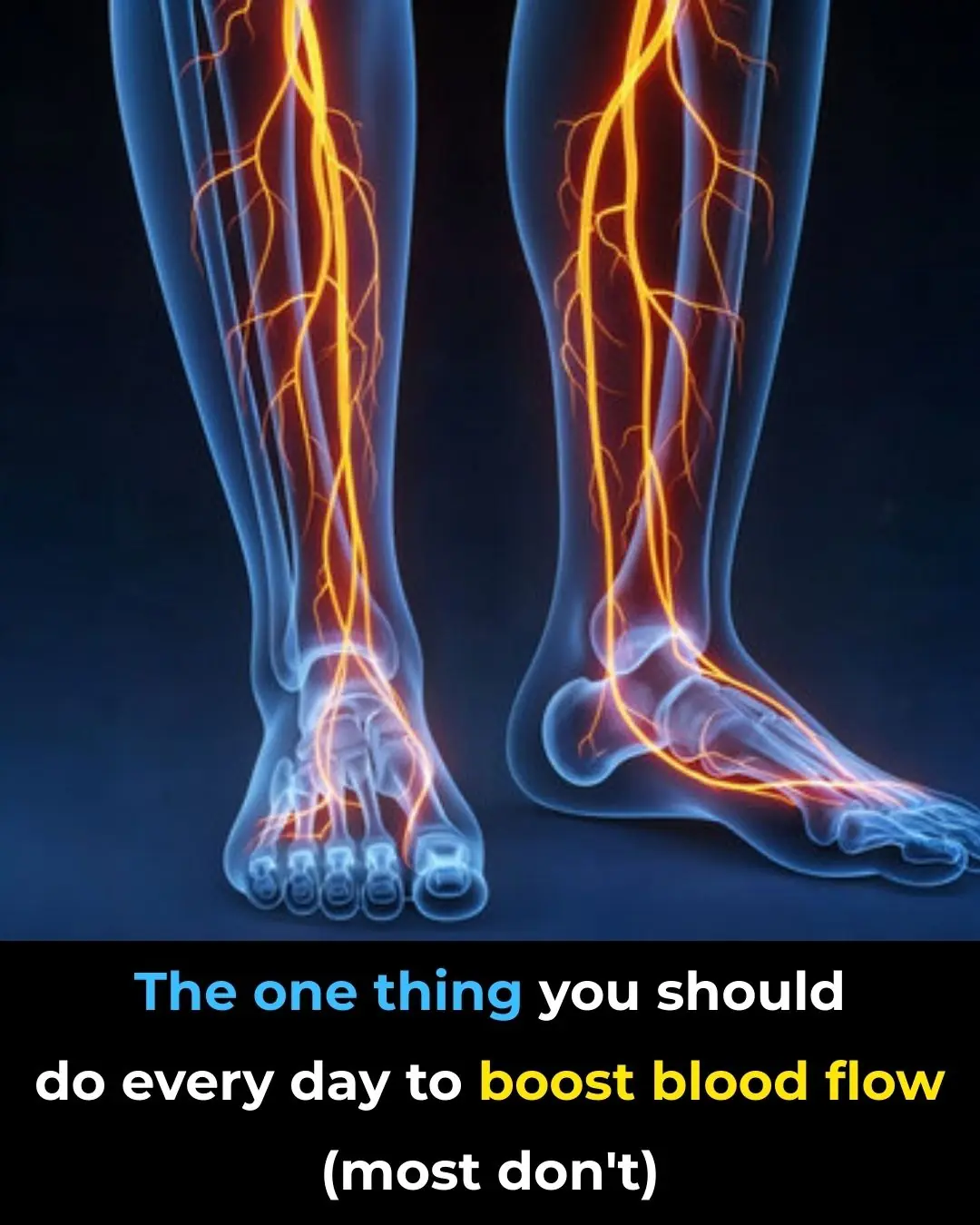
How to Improve Blood Circulation Naturally (Research Based)
The Most Effective Ways to Naturally Get Rid of Clogged Ears
7 powerful vitamins you need for strong, healthy legs
Scientists Discover Protein That Unmasks Cancer Cells, Boosting the Immune System’s Power
4 alarming symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency you can’t ignore!
10 Scientifically Backed Reasons Why You Should Consume Ginger Everyday
News Post

11 dishes you should never cook in an air fryer; don't try it or you'll regret it.

Put Bay Leaves in the Corners of Their Kitchen

The Simple Nighttime Habit That Can Help You Fall Asleep Faster

🌙 If You Notice These 3 Signs at Night, Your Kidneys Are Likely in Great Shape

Diagnosed with terminal cancer that had metastasized to the brain, the woman went for a check-up and burst into tears upon learning that her husband and son were the culprits

Doctors warn: 4 types of inflammation can easily turn into cancer in just one year if treatment is delayed

Why Some People Rub Onions on Their Windows

Harbhajan Singh’s Royal Gift: A Gold‑Plated iPhone 17 Pro Max ✨📱🏏

Kumar Sangakkara: Greatness in Simplicity 🏏❤️

Smart Money Choices: Shivani Gera’s Lesson in Real Wealth 💰🌍

Mukesh Ambani’s ₹7 Lakh Crore Vision: Gujarat at the Heart of India’s Next Decade 🚀🇮🇳

Chai Guy LA: A Bihari Street Vendor’s Viral Rise in California 🌍☕

Sridhar Vembu’s Divorce Settlement: A $1.7 Billion Shockwave in Global Business ⚖️🌍

Triple Therapy Linked to Lower Lung Clearance Index in Children With Cystic Fibrosis

You're doing it all wrong. Here’s the right way to set your thermostat in winter

Drink Water First: Hydration on Waking May Sharpen the Brain More Than Your Morning Coffee

Why Sugar Matters More Than Cholesterol in Heart Disease Risk

Green Smoothies and Weight Management: What Cucumber and Lemon Drinks Can Realistically Do
