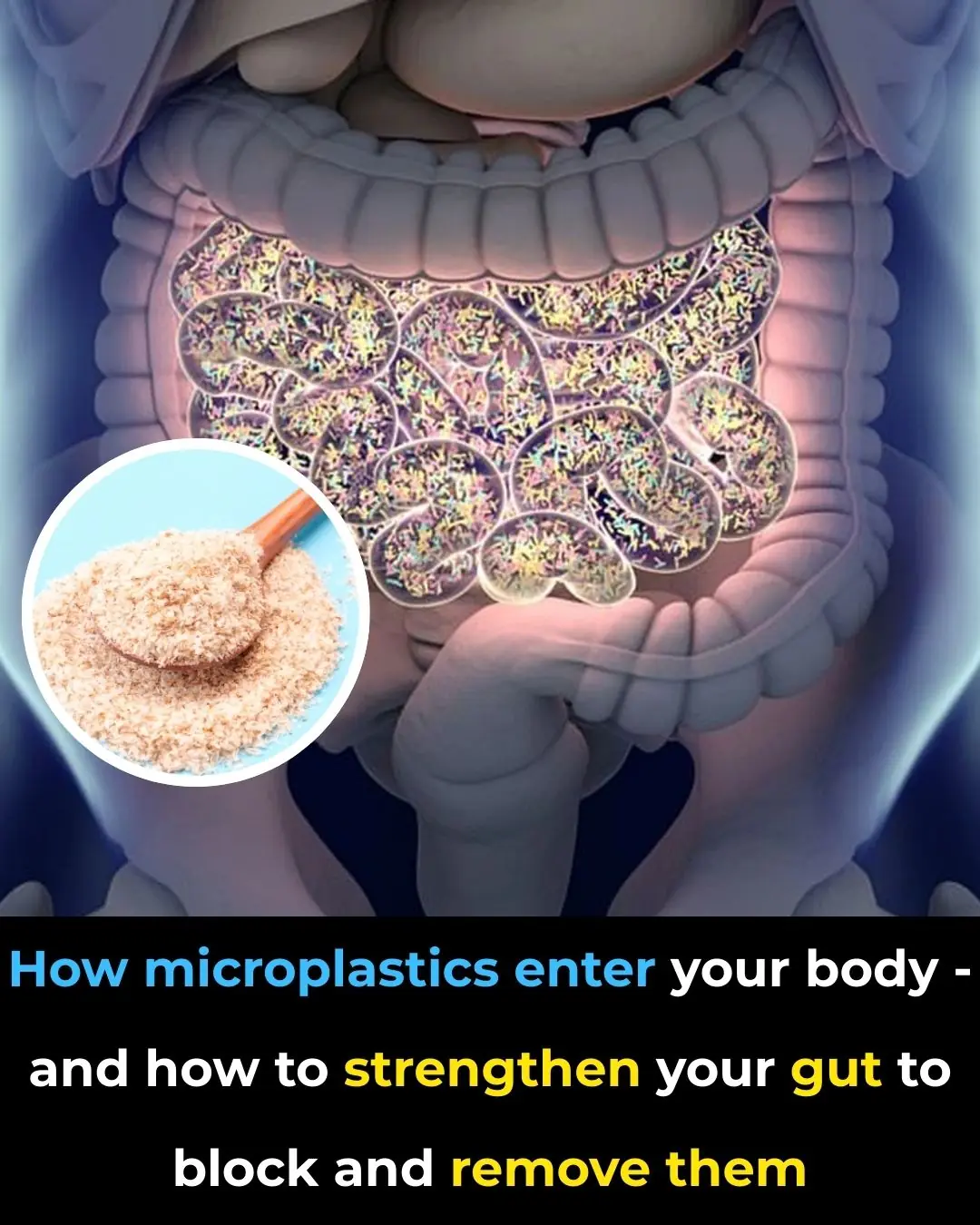
How Microplastics Enter Your Body — And How to Strengthen Your Gut to Block and Remove Them
Microplastics are no longer just an environmental problem — they are a human health problem. These invisible plastic fragments, and their even smaller cousins called nanoplastics, have now been detected in human blood, lung tissue, the digestive system, the brain, and even inside arterial plaque. Exposure is unavoidable: from water bottles and food packaging to dust in the air.
But here’s the empowering part: your body has a natural system designed to block, trap, and remove these particles — your gut.
Strengthening your gut is the single most effective strategy to reduce microplastic absorption and increase elimination.
This CKD Health article breaks down the science and gives you practical, evidence-backed steps to support your liver, kidneys, arteries, and digestive tract — the systems most affected by microplastic exposure.
Key Takeaways
-
Your gut is the frontline defense against microplastics entering your bloodstream.
-
Strengthening the gut barrier helps prevent microplastic absorption.
-
Soluble fiber acts like a sponge, binding toxins and helping flush them out in stool.
-
Polyphenols reduce inflammation, support gut bacteria, and improve detoxification.
-
Hydration and regular bowel movements are essential for removing plastics from your body.
1. Strengthen the Gut Barrier — Your First Line of Defense
Your intestinal lining is only one-cell thick, but it is designed to be highly selective — letting nutrients in while keeping toxins OUT.
When the gut barrier becomes weakened (“leaky gut”), gaps form, allowing microplastics and inflammatory molecules to leak into your bloodstream.
Microplastics are tiny enough to slip through weakened junctions.
What strengthens the gut wall?
✔ Collagen & Bone Broth
Provide amino acids (glycine, proline) your body uses to rebuild gut tissue.
✔ L-Glutamine
The primary fuel source for intestinal cells. Taking 3–5 g a few times per week helps repair leaky gut.
✔ Zinc & Vitamin D
Critically important for tight junction integrity.
A strong gut wall = fewer microplastics absorbed.
2. Remove Gut-Damaging Substances — Especially Emulsifiers
Some of the worst offenders for gut inflammation are emulsifiers found in packaged foods.
The most harmful: Polysorbate 80 — used to deliberately create gut inflammation in lab studies.
It destroys the mucus layer that protects your gut lining, increasing permeability and inflammation, making microplastic absorption MUCH easier.
Avoid foods containing:
-
Polysorbate 80
-
Polysorbate 60
-
Carboxymethylcellulose
-
Processed sauces
-
Ice creams and packaged dressings
Pair this with stress reduction — because chronic cortisol directly weakens the gut lining.
3. Use Soluble Fiber to “Trap & Remove” Microplastics
Soluble fiber acts like a gel sponge, binding bile acids in the intestines.
Why does this matter?
Bile is capable of binding fat-soluble toxins — including microplastics.
When soluble fiber binds bile, it:
-
Forms a fiber–bile–toxin complex
-
Prevents microplastic absorption
-
Removes them through stool
This is the most effective, natural elimination pathway.
Best soluble fiber sources:
-
Chia seeds
-
Flaxseeds
-
Psyllium husk
-
Oats
-
Apples
Studies show microplastics are consistently found in stool — meaning elimination works. Fiber makes this process far more efficient.
4. Hydration + Transit Time — The Forgotten Detox Tools
For detoxification to work, your gut must move regularly.
Slow transit = more time for microplastics to be absorbed.
Proper hydration:
-
Supports bowel movement
-
Helps soluble fiber form its gel
-
Enhances kidney filtration
-
Prevents constipation (reducing toxin reabsorption)
Aim for filtered water and steady hydration throughout the day — not chugging all at once.
5. Polyphenols — Anti-Inflammatory Powerhouses for the Gut
Polyphenols give plants their color and support your gut microbiome while reducing inflammation.
Why they matter for microplastics:
-
Reduce oxidative stress caused by plastics
-
Strengthen gut barrier function
-
Feed beneficial gut bacteria (prebiotic effect)
-
Produce powerful postbiotics that repair cells
Best polyphenol-rich foods:
-
Berries
-
Pomegranates
-
Green tea
-
Turmeric
-
Dark leafy greens
Postbiotics like urolithin A, created from polyphenols, reduce inflammation throughout the body — including the brain and cardiovascular system, where microplastics are now being found.
Conclusion
You can’t completely avoid microplastics — but you CAN dramatically reduce how many enter your bloodstream and tissues.
Your gut is your strongest line of defense.
By:
-
Strengthening your gut barrier
-
Eliminating emulsifiers
-
Increasing soluble fiber
-
Staying hydrated
-
Eating polyphenol-rich foods
…you empower your body to block microplastic absorption and enhance removal, protecting your liver, kidneys, heart, and immune system.
Your environment may be filled with plastic —
but the internal environment of your gut is something you CAN control.
News in the same category


A Natural Pain Reliever for Legs, Varicose Veins, Rheumatism, and Arthritis
Colon Cancer: Why Early Screening Saves Lives

Magnesium: The Benefits, the Risks, and the Safe Way to Take It — Especially for Your Kidneys
H. pylori Infection: Symptoms and How It Damages Your Stomach

7 Warning Signs Your Heart Isn’t Healthy — And 7 Symptoms You Should Never Ignore
Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Causes and Red-Flag Symptoms
16 Early Warning Signs Your Liver Is Sluggish And Toxins Are Being Stored In Your Fat Cells
The #1 way to flush microplastics from your body (It’s shockingly simple)

12 Foods That Protect the Heart in Surprising Ways

12 Herbal Remedies That Actually Work: Effective Natural Solutions for Common Ailments
Pulmonary Fibrosis: Early Signs and Treatment Options

Whooping Cough in Adults: The Unexpected Comeback
Tuberculosis Symptoms: What You Need to Know Early
🌿 How to Naturally Support Wart & Skin Tag Removal (Using a Simple DIY Remedy)
Doctors reveal the surprising reason your legs are the first to fail
🧄 Garlic’s Real Health Benefits — What Science Says About This Ancient Remedy
This One Simple Move at Night Stops Leg Cramping Fast

This ancient spice opens your arteries like magic and supercharges your heart
News Post

Two Teens Mock Poor Old Lady On Bus

Your $2 Bill May Be Worth a Lot More Than You Think

Two Teens Mock Poor Old Lady On Bus

The Spice That Protects: The Remarkable Health Power of Cloves

Ignite Unstoppable Mornings: The Banana–Coffee Elixir You Need Now

The Homemade Garlic & Lemon Secret to Strengthen and Lengthen Your Nails

4 Fruits You Should Eat in Moderation After Age 60 — And How to Enjoy Them Without Losing Muscle

Cloves to Eliminate Nail Fungus Naturally

A Natural Pain Reliever for Legs, Varicose Veins, Rheumatism, and Arthritis

Colon Cancer: Why Early Screening Saves Lives

Magnesium: The Benefits, the Risks, and the Safe Way to Take It — Especially for Your Kidneys

H. pylori Infection: Symptoms and How It Damages Your Stomach

7 Warning Signs Your Heart Isn’t Healthy — And 7 Symptoms You Should Never Ignore

The Genius Reason People Pour Baking Soda Down the Sink — And Why You Should Too

Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Causes and Red-Flag Symptoms

16 Early Warning Signs Your Liver Is Sluggish And Toxins Are Being Stored In Your Fat Cells

Meet Our Cosmic Neighbor — The Andromeda Galaxy (M31)

The #1 way to flush microplastics from your body (It’s shockingly simple)