
5 warning signs your heart is abnormally weak for your age

As we age, it’s a sad reality that our bodies begin to slow down. Activities that once felt effortless, such as climbing a flight of stairs, may now seem like challenging tasks. While it’s completely natural to experience a decrease in vitality as you grow older, persistent fatigue and shortness of breath can signal something more serious — that your heart may not be functioning as well as it should.
What is Heart Failure?
The primary role of your heart is to pump oxygen-rich blood throughout your body, ensuring that all of your organs and tissues receive the nutrients and oxygen they need to function. When your heart isn’t pumping effectively or efficiently, this condition is known as heart failure.
It's important to note that heart failure doesn’t mean your heart has stopped working. Instead, it means that your heart requires additional support to help it perform its role. Although heart failure can develop at any age, it is most commonly seen in older adults and typically worsens gradually over time.
Unfortunately, many individuals mistake the early symptoms of heart failure for the normal effects of aging. However, what is really happening is that the heart is becoming weaker, often without the person even realizing it. If left unchecked and untreated, heart failure can lead to more severe complications, including cardiac arrest.
The F.A.C.E.S. Acronym: A Simple Way to Recognize Heart Failure Symptoms
To help both doctors and patients easily identify the symptoms of heart failure, the Heart Failure Society of America has developed a simple acronym known as F.A.C.E.S. This stands for:
-
F = Fatigue: When the heart struggles to pump enough oxygen-rich blood to meet the body's energy demands, fatigue or a general feeling of tiredness sets in.
-
A = Activity Limitation: People with heart failure often find it difficult to perform their usual activities due to excessive tiredness and shortness of breath. Everyday tasks may seem overwhelming.
-
C = Congestion: Fluid can build up in the lungs, causing symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
-
E = Edema (Swelling): When the heart cannot pump blood efficiently, fluid can accumulate in the lower extremities such as the ankles, legs, thighs, and abdomen. This buildup of fluid may lead to rapid weight gain.
-
S = Shortness of Breath: Fluid in the lungs can hinder the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, making it harder to breathe. You may also experience difficulty breathing when lying down, as gravity causes fluid to shift toward the lungs.
What Causes Heart Failure?
Heart failure typically occurs when the muscle tissue of the heart becomes damaged. This damage can arise from several health conditions, including:
-
Coronary Heart Disease: This occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become clogged with fatty substances (atherosclerosis), which can lead to angina or heart attacks.
-
High Blood Pressure: Chronic high blood pressure puts extra strain on the heart, potentially weakening its function over time.
-
Cardiomyopathy: This refers to diseases that affect the heart muscle, making it harder for the heart to pump blood effectively.
-
Heart Rhythm Problems (Arrhythmias): Conditions like atrial fibrillation can disrupt the heart's normal rhythm, leading to inefficient blood circulation.
-
Heart Valve Problems: Damaged or dysfunctional heart valves can hinder the normal flow of blood through the heart.
-
Congenital Heart Disease: Birth defects that affect the structure and functioning of the heart can lead to heart failure over time.
Other factors that can contribute to heart failure include obesity, anemia, excessive alcohol consumption, an overactive thyroid, and pulmonary hypertension (high pressure in the lungs).
Medications to Avoid if You Have Heart Failure
Managing heart failure often requires the use of several medications. However, some medications can exacerbate the condition or worsen symptoms. It’s crucial to maintain an open line of communication with your healthcare providers to ensure they are aware of all the medications, over-the-counter drugs, and supplements you are taking. Certain drugs to be particularly cautious about include:
-
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Common painkillers such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) can worsen heart failure symptoms by causing the body to retain sodium and fluid. This leads to increased swelling and further stress on the heart.
-
Heartburn and Cold Medications: Many over-the-counter remedies for heartburn or colds contain high amounts of sodium, which can contribute to fluid retention and exacerbate symptoms of heart failure.
-
Supplements: While supplements are often taken to improve health, some contain substances that can interact negatively with heart medications. Always consult with your doctor before adding new supplements to your routine.
The Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Heart failure is a serious condition, but with early detection and appropriate treatment, many individuals can manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. Recognizing the signs and symptoms early, as well as understanding the potential causes, can make a significant difference in the outcome.
It's essential to be proactive about your health, particularly as you age. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider, a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and avoiding harmful habits like excessive alcohol consumption can help maintain your heart’s health and prevent complications related to heart failure.
While aging naturally brings about changes in the body, it’s important to remember that persistent fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling are not inevitable parts of growing older. They can be signs of something more serious that warrants medical attention. By staying informed and vigilant, you can protect your heart and ensure that you continue to live an active and healthy life for years to come.
News in the same category

Low Blood Pressure: When Dizziness Becomes Dangerous

Hypertension Crisis: Warning Signs You Need Immediate Care

Uncontrolled Blood Pressure: Hidden Risks to the Heart and Brain

Shortness of Breath: When It Signals a Serious Lung Problem
High Liver Enzymes: What Blood Tests Are Telling You

How to Reset Your Thyroid to Burn Fat and Activate Your Metabolism

6 Natural Ways To Stop Gum Disease Before It’s Too Late

Plant-Derived Nutrient Cocktail Achieves 100% Kill Rate of Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro

Active Vitamin D Levels, Not Storage Form, Linked to Greater Gut Microbiome Diversity in Older Men

Synergistic Anti-Cancer Effect: Curcumin and Silymarin 'One-Two Punch' Against Colon Cancer Cells

28-Year-Old Woman Develops Lung Cancer in Both Lungs Due to This Common Nighttime Habit

Purple Dead Nettle (Lamium purpureum): A Wild Ally for Circulation and Heart Health

Regular Yogurt Consumption Linked to Reduced Chronic Inflammation: Evidence from a University of Wisconsin Study
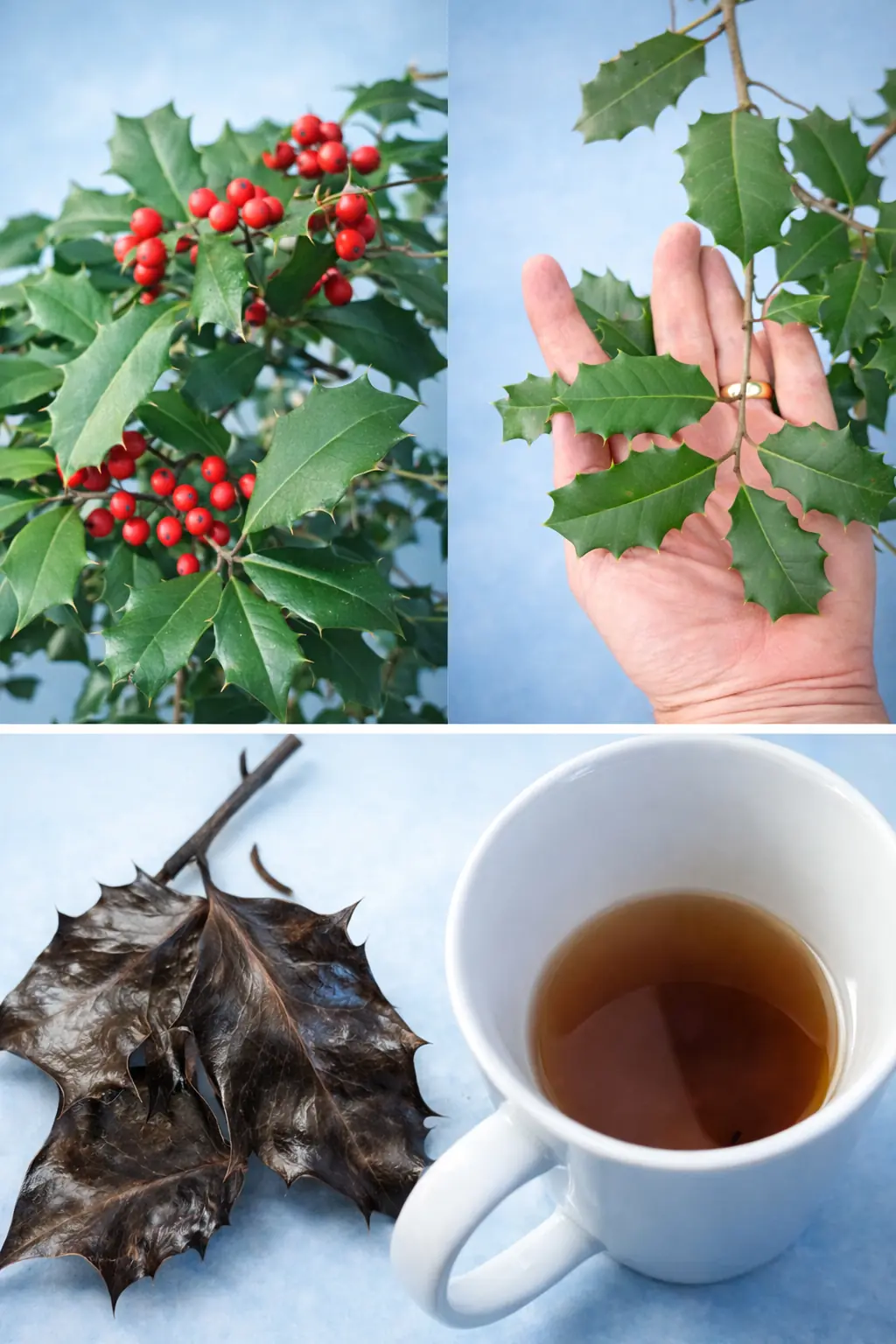

The Hidden Power of American Holly (Ilex opaca): More Than a Holiday Symbol

Oral Glutamine Supplementation Achieves Significant Symptom Relief in Post-Infectious IBS-D

Physician-Scientist Consumes 1,000 Sardines in 30 Days to Test Metabolic Impact

Early-Stage Fatty Liver: 5 Facial Signs You Should Never Ignore
Specific Extremely Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Field Inhibits Melanoma Cancer Cell Growth In Vitro
News Post

Place this bunch of leaves in the bathroom: No unpleasant odors for a whole week, and it will repel mosquitoes and gnats.

Clever tip to get all the sand out of clams in a flash: No need to soak them for a long time, they'll be sparkling clean.

Even a month in space can leave your cells looking older.

Solar Flares Are Growing Hotter and More Powerful, Scientists Warn

The Brain’s Backup Plan: Neuroplasticity and Rehabilitation
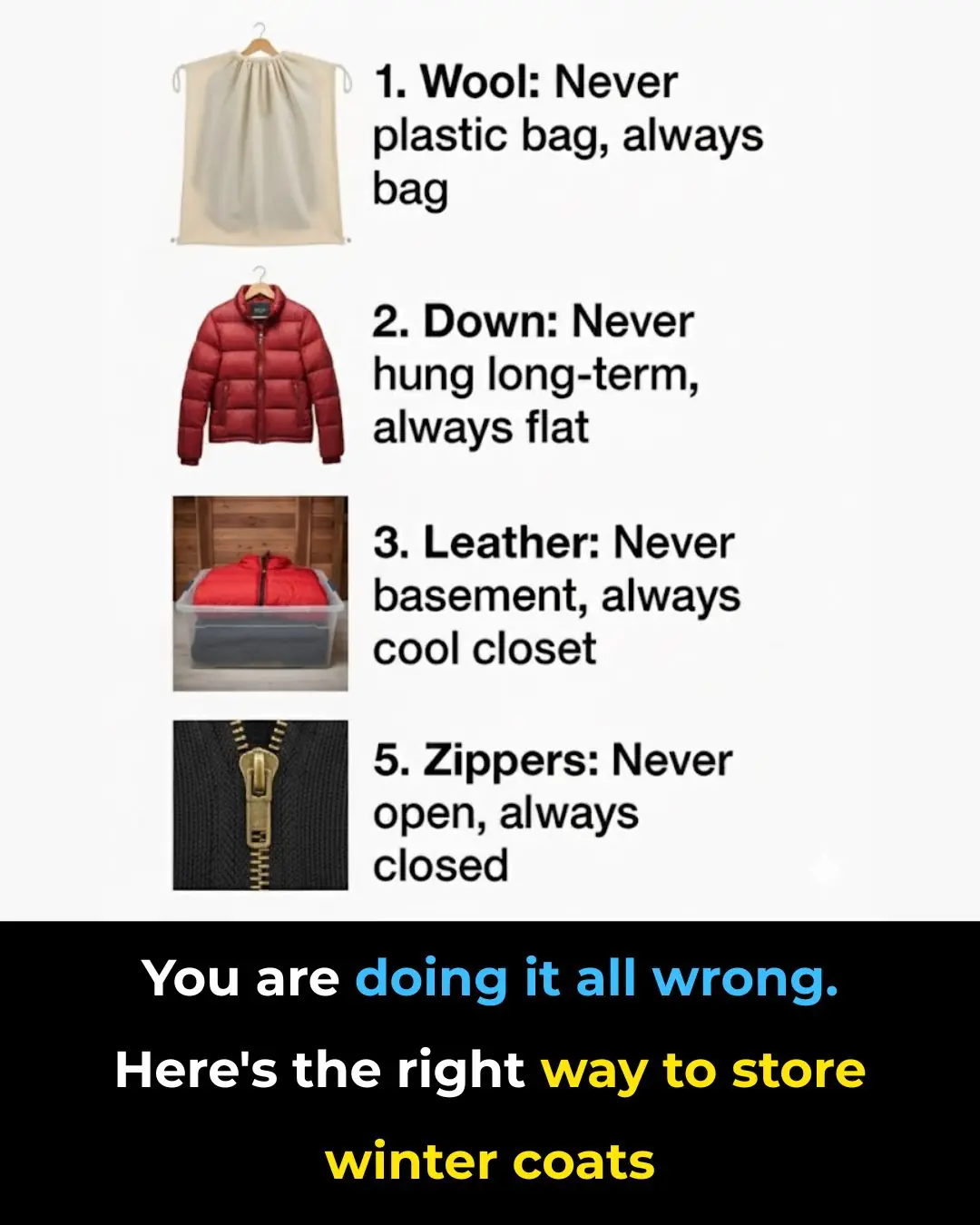
You’re Doing It All Wrong: The Right Way to Store Winter Coats

I Found a Tiny Red Object With Metal Prongs in My Kitchen Drawer — Here’s What It Actually Is

8 Reasons Why Adding Baking Soda to Your Toilet Tank Is a Must-Try Trick

Quick Ways to Stop a Draft Under Your Front Door — While You Wait for the Handyman

Most People Will Go Their Entire Lives Without Knowing What the Decorative Bands on Bath Towels Really Mean

12 Things That Seem Rude But Are Secretly Signs of Wisdom

Japan Just Hit 100,000 Citizens Over 100-Years-Old — Their Longevity Secret Isn’t What You’d Think

High Blood Pressure: Silent Symptoms That Damage Your Body

Low Blood Pressure: When Dizziness Becomes Dangerous

Hypertension Crisis: Warning Signs You Need Immediate Care

Uncontrolled Blood Pressure: Hidden Risks to the Heart and Brain

Shortness of Breath: When It Signals a Serious Lung Problem

High Liver Enzymes: What Blood Tests Are Telling You

Why Highly Intelligent People Enjoy What Most People Avoid
