FATTY PANCREAS DISEASE: THE NEW SILENT THREAT
While fatty liver disease has received significant attention in recent years, a lesser-known but equally dangerous condition is becoming alarmingly common: fatty pancreas disease, or pancreatic steatosis. This occurs when excess fat accumulates within the pancreas — an organ essential for digestion and blood sugar regulation.
Because symptoms appear late and imaging is rarely performed unless a problem is suspected, many people live for years with fatty pancreas without knowing it. Recent research shows strong links between pancreatic fat, diabetes, obesity, chronic inflammation, and pancreatitis.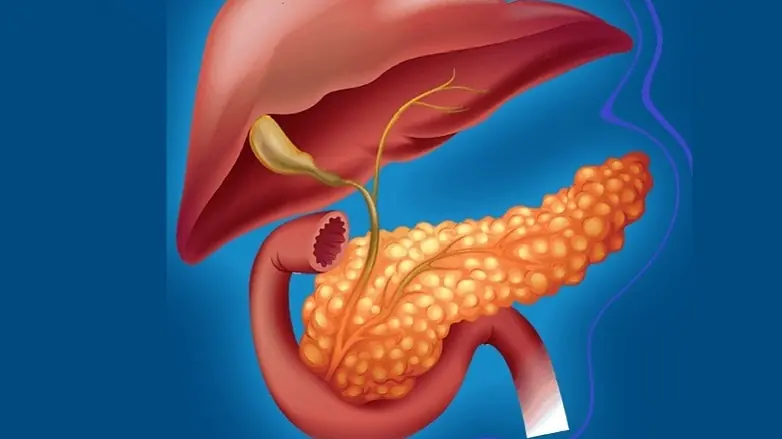
What Is Fatty Pancreas Disease?
Fatty pancreas disease occurs when fat cells infiltrate the pancreas. Over time, the organ becomes weaker, less efficient, and more vulnerable to inflammation.
Scientists now believe pancreatic fat is not simply “stored fat” — it actively triggers:
-
Insulin resistance
-
Inflammation
-
Cell damage
-
Digestive dysfunction
This makes it a powerful predictor of future metabolic diseases.
Why It Matters More Than People Realize
A healthy pancreas is vital for:
-
Digestive enzyme production
-
Blood sugar control (insulin & glucagon)
-
Hormonal balance
When fat accumulates in the pancreas, these functions gradually break down, leading to:
-
Pre-diabetes and diabetes
-
Chronic pancreatitis
-
Malabsorption
-
Weight gain
-
Severe digestive issues
Early Symptoms — Often Overlooked
Fatty pancreas is called a “silent threat” because symptoms are vague or mistaken for other issues:
-
Mild upper abdominal discomfort
-
Bloating after meals
-
Nausea
-
Irregular bowel movements
-
Chronic fatigue
-
Elevated blood sugar
-
Sudden weight gain, especially around the abdomen
Many people attribute these signs to stress, poor sleep, or overeating.
Major Causes
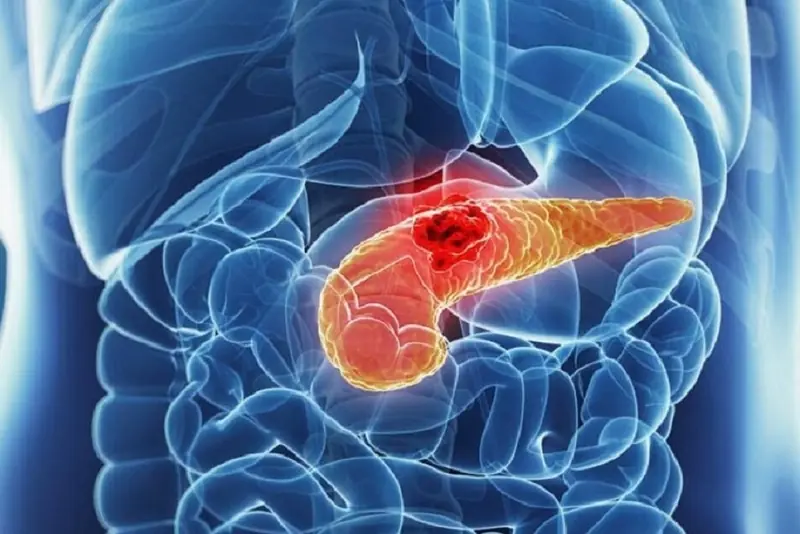
The condition is strongly linked to:
1. Obesity & Visceral Fat
Excess belly fat is one of the strongest predictors of pancreatic fat.
2. Unhealthy Diet
High intake of:
• Processed foods
• Sugary drinks
• Refined carbs
• Fried foods
• Saturated fats
3. Insulin Resistance
A cycle begins: fat increases insulin resistance → insulin resistance leads to more fat storage → pancreas becomes overwhelmed.
4. Fatty Liver Disease
Up to 70% of people with fatty liver also have fatty pancreas.
5. Sedentary Lifestyle
6. Alcohol, Smoking, Genetics
Diagnosis
Fatty pancreas is discovered through:
-
Abdominal ultrasound
-
CT scan
-
MRI / MRCP
-
Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
Because the condition is not widely recognized, many doctors find it accidentally while scanning for something else.
Complications
Ignoring fatty pancreas can lead to:
1. Type 2 Diabetes
The pancreas struggles to produce enough insulin.
2. Chronic Pancreatitis
Inflammation leads to long-term damage and worse digestive function.
3. Pancreatic Insufficiency
The organ stops producing enzymes properly.
4. Higher Heart Disease Risk
Due to strong metabolic links.
Treatment — Focus on Lifestyle Reset
There is no pill that removes pancreatic fat. The only proven treatment is lifestyle change.
1. Weight Reduction (Even 5–10% Works)
Reduces fat inside organs dramatically.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Diet
-
Vegetables, fruits, legumes
-
Whole grains
-
Omega-3 rich foods (fish, chia, walnuts)
-
Minimal added sugars
-
Healthy fats (olive oil, avocado)
3. Eliminate Processed Carbs
4. Exercise Regularly
-
150 minutes/week moderate intensity
-
Strength training 2–3× weekly
5. Improve Gut Health
Fermented foods & fiber help reduce inflammation.
6. Control Blood Sugar
Conclusion
Fatty pancreas disease may be silent, but it is far from harmless. The sooner it is detected, the more manageable it becomes. With the right lifestyle adjustments, the pancreas can recover, drastically reducing risks of diabetes, pancreatitis, and long-term metabolic conditions.
News in the same category


A Natural Pain Reliever for Legs, Varicose Veins, Rheumatism, and Arthritis
Colon Cancer: Why Early Screening Saves Lives
How Microplastics Enter Your Body — And How to Strengthen Your Gut to Block and Remove Them

Magnesium: The Benefits, the Risks, and the Safe Way to Take It — Especially for Your Kidneys
H. pylori Infection: Symptoms and How It Damages Your Stomach

7 Warning Signs Your Heart Isn’t Healthy — And 7 Symptoms You Should Never Ignore
Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Causes and Red-Flag Symptoms
16 Early Warning Signs Your Liver Is Sluggish And Toxins Are Being Stored In Your Fat Cells
The #1 way to flush microplastics from your body (It’s shockingly simple)

12 Foods That Protect the Heart in Surprising Ways

12 Herbal Remedies That Actually Work: Effective Natural Solutions for Common Ailments
Pulmonary Fibrosis: Early Signs and Treatment Options

Whooping Cough in Adults: The Unexpected Comeback
Tuberculosis Symptoms: What You Need to Know Early
🌿 How to Naturally Support Wart & Skin Tag Removal (Using a Simple DIY Remedy)
Doctors reveal the surprising reason your legs are the first to fail
🧄 Garlic’s Real Health Benefits — What Science Says About This Ancient Remedy
This One Simple Move at Night Stops Leg Cramping Fast

This ancient spice opens your arteries like magic and supercharges your heart
News Post

Two Teens Mock Poor Old Lady On Bus

The Spice That Protects: The Remarkable Health Power of Cloves

Ignite Unstoppable Mornings: The Banana–Coffee Elixir You Need Now

The Homemade Garlic & Lemon Secret to Strengthen and Lengthen Your Nails

4 Fruits You Should Eat in Moderation After Age 60 — And How to Enjoy Them Without Losing Muscle

Cloves to Eliminate Nail Fungus Naturally

A Natural Pain Reliever for Legs, Varicose Veins, Rheumatism, and Arthritis

Colon Cancer: Why Early Screening Saves Lives

How Microplastics Enter Your Body — And How to Strengthen Your Gut to Block and Remove Them

Magnesium: The Benefits, the Risks, and the Safe Way to Take It — Especially for Your Kidneys

H. pylori Infection: Symptoms and How It Damages Your Stomach

7 Warning Signs Your Heart Isn’t Healthy — And 7 Symptoms You Should Never Ignore

The Genius Reason People Pour Baking Soda Down the Sink — And Why You Should Too

Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Causes and Red-Flag Symptoms

16 Early Warning Signs Your Liver Is Sluggish And Toxins Are Being Stored In Your Fat Cells

Meet Our Cosmic Neighbor — The Andromeda Galaxy (M31)

The #1 way to flush microplastics from your body (It’s shockingly simple)
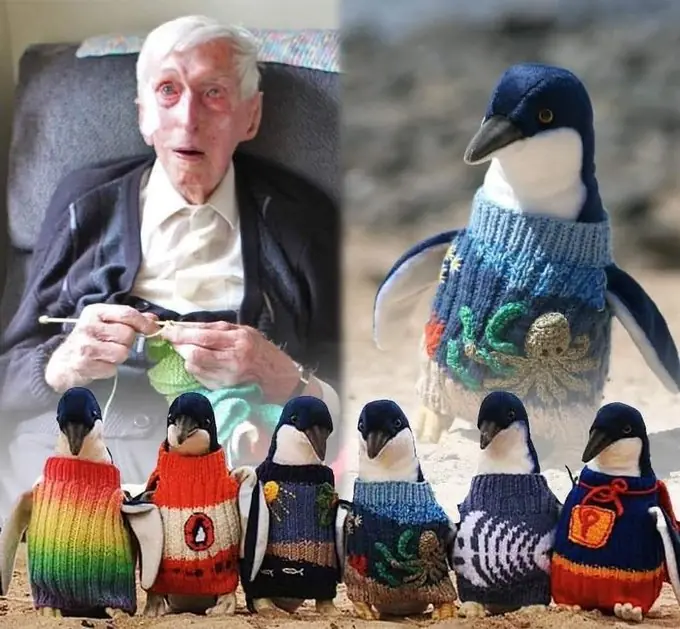

The Heartwarming Story of Alfred “Alfie” Date — Australia’s Oldest Man Who Knitted Sweaters for Injured Penguins

How Sahara Desert Dust Helps Fertilize the Amazon Rainforest — Even From 5,000 Miles Away
