Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Causes and Red-Flag Symptoms
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is not a disease itself but a warning sign that something in the digestive system is seriously wrong. Because symptoms can range from mild to life-threatening, understanding the causes and red-flag warning signs can help you detect problems early and seek medical care before complications arise.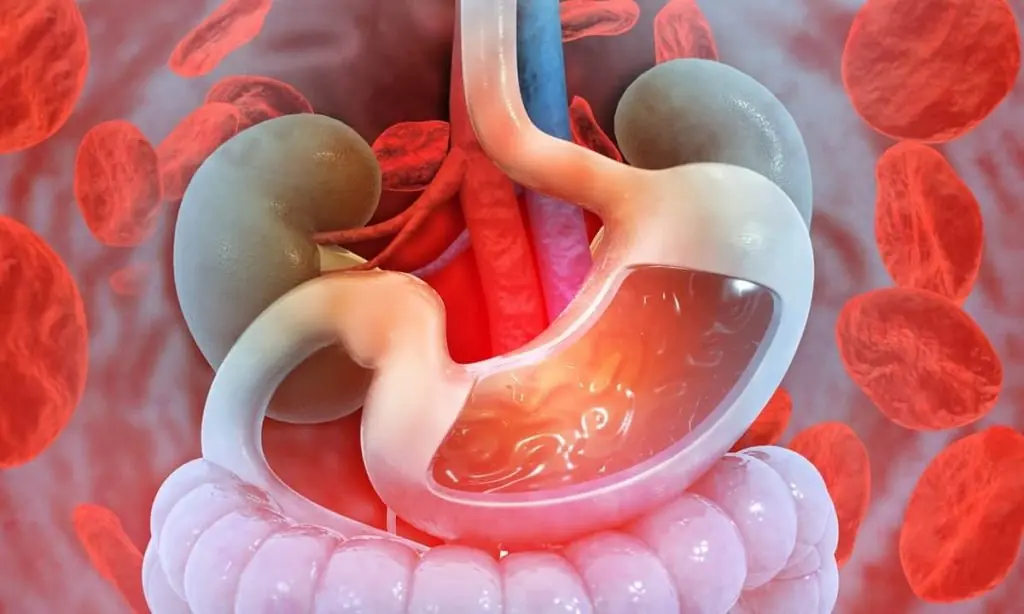
What Is Gastrointestinal Bleeding?
Gastrointestinal bleeding refers to any bleeding that occurs in the digestive tract—from the esophagus and stomach down to the intestines, rectum, and anus. Bleeding may be visible (such as vomiting blood or noticing blood in stool) or hidden, detectable only through tests.
Doctors usually classify GI bleeding into:
-
Upper GI bleeding – bleeding from the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum
-
Lower GI bleeding – bleeding from the colon, rectum, or small intestine
Both types can be dangerous, but upper GI bleeding tends to be more urgent.
Common Causes of GI Bleeding
1. Peptic Ulcers
This is the leading cause of upper GI bleeding. Ulcers develop when stomach acid damages the lining of the stomach or duodenum.
Key triggers include:
-
H. pylori infection
-
Long-term NSAID use (ibuprofen, aspirin)
-
Excess alcohol
-
Smoking
Ulcers can erode blood vessels, causing slow or severe bleeding.
2. Gastritis and Esophagitis
Inflammation caused by alcohol, acidic foods, stress, medications, or infection can irritate the stomach or esophagus lining and cause bleeding.
3. Hemorrhoids
Dilated veins in the rectum or anus cause bright red blood during bowel movements. While common and usually mild, chronic bleeding can lead to anemia.
4. Diverticulosis
Small pouches in the colon wall can rupture and bleed suddenly, causing painless but heavy bleeding.
5. Colon Polyps and Colon Cancer
These growths may bleed slowly over time. Because bleeding is often hidden, cancer can go undetected for years without screening.
6. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis cause chronic inflammation and frequent bleeding.
7. Esophageal Varices
These enlarged veins, common in people with liver disease, can rupture suddenly, causing life-threatening bleeding.
8. Trauma or Swallowing a Foreign Object
Accidents, sharp foods, or injuries can damage the GI tract lining.
Red-Flag Symptoms You Should Never Ignore
1. Vomiting Blood (Hematemesis)
Blood may appear bright red or look like coffee grounds. This is a medical emergency, often caused by ulcers, varices, or severe gastritis.
2. Black, Tarry Stool (Melena)
Black stool suggests digested blood from upper GI bleeding. It must be evaluated immediately.
3. Bright Red Blood in Stool (Hematochezia)
This usually indicates lower GI bleeding from hemorrhoids, diverticulosis, or colon disease. Large amounts require urgent care.
4. Severe or Persistent Abdominal Pain
Pain with bleeding can signal ulcers, bowel inflammation, or even internal rupture.
5. Unexplained Fatigue and Weakness
Slow internal bleeding can lead to chronic anemia, causing fatigue, paleness, dizziness, and rapid heartbeat.
6. Sudden Drop in Blood Pressure or Fainting
This means severe blood loss and requires immediate medical intervention.
How Doctors Diagnose GI Bleeding
Blood Tests
Check hemoglobin levels to determine the extent of blood loss.
Endoscopy
A camera is inserted through the mouth to find bleeding in the upper GI tract.
Colonoscopy
Used for bleeding in the colon or rectum.
CT Scan or Capsule Endoscopy
Helpful when standard tests fail to identify the cause.
Treatment Options
1. Medication
-
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) for ulcers
-
Antibiotics for H. pylori
-
Anti-inflammatory medications for IBD
2. Endoscopic Treatment
Doctors may burn, clip, or inject medication directly into bleeding vessels.
3. Blood Transfusion
Required for severe blood loss.
4. Surgery
For life-threatening bleeding or cancer.
When to Seek Medical Care
Go to the ER immediately if you experience:
-
Vomiting blood
-
Black stool
-
Heavy rectal bleeding
-
Severe abdominal pain
-
Fainting or shock symptoms
Even mild bleeding should be evaluated to rule out serious conditions.
Prevention Tips
-
Limit alcohol and spicy foods
-
Avoid long-term NSAID use
-
Manage stress
-
Treat H. pylori promptly
-
Get regular colonoscopies
-
Maintain a high-fiber diet
Early detection can save your life.
News in the same category


A Natural Pain Reliever for Legs, Varicose Veins, Rheumatism, and Arthritis
Colon Cancer: Why Early Screening Saves Lives
How Microplastics Enter Your Body — And How to Strengthen Your Gut to Block and Remove Them

Magnesium: The Benefits, the Risks, and the Safe Way to Take It — Especially for Your Kidneys
H. pylori Infection: Symptoms and How It Damages Your Stomach

7 Warning Signs Your Heart Isn’t Healthy — And 7 Symptoms You Should Never Ignore
16 Early Warning Signs Your Liver Is Sluggish And Toxins Are Being Stored In Your Fat Cells
The #1 way to flush microplastics from your body (It’s shockingly simple)

12 Foods That Protect the Heart in Surprising Ways

12 Herbal Remedies That Actually Work: Effective Natural Solutions for Common Ailments
Pulmonary Fibrosis: Early Signs and Treatment Options

Whooping Cough in Adults: The Unexpected Comeback
Tuberculosis Symptoms: What You Need to Know Early
🌿 How to Naturally Support Wart & Skin Tag Removal (Using a Simple DIY Remedy)
Doctors reveal the surprising reason your legs are the first to fail
🧄 Garlic’s Real Health Benefits — What Science Says About This Ancient Remedy
This One Simple Move at Night Stops Leg Cramping Fast

This ancient spice opens your arteries like magic and supercharges your heart
News Post

Two Teens Mock Poor Old Lady On Bus

Your $2 Bill May Be Worth a Lot More Than You Think

Two Teens Mock Poor Old Lady On Bus

The Spice That Protects: The Remarkable Health Power of Cloves

Ignite Unstoppable Mornings: The Banana–Coffee Elixir You Need Now

The Homemade Garlic & Lemon Secret to Strengthen and Lengthen Your Nails

4 Fruits You Should Eat in Moderation After Age 60 — And How to Enjoy Them Without Losing Muscle

Cloves to Eliminate Nail Fungus Naturally

A Natural Pain Reliever for Legs, Varicose Veins, Rheumatism, and Arthritis

Colon Cancer: Why Early Screening Saves Lives

How Microplastics Enter Your Body — And How to Strengthen Your Gut to Block and Remove Them

Magnesium: The Benefits, the Risks, and the Safe Way to Take It — Especially for Your Kidneys

H. pylori Infection: Symptoms and How It Damages Your Stomach

7 Warning Signs Your Heart Isn’t Healthy — And 7 Symptoms You Should Never Ignore

The Genius Reason People Pour Baking Soda Down the Sink — And Why You Should Too

16 Early Warning Signs Your Liver Is Sluggish And Toxins Are Being Stored In Your Fat Cells

Meet Our Cosmic Neighbor — The Andromeda Galaxy (M31)

The #1 way to flush microplastics from your body (It’s shockingly simple)
