Expanding Human Perception: Exploring the Limits of Vision and Hearing Through Technology
Human vision is confined to the "visible spectrum" of electromagnetic radiation, which spans wavelengths between approximately 400 nanometers (violet) and 700 nanometers (red). This limited range translates to frequencies between roughly 430 THz (red light) and 770 THz (violet light). Beyond this spectrum, electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet (UV), infrared (IR), X-rays, or radio waves, is entirely invisible to the human eye. This limitation highlights that there is much more happening around us than we can naturally perceive through sight.
Similarly, the range of human hearing falls between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz (20 kHz). Sounds below 20 Hz, known as infrasound, and those above 20 kHz, known as ultrasound, are beyond the capacity of human ears. While these sounds are inaudible to us, various animals, such as elephants, dolphins, and bats, can hear frequencies well beyond what humans can detect. For example, elephants communicate using infrasound, allowing them to send signals over long distances. Bats, on the other hand, use ultrasonic echolocation to navigate and hunt for prey in complete darkness.
These biological constraints remind us that human perception represents only a small fraction of the broader spectrum of reality. Much of the energy and activity that permeates the universe operates beyond the limitations of our senses. In fact, a vast portion of the universe's phenomena is invisible and inaudible to us without the aid of special tools. For instance, phenomena like cosmic radiation, X-rays emitted by distant stars, or the detailed inner workings of biological organisms are all outside the reach of our natural senses.
To expand our perception and uncover the unseen, scientists have developed a range of sophisticated instruments. Infrared cameras, for example, detect heat energy in the form of infrared radiation, allowing us to visualize temperature variations that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye. X-ray machines, widely used in medical imaging, can penetrate the body to reveal internal structures, providing critical insights into human health. Ultrasound scanners, used both in medicine and industry, rely on high-frequency sound waves to create images of soft tissues or to monitor the condition of materials.
These technological advancements illustrate how human ingenuity has overcome the limitations of our biological senses, enabling us to explore and understand aspects of the world that were once hidden. While we may never be able to directly perceive all of the universe’s energy and phenomena, we can now explore them through the aid of artificial extensions of our senses. Instruments like infrared cameras, X-ray machines, and ultrasound scanners have revolutionized fields such as medicine, astronomy, and environmental science, offering us glimpses into realms beyond our natural capabilities.
This knowledge extends not only to the world around us but also to distant parts of the universe. For example, telescopes that detect electromagnetic radiation beyond visible light, such as radio waves or gamma rays, have provided astronomers with valuable data about faraway galaxies, black holes, and the cosmic microwave background—the residual heat left over from the Big Bang. Such discoveries would have been impossible without the ability to perceive beyond the visible spectrum.
In conclusion, while our sensory perception is limited, the development of instruments to extend our abilities has greatly expanded our understanding of both the immediate and the distant universe. These tools allow us to explore phenomena that exist far beyond what our eyes and ears can detect, opening up vast new frontiers for scientific discovery and technological advancement. As technology progresses, we continue to push the boundaries of what we can perceive, gaining deeper insights into the world around us and the universe beyond.
Sources:
-
"The Nature of Light" – American Physical Society. https://www.aps.org
-
"How Bats Use Echolocation" – National Geographic. https://www.nationalgeographic.com
-
"The Role of Infrasound in Animal Communication" – Scientific American. https://www.scientificamerican.com
-
"Infrared Imaging and Medical Applications" – National Institutes of Health. https://www.nih.gov
News in the same category


A Heartwarming Tale of Workplace Compassion: A Father's 262 Days of Paid Leave

Debunking the Myth: Why Humans Did Not Evolve from Monkeys
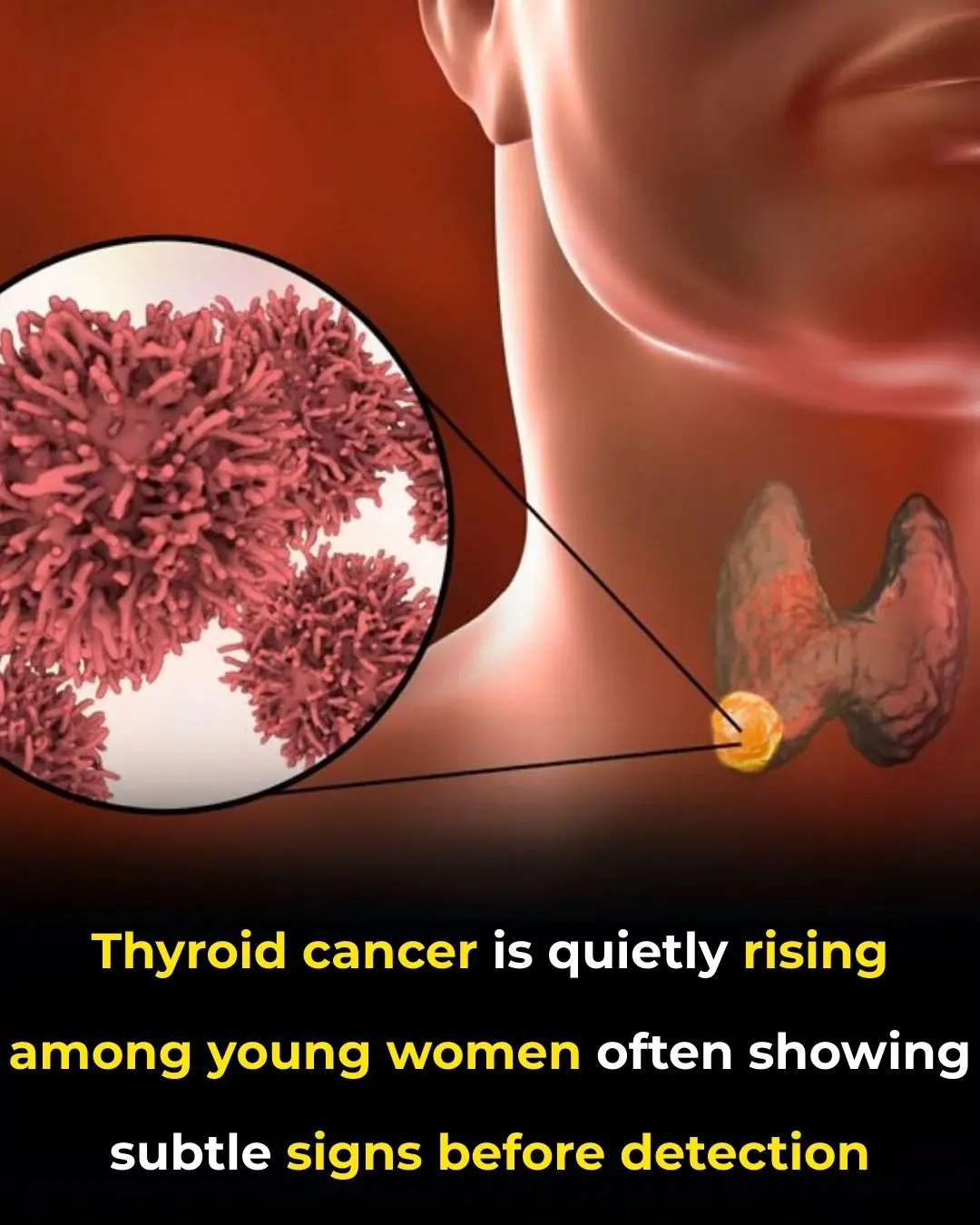
The Hidden Climb of Thyroid Cancer in Younger Women

56 Percent Of Americans Don’t Think We Should Teach Arabic Numerals In School

People Shocked After Finally Realizing What McDonald's Sweet 'N' Sour Sauce Is Really Made From

Eating Kimchi For 12 Weeks Helped People's Immune Cells Get Better At Spotting Viruses While Also Stopping Overreactions

Drunk Raccoon Turns Liquor Store into His Personal Bar Before Passing Out in the Bathroom

Turning Chicken Manure into Renewable Energy: The Netherlands' Circular Economy Solution
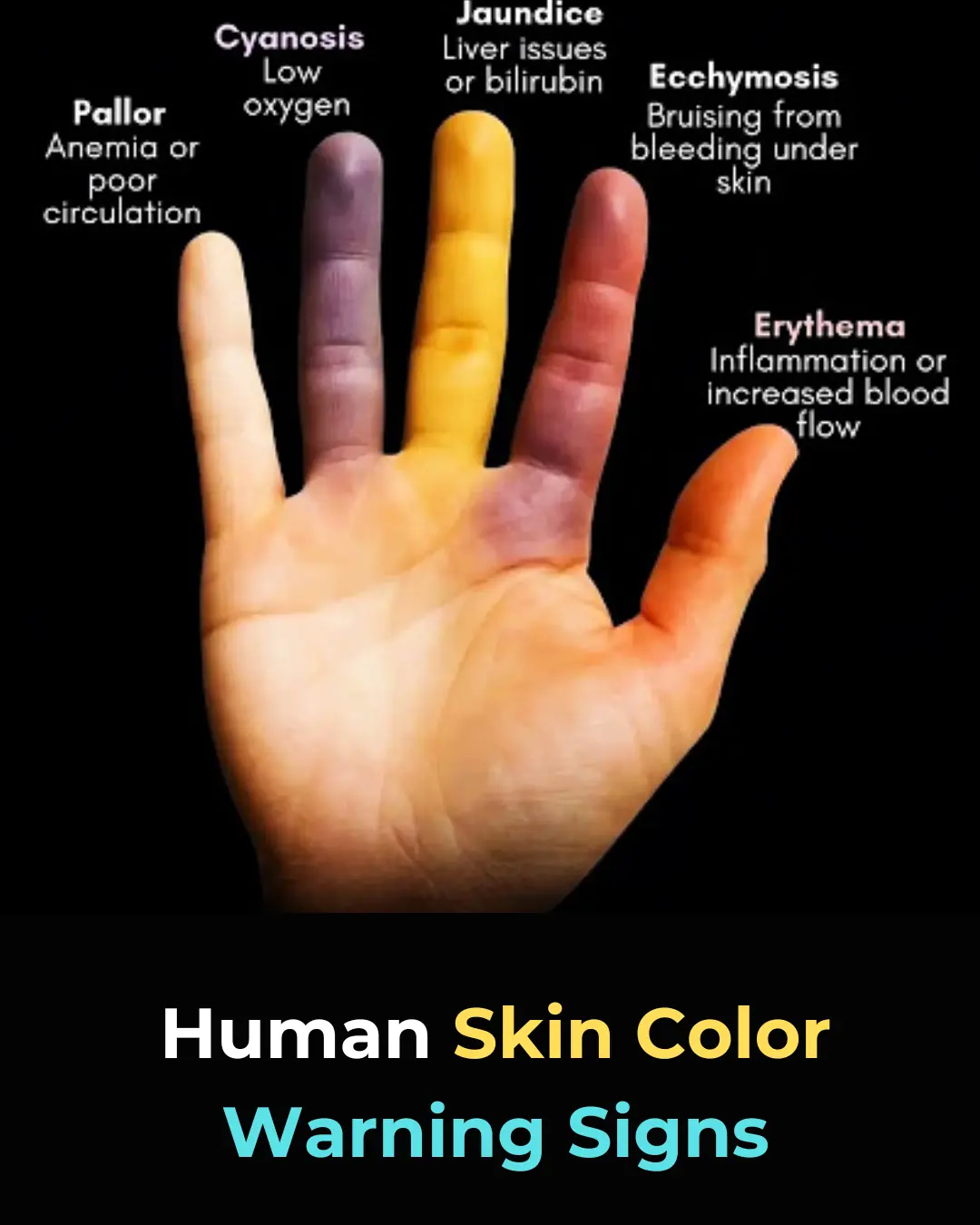
Understanding Skin Color Changes as Early Warning Signs of Health Issues

Rogfast Tunnel: Norway's Record-Breaking Undersea Highway Project

CDC's Historic Decision to End Monkey Testing: A Shift Towards More Humane and Advanced Research Models

Teen Inventor Creates Battery-Free Flashlight Powered Only by Human Body Heat
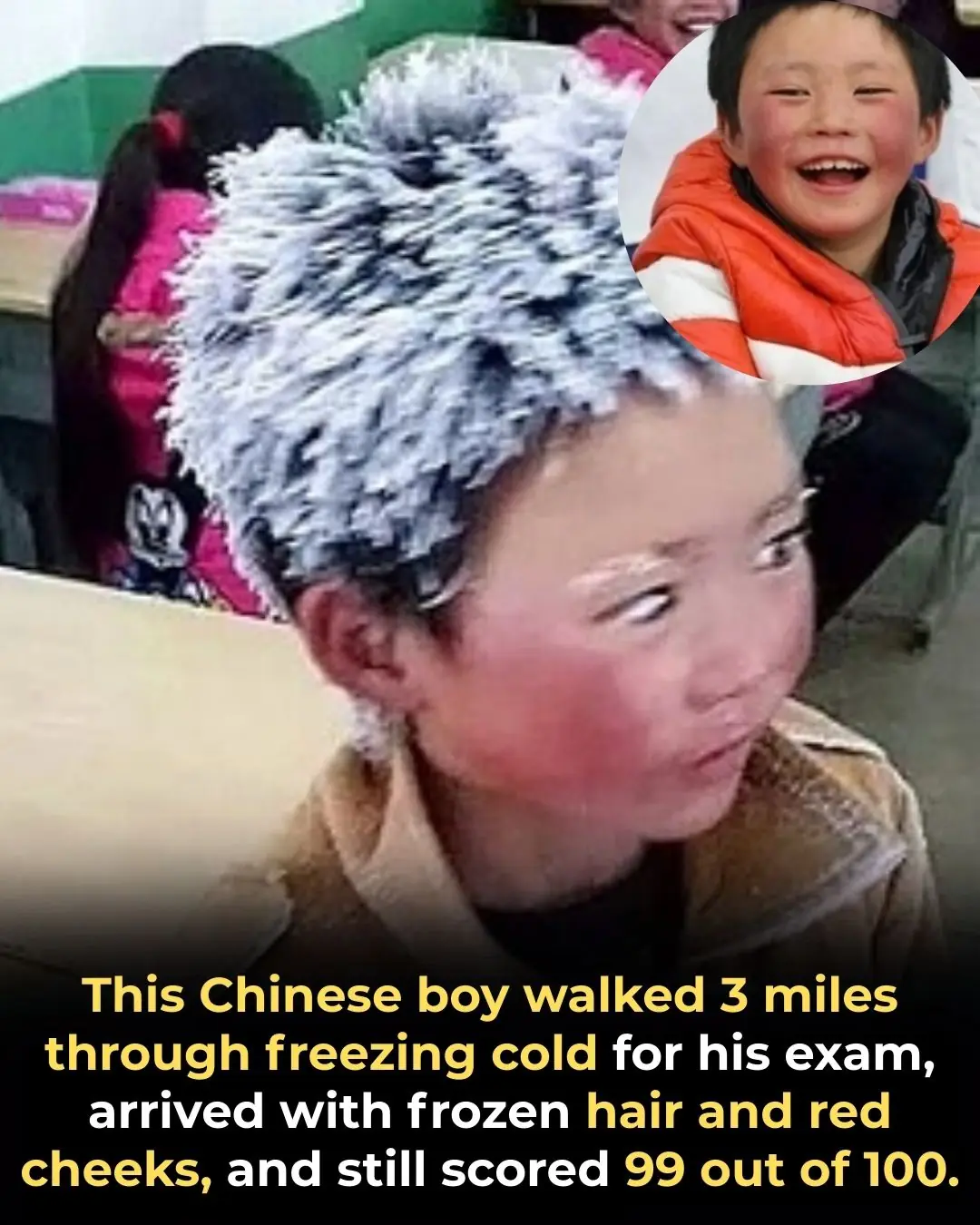

The Boy Who Walked Through Ice: How Wang Fuman Inspired the World

From –4°F to Spring in Minutes: The Incredible 1943 Spearfish Temperature Shock

Saman Gunan: The Diver Who Gave His Life to Save the Wild Boars Team
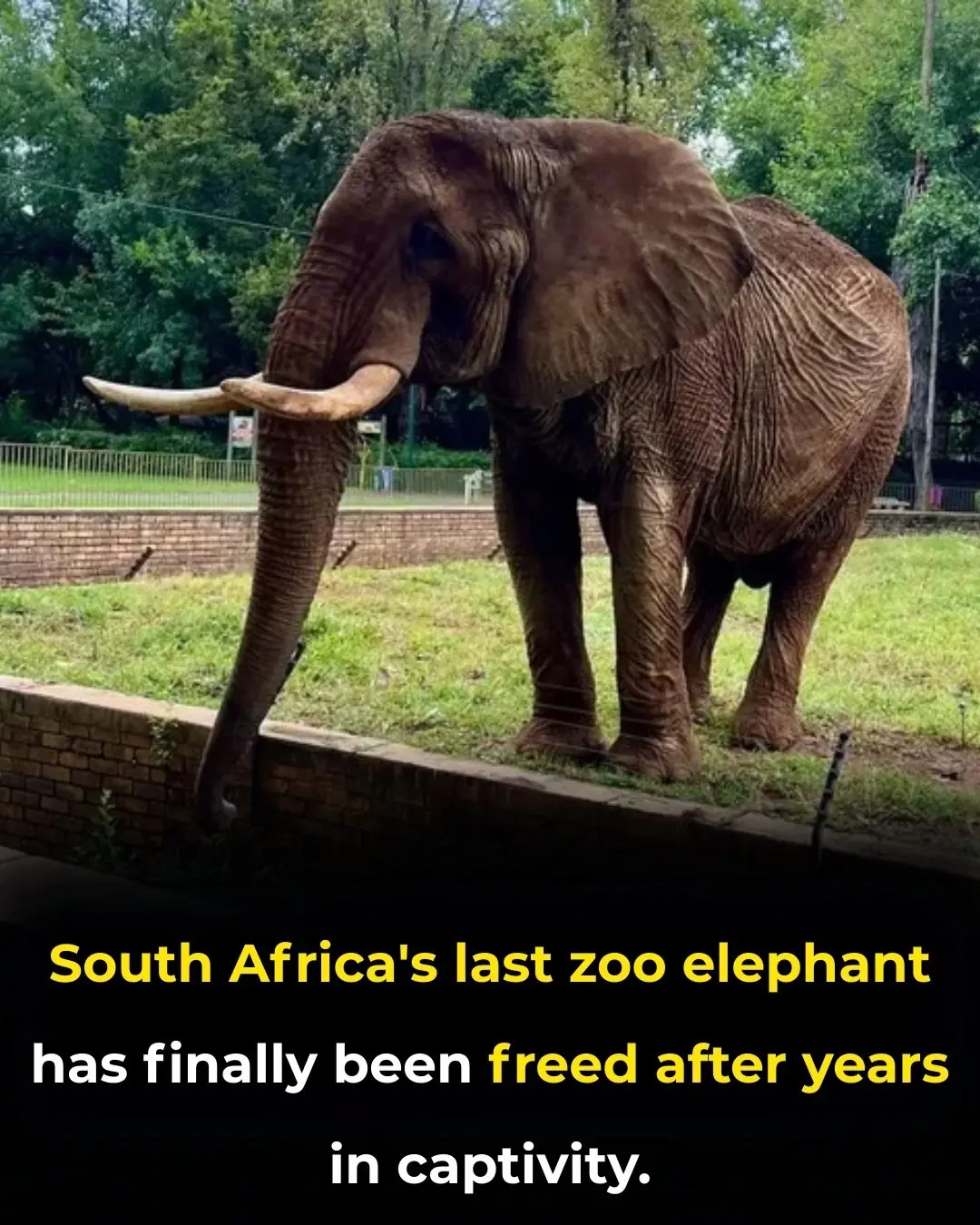

From Circus to Sanctuary: Charley the Elephant Finds Freedom After Four Decades

10 Heartbreaking Reasons Children Stop Visiting Parents

8 Mind-Bending Optical Illusions That Test Your Level of Self-Awareness
News Post

Sip Your Way to Vibrance: The Ultimate Lipton, Cloves, and Ginger Tea for Women’s Wellness
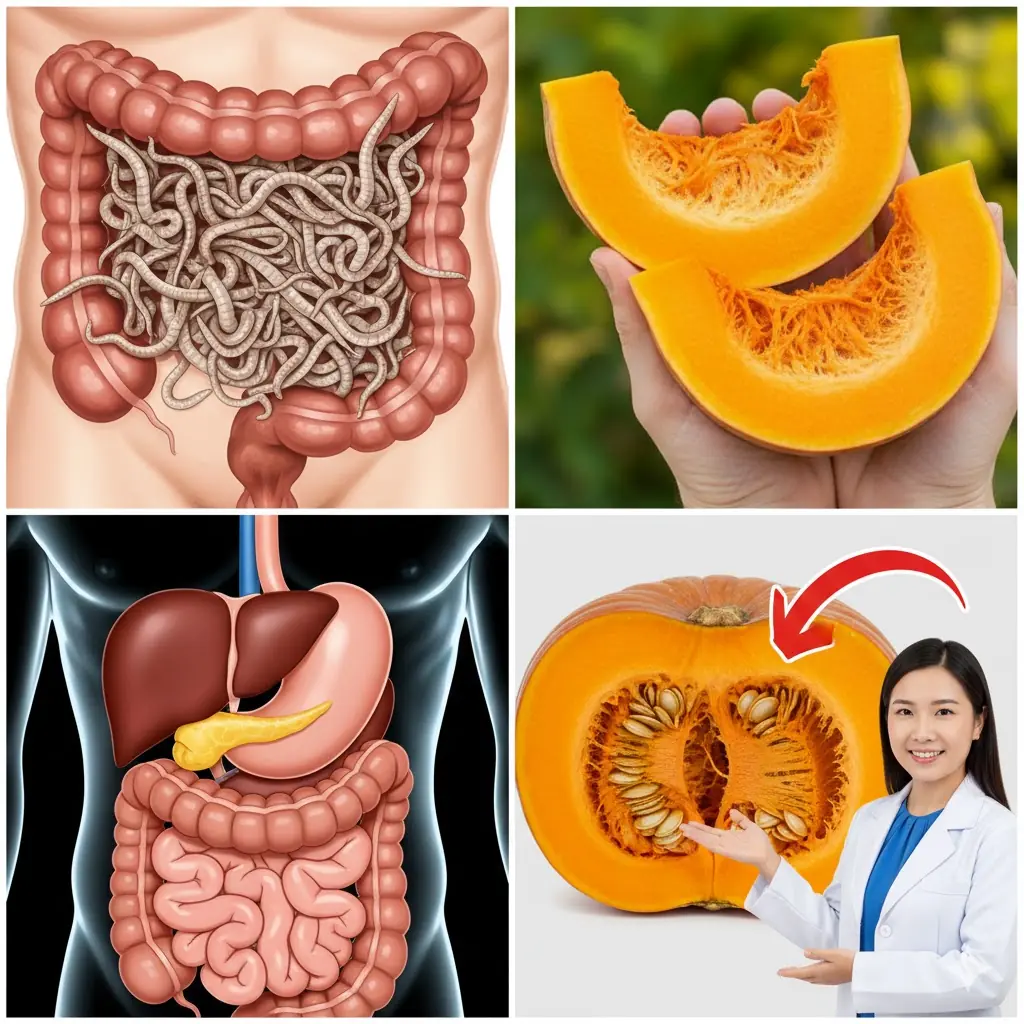
Pumpkin Seeds: Nature’s Fierce Parasite Fighters for a Healthier Gut

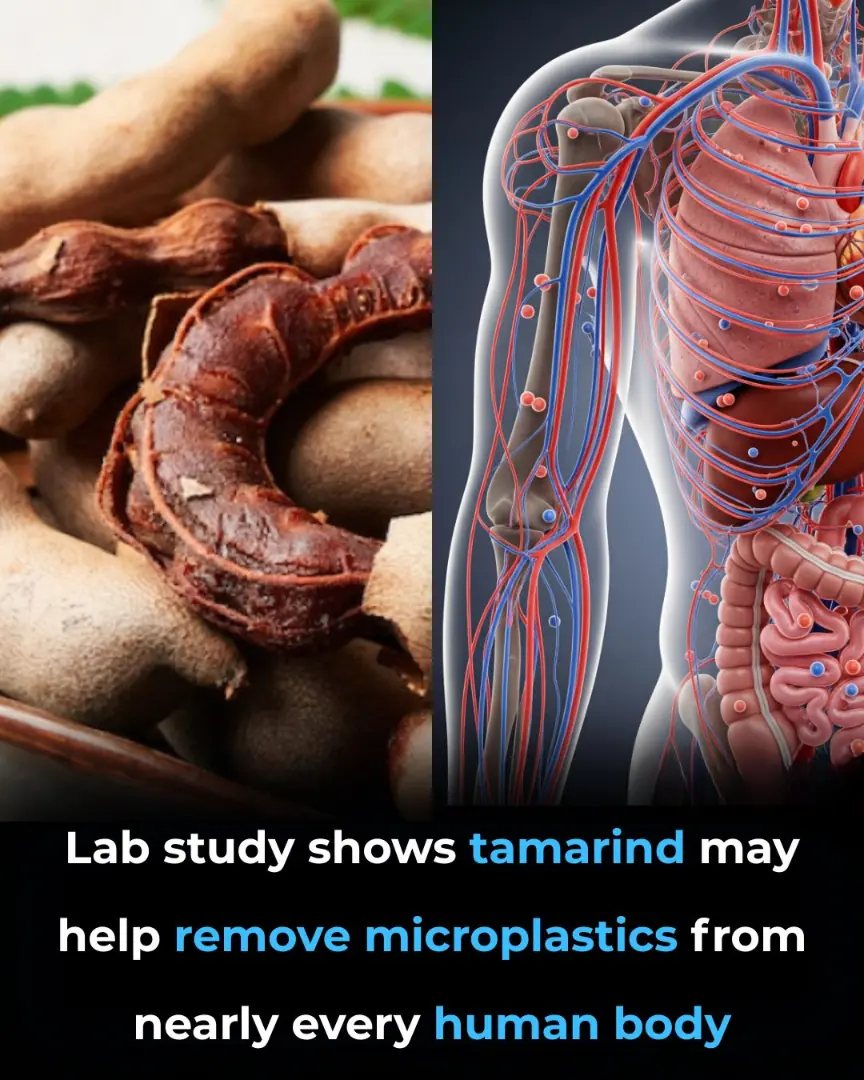
Tamarind: A Promising Natural Solution to Help the Body Clear Microplastics

A Heartwarming Tale of Workplace Compassion: A Father's 262 Days of Paid Leave

Debunking the Myth: Why Humans Did Not Evolve from Monkeys

The Hidden Climb of Thyroid Cancer in Younger Women

56 Percent Of Americans Don’t Think We Should Teach Arabic Numerals In School

From Rain to Runway: How Singapore’s Changi Airport Saves Over 8 Million Gallons of Water a Year

People Shocked After Finally Realizing What McDonald's Sweet 'N' Sour Sauce Is Really Made From

Eating Kimchi For 12 Weeks Helped People's Immune Cells Get Better At Spotting Viruses While Also Stopping Overreactions

Drunk Raccoon Turns Liquor Store into His Personal Bar Before Passing Out in the Bathroom

Turning Chicken Manure into Renewable Energy: The Netherlands' Circular Economy Solution
Why Sleeping on Your Left Side Is the Best Thing You’re Not Doing

Rising Tide of Change: The World’s Coastlines Are Entering a New Era

The Girl Who Said No — And Changed a Nation Forever

Understanding Skin Color Changes as Early Warning Signs of Health Issues

Rogfast Tunnel: Norway's Record-Breaking Undersea Highway Project

CDC's Historic Decision to End Monkey Testing: A Shift Towards More Humane and Advanced Research Models
