
4 alarming symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency you can’t ignore!
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a fundamental role in maintaining overall health, particularly in supporting the nervous system and the production of healthy blood cells. Despite its importance, Vitamin B12 deficiency is more common than many people realize. Studies suggest that anywhere from 2% to 20% of the population may experience low levels of this vitamin, often without obvious or immediate symptoms. This makes the condition especially concerning, as untreated deficiency can lead to serious and long-lasting health problems.
In this article, we will take a closer look at what Vitamin B12 is, why it is so important for the body, the most common symptoms of deficiency, who is at higher risk, and the most effective ways to increase and maintain adequate B12 levels for long-term health.
Key Takeaways
-
Vitamin B12 is crucial for proper nerve function, red blood cell formation, and DNA synthesis.
-
Deficiency symptoms may affect the nervous system, blood, mouth, digestive tract, and eyes.
-
Vegetarians, vegans, older adults, and individuals with digestive disorders are at higher risk.
-
Vitamin B12 levels can be improved through diet, fortified foods, supplements, or medical treatment.
-
Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent irreversible complications.
Understanding Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that is naturally found in animal-based foods such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products. It plays a critical role in producing red blood cells, maintaining nerve health, and supporting normal brain function. Because the human body cannot produce Vitamin B12 on its own, it must be obtained through diet or supplementation.
When B12 levels are insufficient, the body may struggle to carry oxygen efficiently, repair nerve cells, and support normal cognitive processes. Over time, this can lead to a wide range of physical and neurological symptoms.
Why Is Vitamin B12 Important?
Vitamin B12 supports several vital functions in the body:
Nerve Health:
Vitamin B12 is necessary for the formation of myelin, the protective coating that surrounds nerve fibers. This coating allows nerve signals to travel efficiently. A lack of B12 can damage myelin, leading to slowed or disrupted nerve communication.
Red Blood Cell Production:
B12 is essential for producing healthy red blood cells. Without enough of it, red blood cells can become abnormally large and inefficient, resulting in anemia and reduced oxygen delivery to tissues.
DNA Synthesis:
Vitamin B12 plays a key role in DNA synthesis and cell division. This process is especially important for rapidly dividing cells, such as blood cells, and is crucial for overall growth and tissue repair.
Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Identifying the symptoms of Vitamin B12 deficiency early can help prevent long-term damage. These symptoms generally fall into several categories:
1. Neurological Symptoms
The nervous system is particularly sensitive to low B12 levels. Common neurological symptoms include:
-
Numbness or Tingling: A pins-and-needles or burning sensation, especially in the hands and feet.
-
Balance Problems: Difficulty walking, frequent stumbling, or poor coordination.
-
Cognitive Changes: Memory loss, difficulty concentrating, irritability, mood changes, and persistent fatigue.
-
Lhermitte’s Sign: A sudden electric shock-like sensation that travels down the spine when bending the neck forward.
2. Hematological Symptoms
Because Vitamin B12 is vital for blood health, deficiency can cause symptoms related to anemia, such as:
-
Fatigue and Weakness: Persistent tiredness even after adequate rest.
-
Pale or Light Skin: Reduced red blood cells can make the skin appear unusually pale.
-
Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin or eyes caused by the rapid breakdown of abnormal red blood cells.
3. Oral and Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Deficiency may also affect the mouth and digestive system:
-
Glossitis: A swollen, painful, smooth, and red tongue.
-
Loss of Appetite: Reduced hunger, which may contribute to unintended weight loss.
-
Digestive Problems: Issues such as diarrhea, constipation, nausea, or abdominal discomfort.
4. Ocular Symptoms
In more severe cases, Vitamin B12 deficiency can impact vision:
-
Visual Disturbances: Difficulty seeing in low light or changes in color perception.
-
Optic Nerve Damage: Prolonged deficiency can damage the optic nerve, potentially leading to partial or permanent vision loss.
Who Is at Risk?
Certain individuals are more likely to develop Vitamin B12 deficiency:
-
Vegetarians and Vegans: Since B12 is mainly found in animal products, people following plant-based diets must rely on fortified foods or supplements.
-
Older Adults: Aging reduces stomach acid production, which is necessary for B12 absorption.
-
People with Digestive Disorders: Conditions such as Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or a history of gastric surgery can interfere with B12 absorption.
How to Increase Vitamin B12 Levels
If you suspect a deficiency, there are several effective ways to improve B12 levels:
Dietary Sources:
Include B12-rich foods such as beef, poultry, fish, shellfish, eggs, and dairy products.
Fortified Foods:
Many plant-based products, including cereals, nutritional yeast, and non-dairy milks, are fortified with Vitamin B12.
Supplements:
Vitamin B12 supplements are widely available and especially helpful for high-risk individuals. Common forms include:
-
Cyanocobalamin: A synthetic form that the body converts into active B12.
-
Methylcobalamin: A bioactive form that may be better absorbed by some people.
Treatment for Vitamin B12 Deficiency
If a deficiency is confirmed through medical testing, treatment may involve:
-
Dietary Adjustments: Increasing intake of B12-rich or fortified foods.
-
Oral Supplements: Regular use of B12 tablets or capsules.
-
Injections: In severe cases or when absorption is impaired, B12 injections may be required for rapid and effective treatment.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a serious but often overlooked condition that can affect multiple systems in the body. If left untreated, it may lead to lasting neurological damage, anemia, and vision problems. By understanding the symptoms, recognizing risk factors, and taking preventive measures, you can protect your health and well-being. If you suspect a deficiency, consult a healthcare professional for proper testing and personalized treatment. Taking care of your Vitamin B12 levels is a small step that can make a significant difference in your overall health.
News in the same category


A Hard-Earned Lesson for Middle-Aged Parents: Let Go of These Habits, and Your Children Will Naturally Grow Closer
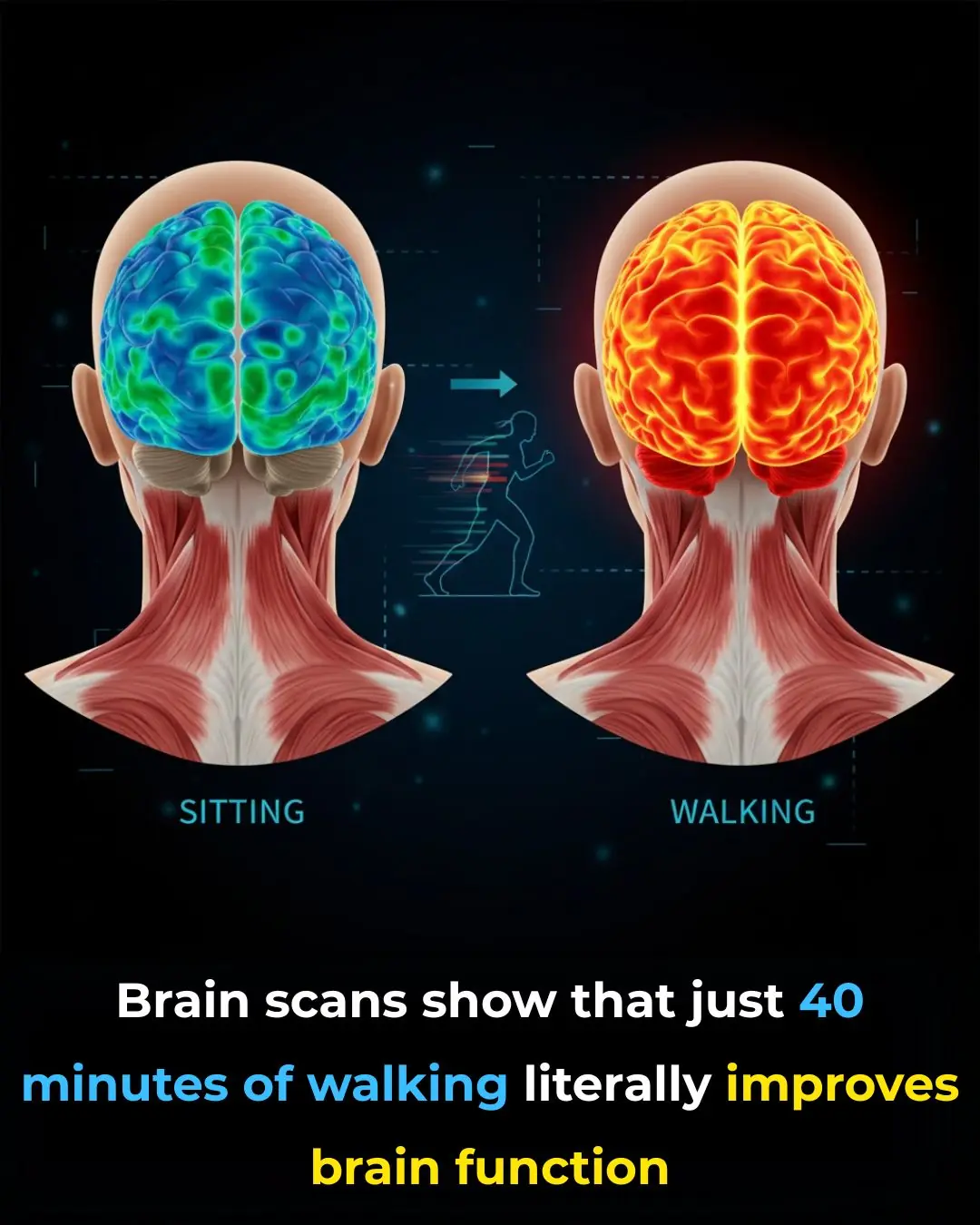
How Walking Activates the Brain: The Hidden Link Between Movement, Focus, and Mental Clarity

It’s Time to Protect Your Stomach: Remove These 5 Popular Vietnamese Breakfast Foods from Your Morning Menu
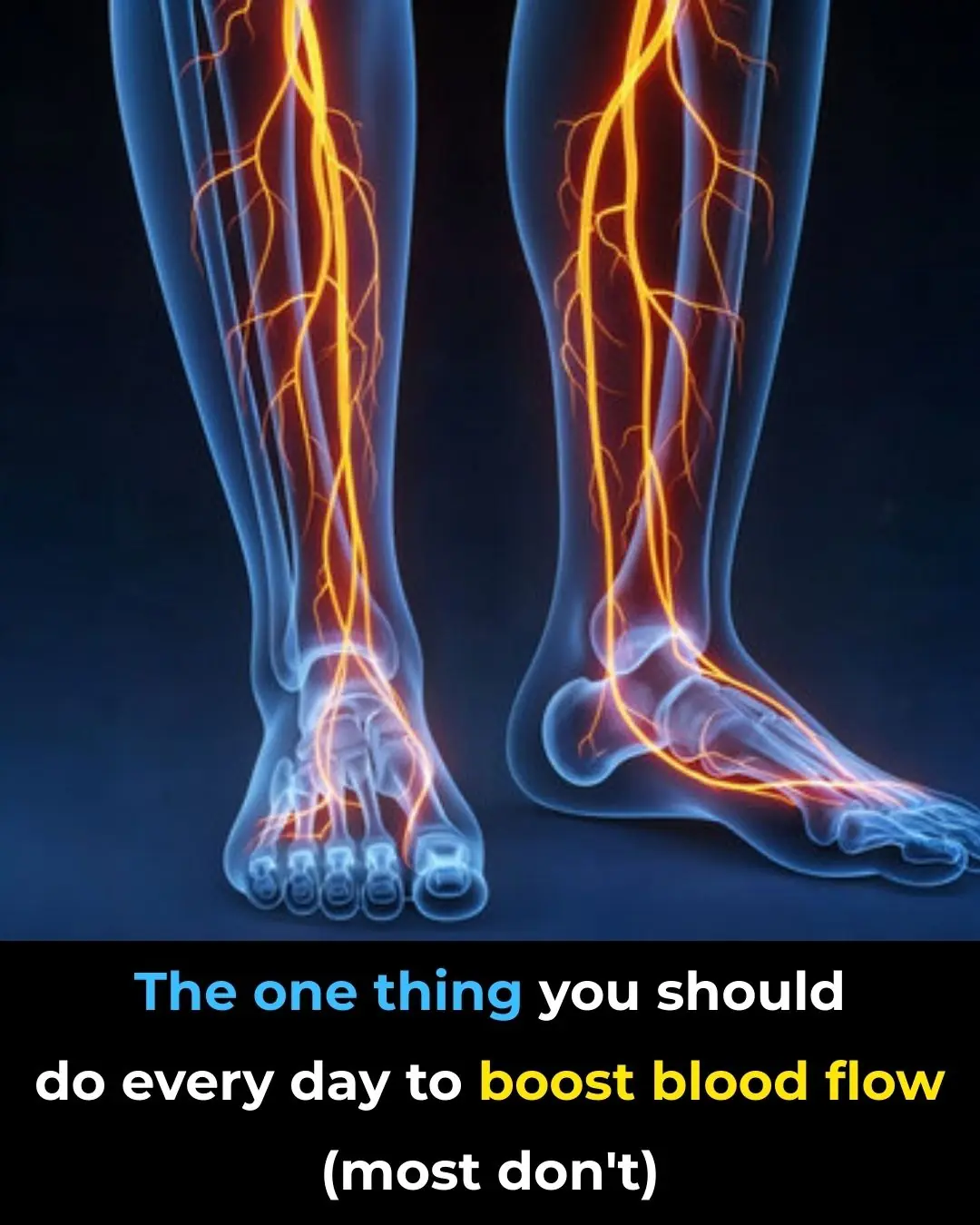
How to Improve Blood Circulation Naturally (Research Based)
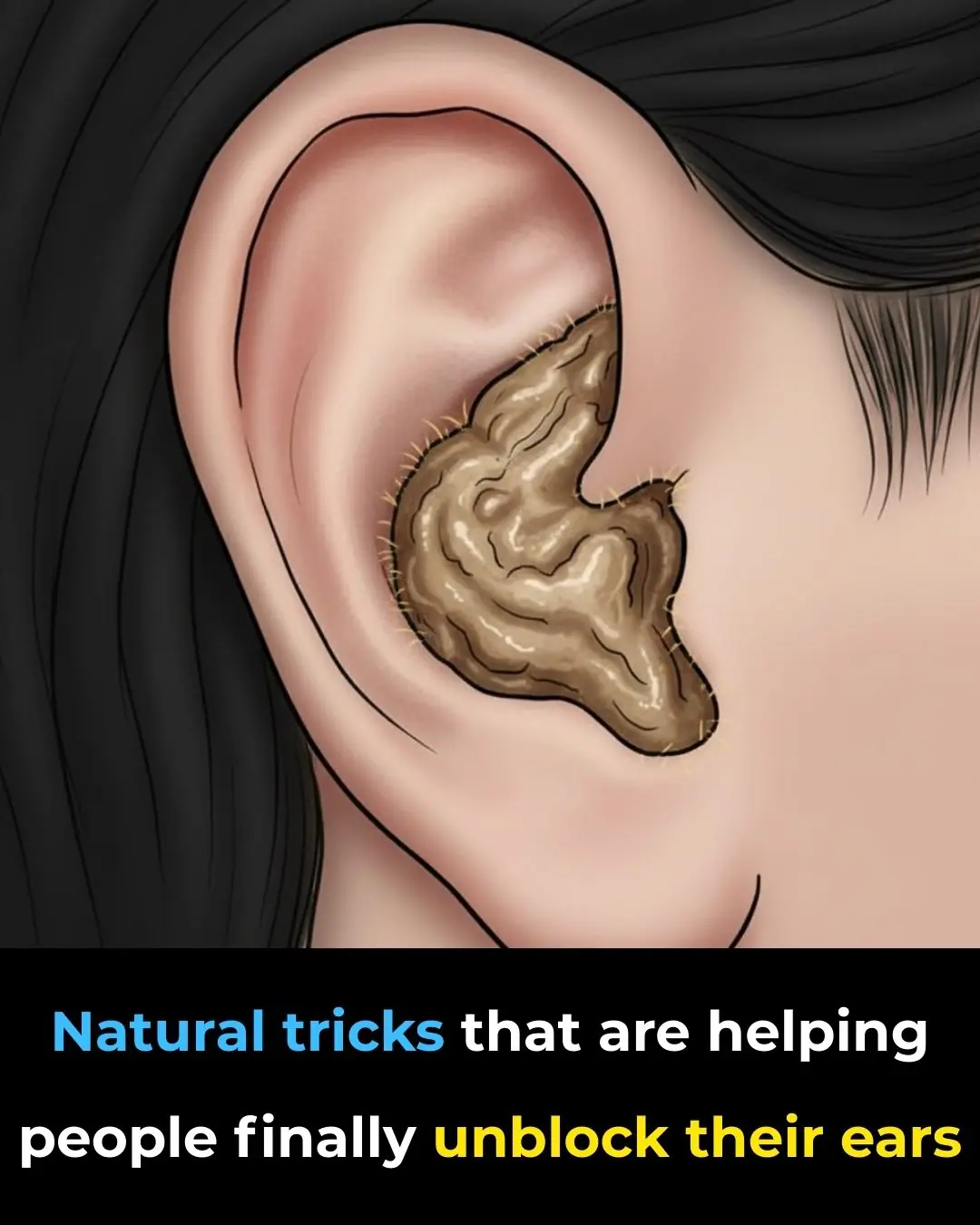
The Most Effective Ways to Naturally Get Rid of Clogged Ears
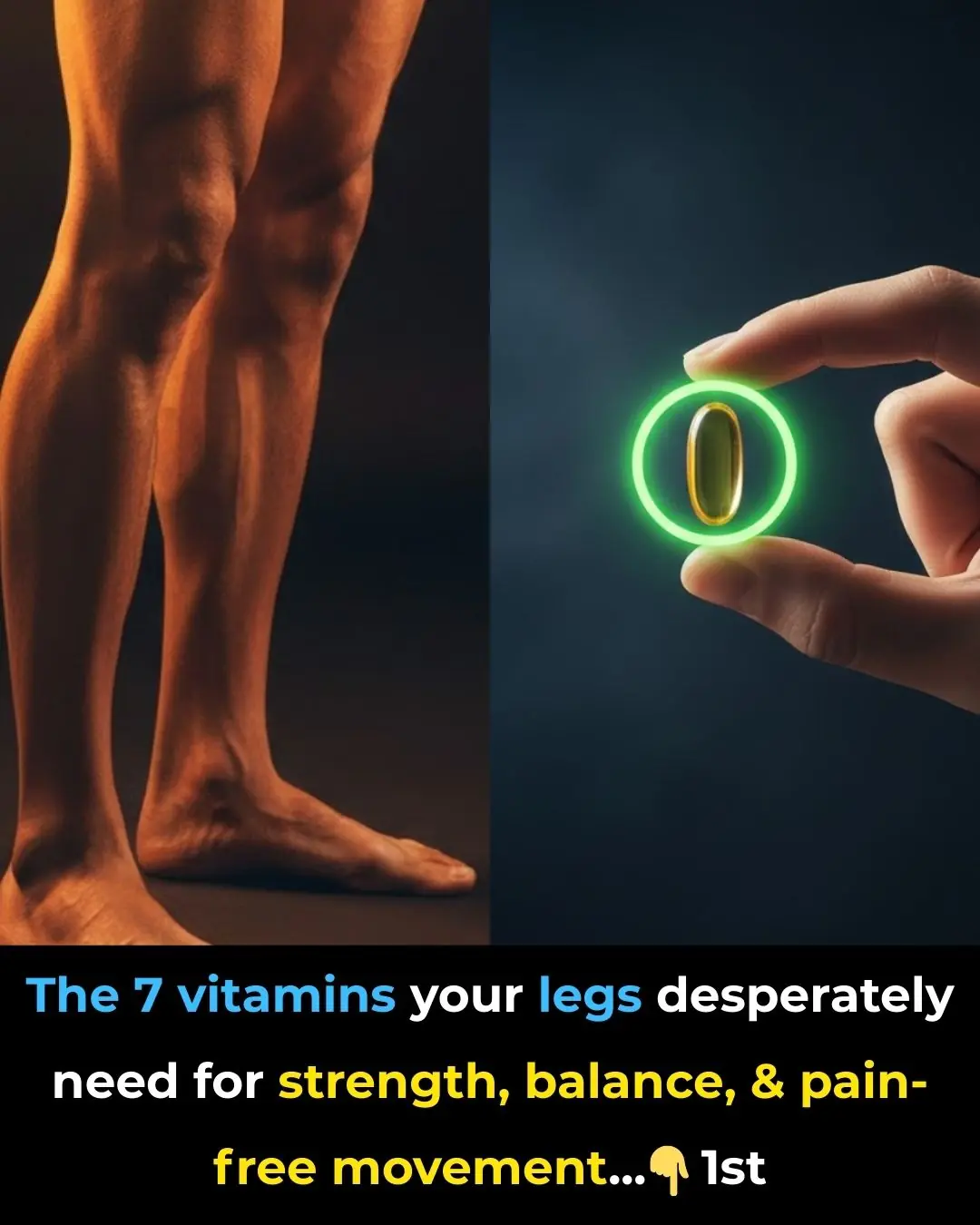
7 powerful vitamins you need for strong, healthy legs
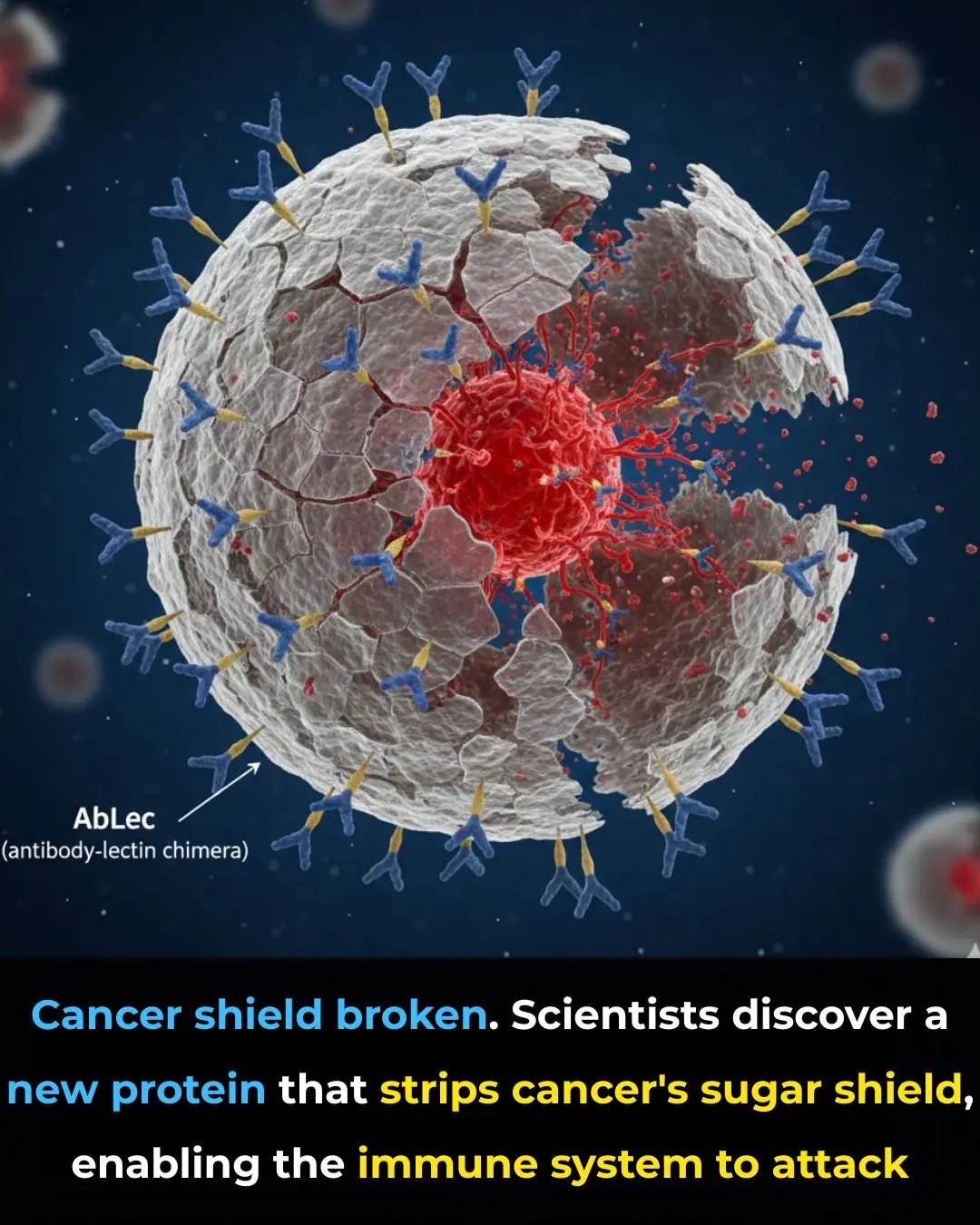
Scientists Discover Protein That Unmasks Cancer Cells, Boosting the Immune System’s Power
10 Scientifically Backed Reasons Why You Should Consume Ginger Everyday
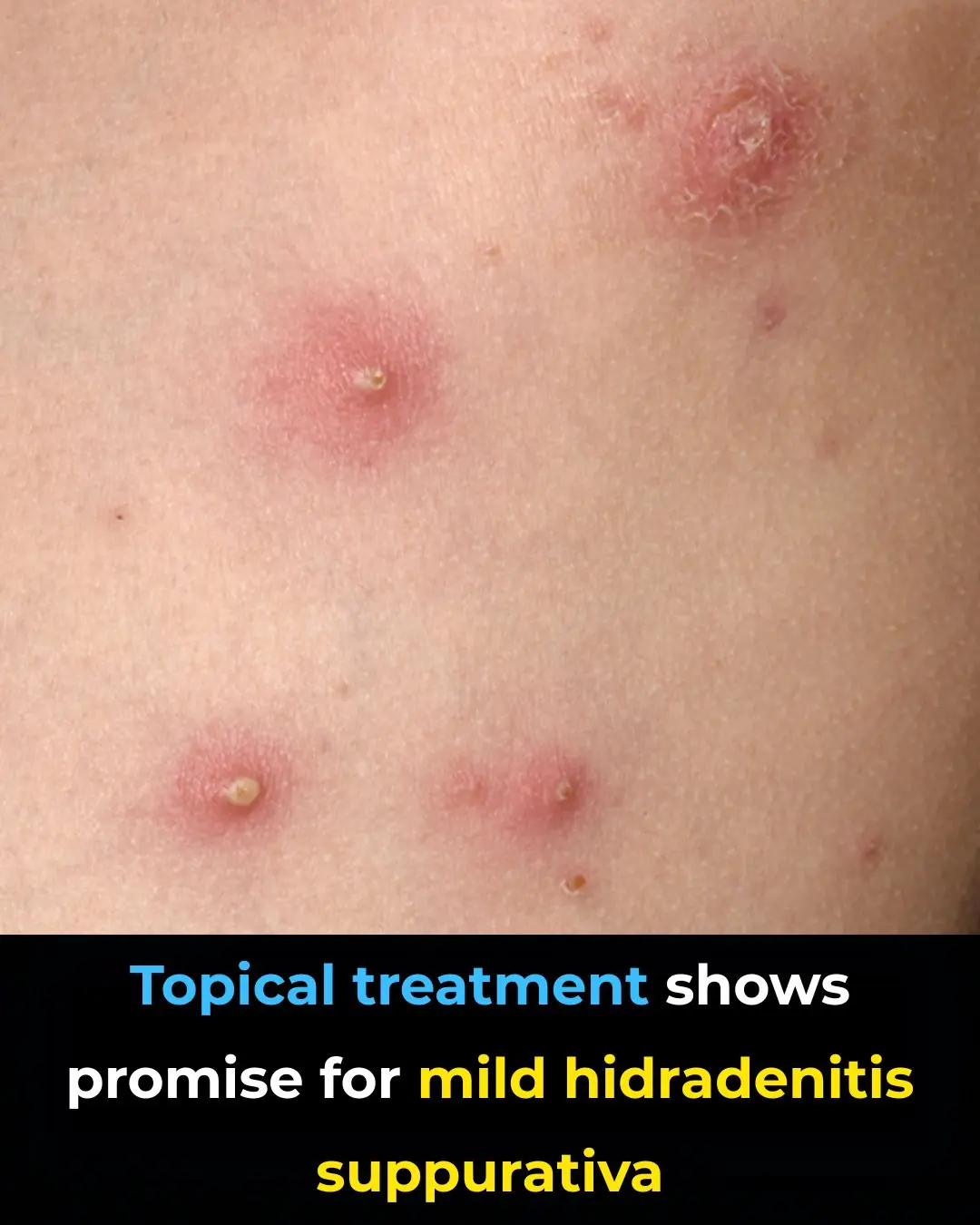
Can Anti-Inflammatory Topical Therapy Fill the Treatment Gap in Mild Hidradenitis Suppurativa?

GIP Reduces Postprandial Glucose Peaks but Does Not Prevent Hypoglycaemia in Men With Type 1 Diabetes

How Swimming Rewires the Brain and Strengthens Cognitive Health

How the Right Foods Boost Immunity and Speed Up Recovery

The Science of Touch: How Hugging Improves Stress, Mood, and Immunity

How Gut Bacteria Influence Anxiety, Stress, and Emotional Well-Being
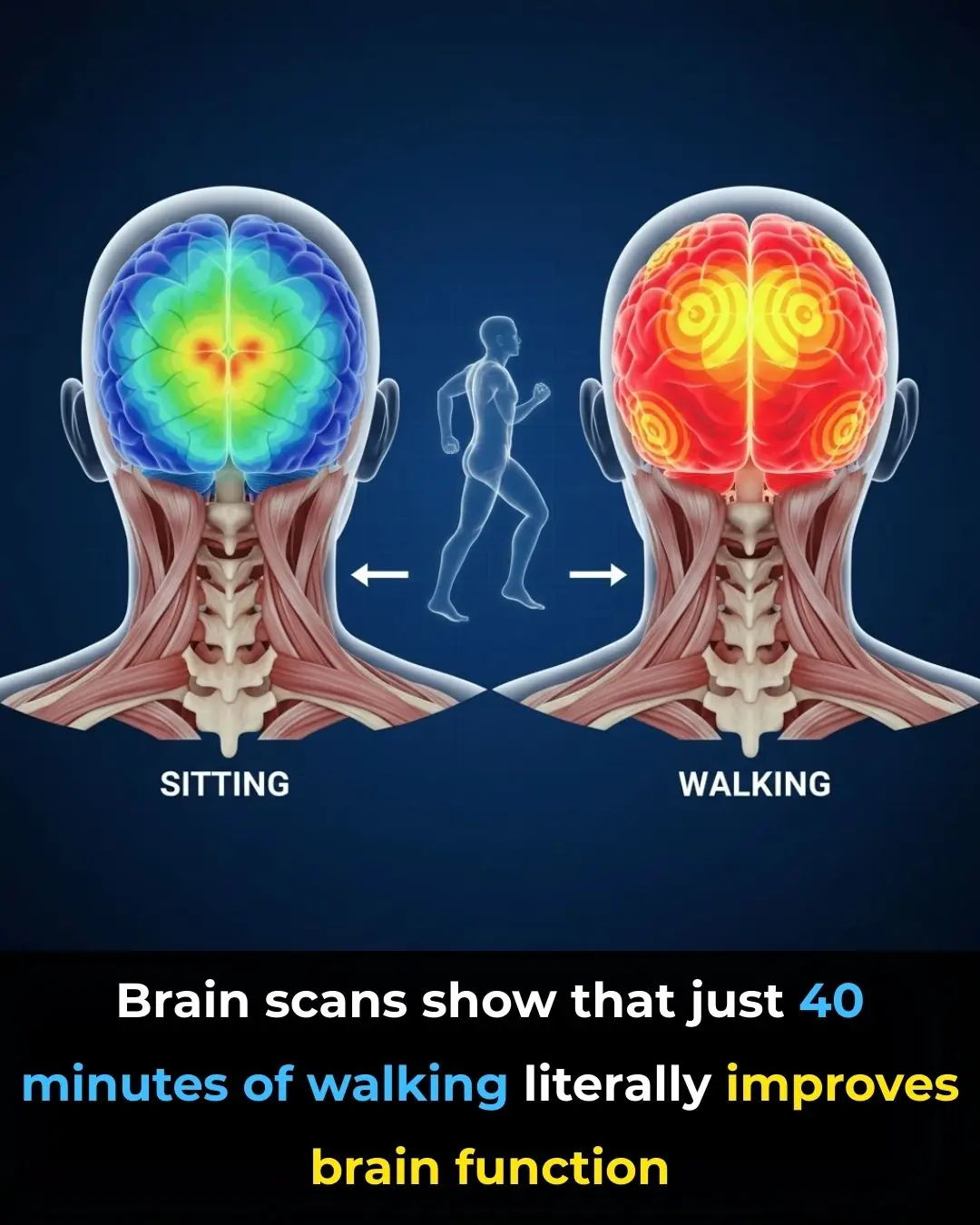
Your Brain on Walking: Why Movement Sparks Mental Clarity
New Protein Breakthrough Helps Immune System Unmask and Destroy Cancer Cells

Using Star Apple Leaves to Treat Acid Reflux: A Traditional Remedy

Early-stage fatty liver disease: 5 obvious signs that can be noticeable on your face; ignoring them could lead to serious health consequences
News Post

Everyone Fears Diabetes, but Diabetes “Fears” These 5 Foods

A Hard-Earned Lesson for Middle-Aged Parents: Let Go of These Habits, and Your Children Will Naturally Grow Closer

How Walking Activates the Brain: The Hidden Link Between Movement, Focus, and Mental Clarity

It’s Time to Protect Your Stomach: Remove These 5 Popular Vietnamese Breakfast Foods from Your Morning Menu
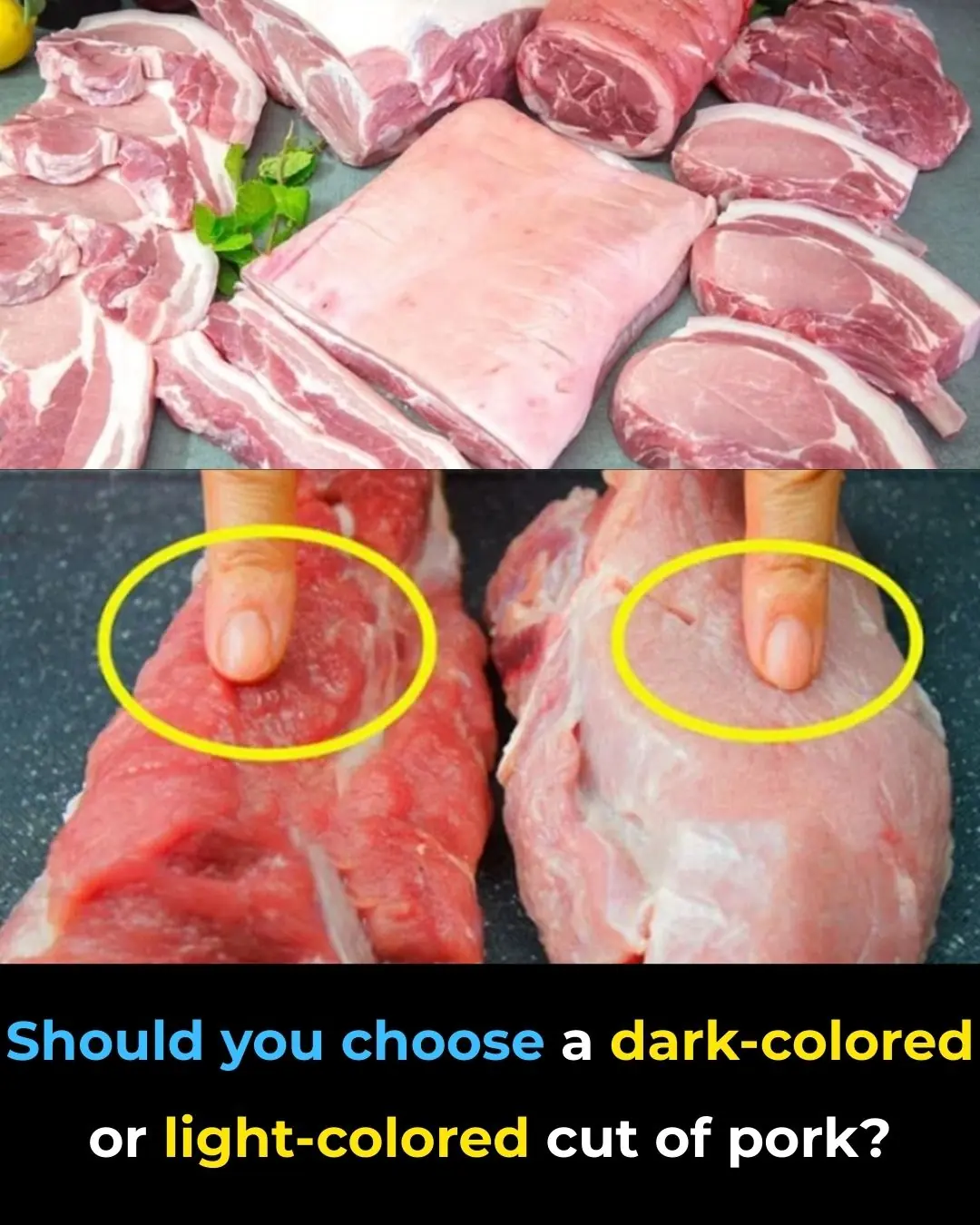

Should You Choose Dark-Colored or Light-Colored Pork?

Tips for growing ginger at home for big, plump tubers that you can enjoy all year round.

Putting these four things in the rice container will not only protect the rice from pests, but also make it taste better.

The secret to cooking fish without a fishy smell: 4 simple spices everyone should try.

Pour this type of water into the electric kettle, and all the limescale will be gone, leaving it sparkling clean like new.

Juelz Santana Dragged Online After Saying Kids “Don’t Really Need to Know How to Read”

Ja Rule 3 Losers Sucker-Punched Me Backstage If I Was Bruce Springsteen, They'd Be in Cuffs!!!

Viola Ford Fletcher, one of the last survivors of the Tulsa Race Massacre, dies at age 111

Sean Duffy urges passengers to dress better, be more polite while flying during ‘busiest Thanksgiving’ ever

Examination of the Hip-Hop Mogul

‘I’ve Stayed Quiet Long Enough’: Kenneka Jenkins’ Mother Makes Explosive Claims About Her Mysterious Death and the $10 Million Settlement
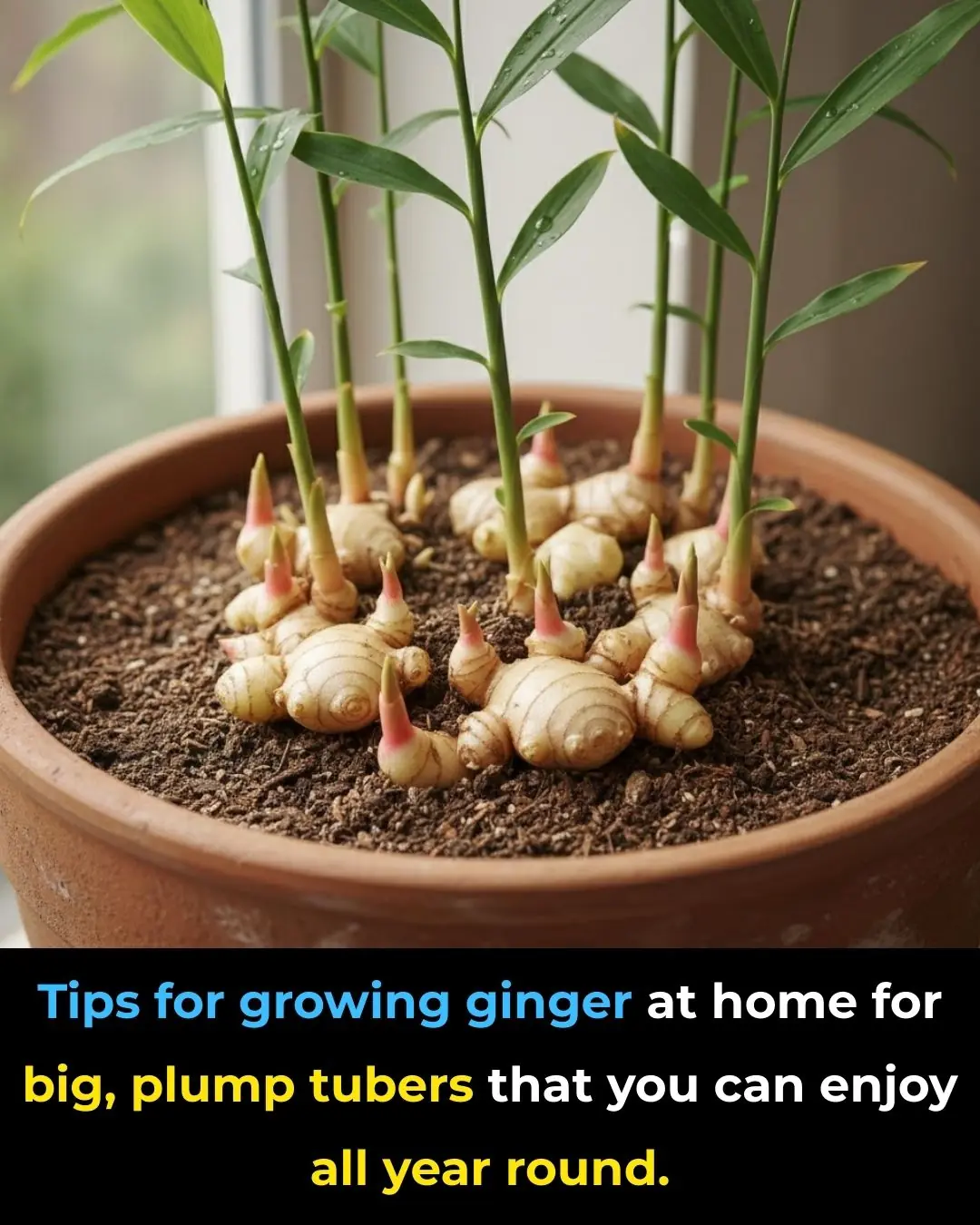

Tips for growing ginger at home for big, plump roots that can be eaten all year round

How to store chili peppers for several months so they stay as fresh as when picked, with plump flesh that doesn’t dry out and retains its flavor

A Clever Alternative to Caramel Coloring: Using Cola to Braise Meat Perfectly

How to Improve Blood Circulation Naturally (Research Based)
