
If you have these two holes in your back, it means…
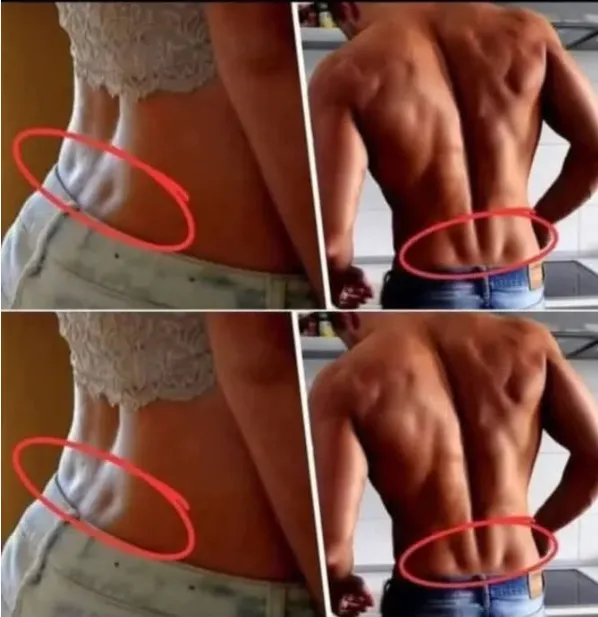
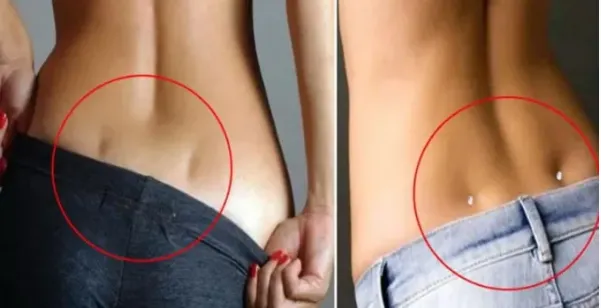
Have you ever noticed two small indentations on your lower back, just above the buttocks? If so, you may have what are commonly known as Venus dimples. These small, symmetrical depressions, often referred to as “dimples of Venus,” have been admired for centuries and are frequently associated with beauty, good health, and physical fitness. Named after Venus, the Roman goddess of love and beauty, these dimples are considered a sign of attractiveness in many cultures.
They are created by a ligament that connects the skin directly to the posterior superior iliac spine, a bony part of the pelvis, which results in the formation of slight indentations on the lower back. These natural features are typically more noticeable in individuals who have lower levels of body fat and well-defined muscles, but they are primarily determined by genetics. If your parents or grandparents have them, there’s a higher likelihood that you might have them too.
While Venus dimples are more commonly talked about in relation to women, men can have similar indentations. In men, these are often called Apollo holes, named after Apollo, the Roman god of strength and athleticism. Apollo holes are thought to carry the same meanings as Venus dimples: signs of good health, strong circulation, and a well-maintained physique. Both Venus dimples and Apollo holes are typically more visible in people who lead active lifestyles, engage in regular physical exercise, and maintain a healthy weight. Although having these dimples is mostly genetic, keeping fit can enhance their appearance, making them stand out even more on a toned and lean body.
Many people view these dimples as aesthetically pleasing, and over time, they’ve gained a reputation as an attractive and desirable physical trait. In today’s fitness-focused world, these dimples are sometimes considered markers of a healthy, active lifestyle. Some fitness enthusiasts even aim to make them more prominent by reducing body fat and building strong core muscles. However, it’s important to understand that while exercise and diet can enhance their visibility, Venus dimples and Apollo holes cannot be developed if the underlying ligament structure is not present. They are a natural part of your body’s anatomy and cannot be created artificially through workouts or other physical training alone.
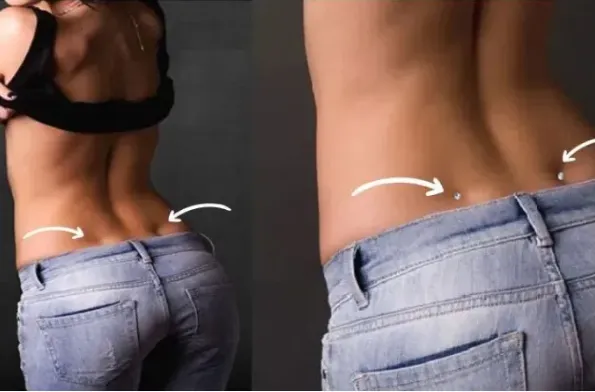
Beyond their visual appeal, there are also beliefs about the potential health benefits associated with Venus dimples. Some suggest that individuals with these dimples may experience better blood circulation, particularly in the pelvic region. This enhanced circulation is thought to contribute to increased sexual pleasure and potentially easier orgasms. While scientific evidence supporting these claims is limited, this idea has become a popular theory in discussions about human anatomy and wellness. Additionally, because Venus dimples are often visible in people who are physically fit and maintain a healthy weight, they are commonly viewed as indicators of vitality, good circulation, and overall well-being
For centuries, both Venus dimples and Apollo holes have fascinated people and sparked curiosity about their significance. In modern times, they have become even more popular thanks to the influence of social media and the fitness industry, where they are often showcased as symbols of a toned and healthy body. Many people who have these dimples consider them a point of pride, while others see them as a physical characteristic that adds to their attractiveness. Even though they are small features, they hold a lot of cultural meaning and are frequently admired for what they represent—youth, health, and fitness.

News in the same category


Soap Left on Plates? British Dishwashing Method Sparks International Debate
Medicine Breaks New Ground as Ultrasound Builds Tissue Without Surgery

A Heartbreaking Survival Trick: How a Stray Cat Learned to Hide His Pain

Bears Turn Honey Theft Into a Surprising Taste Test in Turkey

Scientists Say Your Butt Shape May Say More About Your Health Than You Think
The Rare Condition That Makes Human Bones Slowly Vanish

A Hidden Consequence of Tick Bites You Should Know About

Smoking, Obesity, and Hypertension: The Leading Risk Factors for Kidney Cancer

When Blue Wings Return: A Second Chance for the Spix’s Macaw

Three Friends, One Hive, and a Very Bad Idea

Measles Cases Hit 30-Year High in the US, Raising Urgent Public Health Concerns

Why Skipping Housework on New Year’s Day Might Bring You Good Luck

Millie Bobby Brown’s Reaction to Eleven’s Ending Goes Viral After Stranger Things Finale

Baby Name Expert Predicts the Most Popular Naming Trends for 2026

No Fines, No Enforcement: How Trust Worked During Japan’s Toll System Failure

This “Easy” Puzzle for Kids Is Completely Stumping Adults

Beavers Build a Dam in the Czech Republic, Solving a Years-Long Environmental Problem

Social Media Users Agree on the Most Painful Physical Experience — and It’s Not What You’d Expec

James Webb Space Telescope Reveals Hidden Mid-Infrared Flares from the Milky Way’s Central Black Hole
News Post

Google Chooses India for Pixel 10 Manufacturing: A Landmark for Make in India 🚀🇮🇳📱

Dr. Navneet Jain of Indore: A Patriot in a White Coat 💉🇮🇳❤️

A New Beginning for Gabbar

A Labourer’s Gift of Hope: The Inspiring Story of Anjiney Yadav 🚲❤️🇮🇳

India Becomes the World’s Second‑Largest Road Network: A Milestone in Connectivity 🛣️🇮🇳🚀

Adding Yoga to Opioid Use Disorder Care May Speed Recovery From Opioid Withdrawal

Sunlight at Work Beats Artificial Light for Glucose Control in Type 2 Diabetes
Bariatric Surgery or GLP-1 Receptor Agonists? Long-Term Effects on Fat Loss and Body Composition

How to Whiten Laundry Naturally

Harvard Doctor Reveals Foods You Should Avoid to Prevent Inflammation

If You Have Fig Leaves, You Have Gold—and You Didn’t Even Know It

Doctor Warns of Mesotherapy’s Risky Side, Causing Reptile-Like Skin

It’s surprising how unclear the link between chicken color and quality still is for many people

🤧 Constant Phlegm in Throat? The Real Causes (and How to Actually Get Rid of It)

Why Daily Showers After 65 May Do More Harm Than Good
Scientists Discover Alarming Substance in Human Blood, Raising Serious Concerns
7 easy ways to quickly unclog your lymph nodes to reduce swelling and flush out toxins

What Really Happens When You Eat a Banana Before Bed

Natural Ways to Relieve Cough and Chest Congestion
