
Growing Organs from Your Own Cells
Growing Organs from Your Own Cells
The Future of Medicine: The Promise of Growing Organs from Your Own Cells
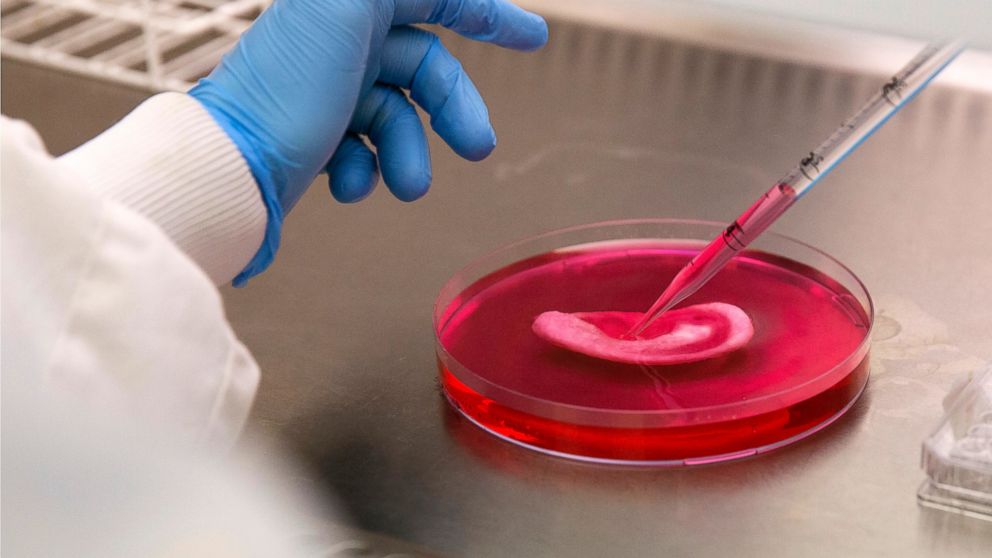
In recent years, the world of medicine has seen incredible breakthroughs, and one of the most exciting developments is the ability to grow complex tissues and organs from a person’s own cells. Renowned theoretical physicist Michio Kaku has predicted that in the near future, medical science will evolve to the point where organ failure becomes a thing of the past. “Already from your own cells, scientists can grow skin, cartilage, noses, blood vessels, bladders, and windpipes. In the future, scientists will grow more complex organs, like livers and kidneys. The phrase ‘organ failure’ will disappear,” Kaku says. This vision of the future is not far from reality, and it opens up new possibilities for the treatment of organ diseases and the advancement of personalized medicine.
The Power of Regenerative Medicine
The idea of growing organs from one’s own cells may seem like science fiction, but it is grounded in a field of study known as regenerative medicine. Regenerative medicine involves the use of stem cells and tissue engineering to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs. Scientists have already made significant progress in creating functional tissues from a patient’s own cells, which greatly reduces the risk of rejection that can occur with donor organs.
For instance, researchers have successfully grown skin for burn victims, cartilage for joint repair, and blood vessels for patients with circulatory issues. Bladders and windpipes have also been successfully grown and transplanted into patients. These advances show that the process of growing organs is not only possible but is already being applied in clinical settings.
Growing More Complex Organs: A Step Toward the Future
While growing simple tissues is already a reality, the challenge now lies in creating more complex organs, such as livers and kidneys. These organs have intricate structures and perform highly specialized functions that are difficult to replicate. However, scientists are making strides in this area. For example, researchers are working on developing liver tissue using stem cells, which could one day lead to fully functional, lab-grown livers for transplant. Similarly, scientists are exploring ways to grow kidneys and even heart tissues, which could alleviate the shortage of organs available for transplant.
One approach to growing complex organs involves using 3D bioprinting technology, which allows scientists to “print” tissues layer by layer using living cells. This technology has the potential to create organs with highly organized structures that mimic the complexity of human organs. With this technology, it’s possible that in the future, we could grow entire organs such as livers, kidneys, or even hearts from a patient’s own cells.
The Benefits of Personalized Organ Growth
One of the most significant advantages of growing organs from a person’s own cells is the reduction of the risk of organ rejection. In traditional organ transplants, patients must take immunosuppressive drugs to prevent their bodies from rejecting the new organ, which can have harmful side effects. However, with lab-grown organs created from a patient’s own cells, the risk of rejection is dramatically reduced, as the organ is genetically identical to the patient’s body.
In addition, personalized organs would eliminate the need for long waiting lists and organ shortages. Every year, thousands of people around the world die waiting for organ transplants. By growing organs on demand, this crisis could be alleviated, offering new hope to patients in need.
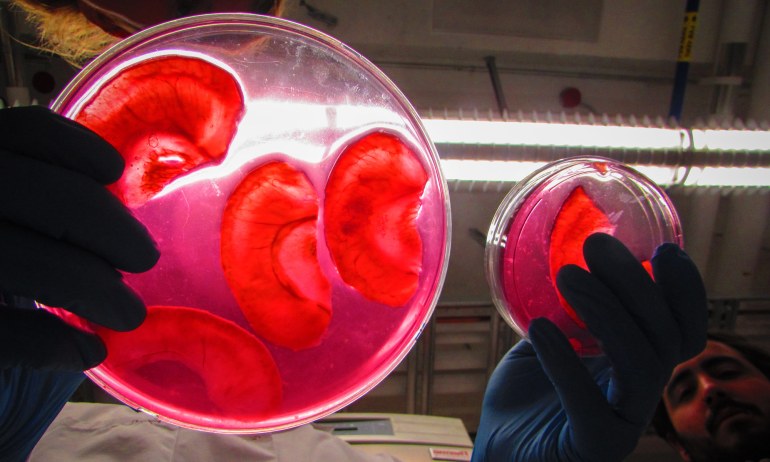
Overcoming Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the potential for organ growth is immense, there are still several hurdles to overcome. One of the biggest challenges is the complexity of replicating the full functionality of organs like the liver or kidney. Organs are not just collections of cells; they have complex vascular systems and intricate tissue structures that must work together to function properly. Scientists are still working to understand how to create these structures and ensure that lab-grown organs can perform all the necessary tasks.
There are also ethical considerations to address. As we move toward growing human organs in labs, questions around the use of stem cells, genetic manipulation, and the potential for organ trafficking must be carefully considered. These ethical issues will require regulation and oversight to ensure that the technology is used responsibly and safely.
Conclusion
Michio Kaku’s vision of a future without organ failure is one that seems increasingly achievable. As scientists continue to refine techniques for growing organs from a patient’s own cells, the possibilities for treating organ failure become limitless. The ability to create personalized, lab-grown organs could revolutionize medicine, eliminating the need for organ transplants and offering a future where organ failure is no longer a death sentence. While challenges remain, the promise of regenerative medicine is a beacon of hope for patients and families affected by organ failure, and it is a testament to the remarkable advances of modern science.
News in the same category


Five Parts of Fish That Are Dirty and Potentially Toxic — The First One Is Often Mistaken as Healthy but Can Be Fatal

Health Benefits of Boiled Green Bananas

How to Drink Lemon Turmeric Water in the Morning to Support Liver and Kidney Detox Without Harming the Stomach

Can Relative Fat Mass Replace BMI in Assessing Obesity?

When Women Target Other Women: The Hidden Wounds of Bullying in Medicine

Most Doctors Won’t Tell You, But This Can Cut Heart Attack & Stroke Risk By 80%

The Best Proven Ways to Heal Scars Naturally (Evidence Based)
16 Warning Signs of Poor Blood Circulation and How to Treat It
The Best Home Remedies For Getting Rid of Ear Infection

Daily Step Counts Combined With Genetic Risk Can Better Predict Type 2 Diabetes

Gestational Diabetes Rates Surge Across the United States

Why Does Lung Cancer Affect Non-Smokers? A Hidden Culprit in the Kitchen That Many People Overlook
6 Foods You Absolutely Need To Avoid If You Suffer From a Thyroid Disorder
Gastroenterologist says this is the #1 drink for gut health
Top 5 drinks to INSTANTLY improve leg circulation and blood flow

Five Morning Habits That May Quietly Increase Cancer Risk

Natural Home Remedies for Cough and Sore Throat
People with weak kidneys often do these 4 things every day: If you don't stop soon, it can easily damage your kidneys
I spent a couple of nights at my friend’s previous apartment and saw these unusual bumps
News Post

6 Things People Who Live to 100 Do Every Week to Stay Healthy

Michael B. Jordan Opens Up to David Letterman About His Future: ‘I Want Children’

Costco’s Bold Experiment: Housing Above the Warehouse 🏢🥤🌭

Graham Walker’s $240 Million Gift: Rewarding Loyalty and Hard Work 💼💰

New York City Pushes Forward on Animal Welfare: Rodeo Ban Gains Momentum 🐮✨

Marlon Wayans Clarifies He Never Defended Diddy During His 50 Cent Rant

Snoop Dogg Becomes Team USA’s First Honorary Coach for 2026 Olympic Winter Games

Seven Foods That Rarely Spoil: Still Safe to Eat Even After the Expiration Date

Five Parts of Fish That Are Dirty and Potentially Toxic — The First One Is Often Mistaken as Healthy but Can Be Fatal

Jason Collins announces he is battling stage 4 brain cancer: 'I'm going to fight it'

Health Benefits of Boiled Green Bananas
Kevin Hart Inks Licensing Deal for His Name

How to Restore a Worn Non-Stick Pan Instead of Throwing It Away

Michael B. Jordan Wanted to Change His Name Because of the Other Michael Jordan

How to Drink Lemon Turmeric Water in the Morning to Support Liver and Kidney Detox Without Harming the Stomach

Why Adding Milk Thistle to Your Routine May Support Liver Health Naturally

How a Simple Daily Habit with Cloves and Cinnamon Supports Vitality and Intimacy in Later Years

Natural Healing at 60: A Simple Banana Peel, Mint, and Turmeric Drink for Daily Wellness
The Herb That Could Transform Your Health Naturally
