Sudden Cardiac Arrest: What Makes It Deadly and How to Respond
Understanding why sudden cardiac arrest is so deadly — and knowing how to respond immediately — can dramatically improve survival outcomes.
What Is Sudden Cardiac Arrest?
Sudden cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood effectively. This is caused by a malfunction in the heart’s electrical system, most commonly a life-threatening arrhythmia such as ventricular fibrillation.
When the heart stops, oxygen-rich blood can no longer reach the brain and vital organs. Loss of consciousness occurs within seconds, and death can follow within minutes if no action is taken.
It is important to distinguish cardiac arrest from a heart attack. A heart attack is caused by blocked blood flow to the heart muscle, while cardiac arrest is an electrical failure. However, a heart attack can trigger cardiac arrest.
Why Sudden Cardiac Arrest Is So Deadly
1. It Happens Without Warning
Many victims have no obvious symptoms beforehand. Even people who appear healthy may suddenly collapse.
2. The Brain Cannot Survive Without Oxygen
Permanent brain damage can begin after just 4–6 minutes without oxygen.
3. Survival Depends on Immediate Action
Each minute without CPR or defibrillation reduces survival chances by up to 10%.
4. Most Events Occur Outside Hospitals
The majority of cardiac arrests happen at home or in public places where immediate medical help is not available.
Common Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest
-
Coronary artery disease
-
Previous heart attack
-
Cardiomyopathy
-
Congenital heart defects
-
Severe electrolyte imbalances
-
Drug overdose
-
Extreme physical exertion
-
Electrical abnormalities of the heart
Warning Signs That May Appear Before Cardiac Arrest
Although sudden cardiac arrest often strikes without warning, some people experience symptoms hours or days before, including:
-
Chest pain or discomfort
-
Shortness of breath
-
Extreme fatigue
-
Dizziness or fainting
-
Heart palpitations
These symptoms should never be ignored.
How to Respond to Sudden Cardiac Arrest
Step 1: Call Emergency Services Immediately
Every second matters.
Step 2: Begin CPR
Push hard and fast in the center of the chest at a rate of 100–120 compressions per minute.
Step 3: Use an AED if Available
Automated external defibrillators analyze heart rhythm and deliver a shock if needed.
Step 4: Continue Until Help Arrives
Do not stop unless the person regains consciousness or professionals take over.
Can Sudden Cardiac Arrest Be Prevented?
While not all cases can be prevented, risk can be reduced by:
-
Managing blood pressure and cholesterol
-
Treating heart disease early
-
Avoiding smoking and recreational drugs
-
Maintaining healthy electrolytes
-
Undergoing cardiac screening if at high risk
Conclusion
Sudden cardiac arrest is deadly because it offers no second chances. Knowledge, preparedness, and fast action save lives. Learning CPR and recognizing warning signs can turn ordinary people into lifesavers.
News in the same category


No More Fillings? Scientists Successfully Grow Human Teeth in the Lab

Lab Study Shows Dandelion Root Kills Over 90% of Colon Cancer Cells In Just Two Days

7 Red Flag Phrases Narcissists Use to Exert Control During Arguments

If These 8 Activities Energize You Instead of Drain You, You’re Likely a Highly Intelligent Introvert
Inflammation Is On Your Plate: 20 Foods That Harm Your Body And 20 That Heal
The Hidden Power of Garlic: 7 Powerful Uses Beyond Cooking

Inflammation Is On Your Plate: 20 Foods That Harm Your Body And 20 That Heal

Children Who Are Hugged Often Have Stronger Immune Systems, Studies Show

1 Cup to Cleanse Your Lungs of Phlegm and Toxins

Study Finds This Popular Sweetener Damages the Brain’s Protective Barrier

Highly Contagious Stomach Bug Doubles in Midwest Ahead of Holiday Season

Lactose Intolerance: Why It Develops Later in Life and How to Manage It
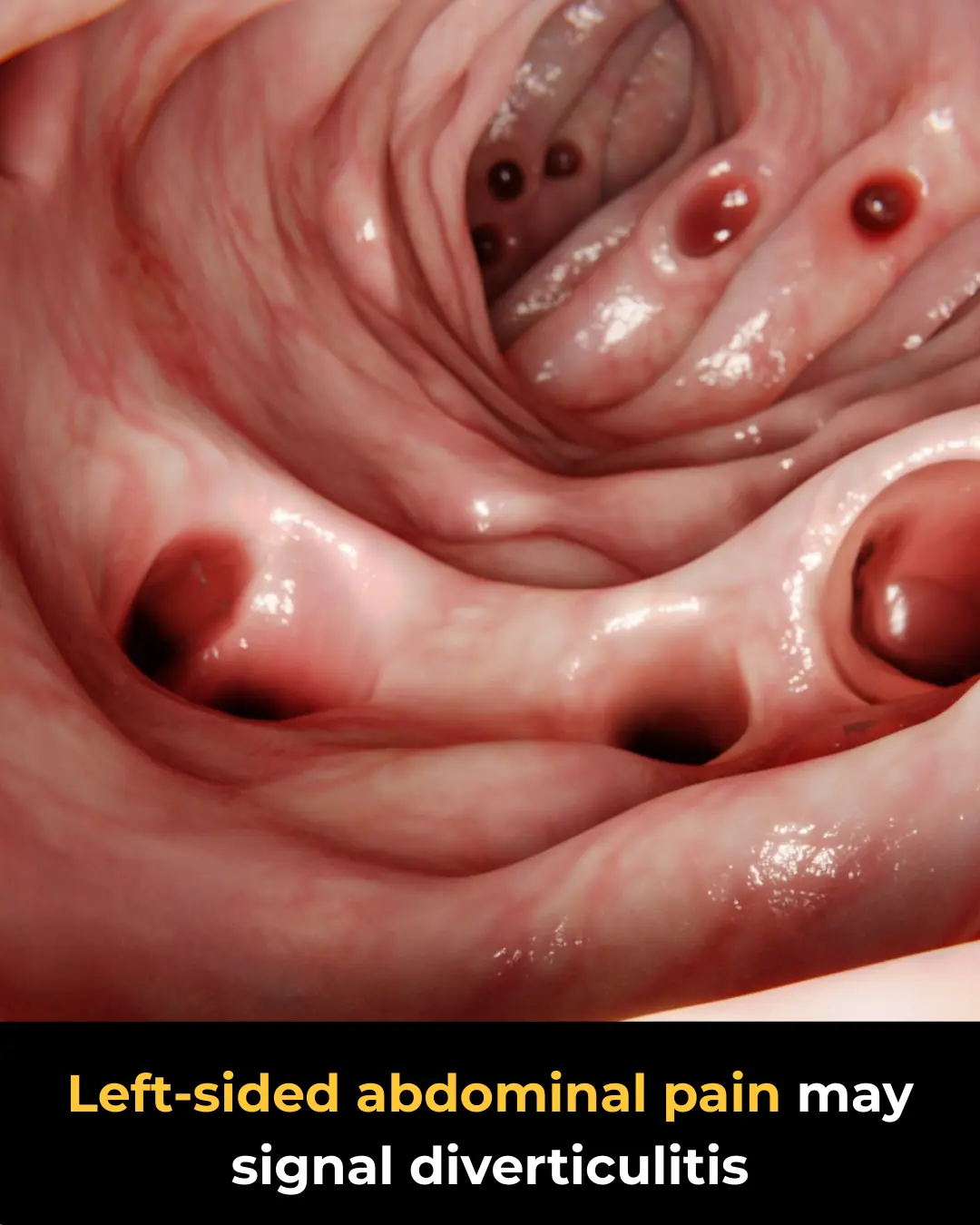
Diverticulitis: Pain Patterns and Treatment Guidelines
Hypertensive Crisis: Symptoms That Require Immediate Attention
High Triglycerides: Why They Matter More Than You Think

Angina Pain: What It Really Means and When to Seek Help

The Hidden Deficiency Ruining Your Eyesight (And How to Fix It)
Understanding Tinnitus Causes and Impact
News Post

Tiny Pumpkin Toadlet Discovered in Brazil's Atlantic Forest: A New Species of Vibrantly Colored Frog

Overview Energy's Bold Plan to Beam Power from Space to Earth Using Infrared Lasers

Japan’s Ghost Homes Crisis: 9 Million Vacant Houses Amid a Shrinking Population

Japan’s Traditional Tree-Saving Method: The Beautiful and Thoughtful Practice of Nemawashi

Swedish Billionaire Buys Logging Company to Save Amazon Rainforest
The Farmer Who Cut Off His Own Finger After a Snake Bite: A Tale of Panic and Misinformation

Meet Jonathan: The 193-Year-Old Tortoise Who Has Witnessed Three Centuries

Hawaii’s Million Mosquitoes a Week: A Bold Move to Save Endangered Birds

Scientists Achieve Historic Breakthrough by Removing HIV DNA from Human Cells, Paving the Way for a Potential Cure

Belgium’s “Pay What You Can” Markets: Redefining Access to Fresh Food with Community and Solidarity

China's Betavolt Unveils Coin-Sized Nuclear Battery with a Potential 100-Year Lifespan

Japan’s Morning Coffee Kiosks: A Quiet Ritual for a Peaceful Start to the Day

13-Year-Old Boy From Nevada Buys His Single Mother a Car Through Hard Work and Dedication

ReTuna: The World’s First Shopping Mall Built on Repair, Reuse, and the Circular Economy

Liver Damage Linked to Supplement Use Is Surging, Sparking Scientific Alarm

No More Fillings? Scientists Successfully Grow Human Teeth in the Lab

Lab Study Shows Dandelion Root Kills Over 90% of Colon Cancer Cells In Just Two Days

7 Red Flag Phrases Narcissists Use to Exert Control During Arguments

Although they're both peanuts, red-shelled and white-shelled peanuts have significant differences. Read this so you don't buy them indiscriminately again!

