The Surprising Health Benefits of Boiled Eggs
Boiled eggs have been a dietary staple for centuries. Simple to prepare, affordable, and highly versatile, they remain one of the most nutritionally complete whole foods available. Beyond convenience, growing scientific evidence suggests that moderate egg consumption can provide a range of meaningful health benefits.
For years, eggs were criticized because of their cholesterol content. However, more recent research indicates that for most healthy individuals, dietary cholesterol from eggs has minimal impact on blood cholesterol levels. In fact, eggs contain several nutrients that may support heart health, brain function, and overall wellness when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
Here’s why the humble boiled egg deserves a regular place in your meal plan.
1. A High-Quality Protein Source
Each boiled egg contains approximately 6–7 grams of complete protein. This means it provides all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own.
Protein plays a critical role in:
-
Muscle repair and maintenance
-
Tissue growth
-
Enzyme and hormone production
-
Immune function
As people age, preserving lean muscle mass becomes increasingly important for mobility, metabolism, and injury prevention. Including boiled eggs in daily meals can help support muscle retention and recovery. Athletes, active individuals, and older adults may particularly benefit from this easily digestible protein source.
In addition, egg protein has a high biological value, meaning the body can efficiently absorb and use it.
2. Supports Eye Health
Boiled eggs are rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, two carotenoid antioxidants that accumulate in the retina. These compounds help protect the eyes from oxidative damage caused by blue light exposure and environmental stress.
Regular intake of lutein and zeaxanthin has been associated with a lower risk of:
-
Age-related macular degeneration
-
Cataracts
-
Visual decline in older adults
The yolk contains these protective nutrients, which are more bioavailable from eggs than from many plant sources due to the presence of healthy fats that enhance absorption.
Including one or two boiled eggs several times per week may contribute to long-term eye health.
3. Enhances Brain Function and Memory
Eggs are one of the richest natural sources of choline, a nutrient essential for brain development and cognitive performance. Choline is necessary for producing acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in:
-
Memory formation
-
Learning
-
Focus
-
Mood regulation
Adequate choline intake may help reduce the risk of cognitive decline later in life. It is also particularly important during pregnancy for fetal brain development.
Because many adults do not meet recommended choline intake levels, adding boiled eggs to the diet can be a practical way to support brain health.
4. Helps Control Appetite and Weight
Boiled eggs are highly satiating due to their combination of protein and healthy fats. Foods rich in protein promote fullness and help stabilize blood sugar levels, reducing sudden cravings.
Eating eggs at breakfast or as a snack may:
-
Decrease overall calorie intake throughout the day
-
Reduce snacking on processed foods
-
Improve appetite control
Unlike refined carbohydrates that cause energy spikes and crashes, eggs provide steady, sustained energy. For individuals seeking weight management without restrictive dieting, replacing processed snacks with boiled eggs can be a simple and effective strategy.
5. Provides Essential Vitamins and Minerals
Boiled eggs deliver a concentrated package of important nutrients, including:
-
Vitamin B12: Supports red blood cell production and neurological health.
-
Vitamin D: Essential for bone strength, immune function, and calcium absorption.
-
Selenium: A powerful antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative stress and supports thyroid function.
-
Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): Supports energy production.
-
Iron and Zinc: Important for immune health and oxygen transport.
This nutrient density makes eggs particularly valuable for individuals with increased nutritional needs, including older adults and those with limited dietary variety.
6. May Support Heart Health (When Consumed Moderately)
While eggs contain cholesterol, current evidence suggests that for most people, moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) does not significantly increase the risk of heart disease.
Eggs can actually improve levels of HDL (“good”) cholesterol in some individuals. They also contain antioxidants and nutrients that help reduce inflammation — a key factor in cardiovascular disease.
However, individuals with specific medical conditions such as familial hypercholesterolemia or certain cardiovascular risks should consult a healthcare provider regarding appropriate intake.
7. Affordable and Accessible Nutrition
Unlike many so-called “superfoods,” boiled eggs are widely available and inexpensive. They require no special preparation skills and can be stored conveniently for quick meals or snacks.
This accessibility makes them a practical tool for improving overall diet quality without increasing grocery costs.
Final Thoughts
Boiled eggs are far more than a traditional breakfast item. They are a nutrient-dense, protein-rich food that can support:
-
Muscle maintenance
-
Eye protection
-
Brain function
-
Appetite control
-
Immune health
-
Bone strength
When enjoyed as part of a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, boiled eggs can contribute meaningfully to long-term health.
Simple, affordable, and backed by growing scientific understanding, boiled eggs demonstrate that sometimes the most powerful foods are also the most familiar.
News in the same category

Doctors Are Amazed: Two Vegetables That Boost Collagen in the Knees and Relieve Joint Pain

Doctors warn 5 everyday habits are slowly killing your kidneys
9 Powerful Home Remedies to Eliminate Fungal Infections (Daad, Khaj, Khujli) Naturally and Fast

Longevity doctor who ‘reversed his biological age’ shares advice for people over 30

Tea for Swollen Legs: A Natural Remedy for Water Retention and Poor Circulation

🌿 What Rosemary Can Actually Do
Early Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
🩺 If Your Legs Feel Heavy, Cold, or Tingly—Here’s What It Means (And How to Improve Circulation Naturally)
10 Warning Signs It’s Time to Cut Back on Caffeine

What Does an Itchy Left Hand Mean

It's a pain killer, helps relieve leg pain, varicose veins, rheumatism, and arthritis...👇

4 Fruits You Should Eat in Moderation After 60 — And How to Enjoy Them Without Losing Muscle
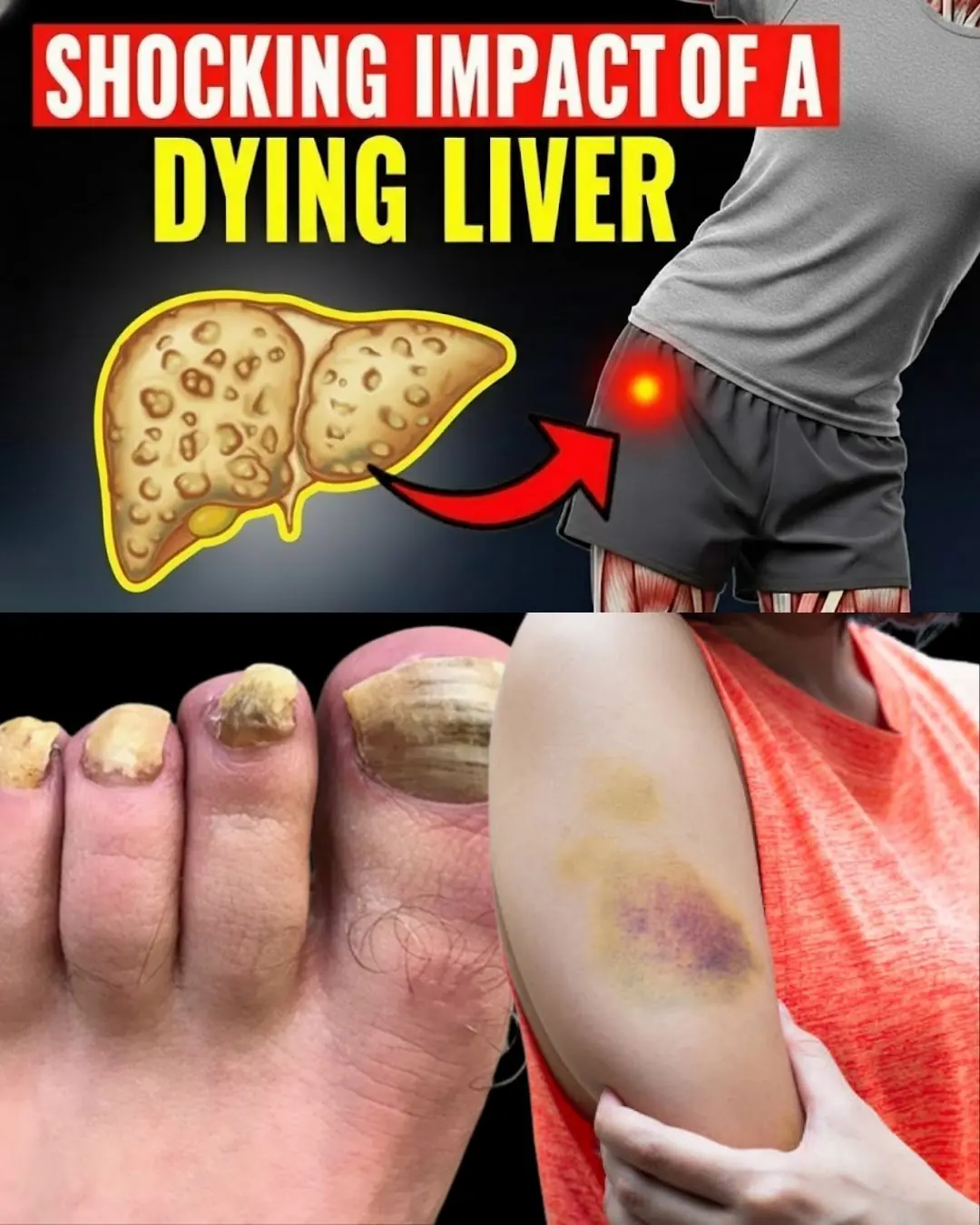
15 Strange Early Signs of Liver Failure That Even Doctors Often Miss

Why Your Cat Chooses to Sleep With You

10 Conditions Ginger Can Help Manage Naturally
What To Know About Chronic Kidney Failure

Harvard Doctor Reveals Foods You Should Avoid to Prevent Inflammation

Silent Cancer Signs: 3 Persistent Pains Your Body Uses as Early Warnings
News Post
He Fired Six Maids—Then One Video Ended His Sister

🚨 Recurrent Yeast Infections? STOP Doing These Things Immediately!

Euphorbia Hirta (Asthma-plant): Traditional Uses and Applications

Doctors Are Amazed: Two Vegetables That Boost Collagen in the Knees and Relieve Joint Pain

Doctors warn 5 everyday habits are slowly killing your kidneys

9 Powerful Home Remedies to Eliminate Fungal Infections (Daad, Khaj, Khujli) Naturally and Fast

Longevity doctor who ‘reversed his biological age’ shares advice for people over 30

Tea for Swollen Legs: A Natural Remedy for Water Retention and Poor Circulation

Grandma Had the Maid Arrested… Then the Kid Spoke Up

Both Carrying His Child

Billionaire Fires Server at Daughter’s Funeral—Then Sees THIS

🌿 What Rosemary Can Actually Do

Early Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer

🩺 If Your Legs Feel Heavy, Cold, or Tingly—Here’s What It Means (And How to Improve Circulation Naturally)

10 Warning Signs It’s Time to Cut Back on Caffeine

🥦 3 Vegetables That Support Cancer Prevention — Backed by Science

What Does an Itchy Left Hand Mean

Bouncer Destroys Veteran’s Medals—Then Learns What He Just Touched
